Abstract
The spin-weighted spherical harmonics (by Newman and Penrose) form an orthonormal basis of  on the unit sphere Ω and have a huge field of applications. Mainly, they are used in quantum mechanics and geophysics for the theory of gravitation and in early universe and classical cosmology. Furthermore, they have also applications in geodesy. The quantity of formulations conditioned this huge spectrum of versatility. Formulations we use are for example given by the Wigner D-function, by a spin raising and spin lowering operator or as a function of spin weight.
on the unit sphere Ω and have a huge field of applications. Mainly, they are used in quantum mechanics and geophysics for the theory of gravitation and in early universe and classical cosmology. Furthermore, they have also applications in geodesy. The quantity of formulations conditioned this huge spectrum of versatility. Formulations we use are for example given by the Wigner D-function, by a spin raising and spin lowering operator or as a function of spin weight.
We present a unified mathematical theory which implies the collection of already known properties of the spin-weighted spherical harmonics. We recapitulate this in a mathematical way and connect it to the notation of the theory of spherical harmonics. Here, the fact that the spherical harmonics are the spin-weighted spherical harmonics with spin weight zero is useful.
Furthermore, our novel mathematical approach enables us to prove some previously unknown properties. For example, we can formulate new recursion relations and a Christoffel-Darboux formula. Moreover, it is known that the spin-weighted spherical harmonics are the eigenfunctions of a differential operator. In this context, we found Green’s second surface identity for this differential operator and the fact that the spin-weighted spherical harmonics are the only eigenfunctions of this differential operator.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution.
References
Bieberbach, L.: Theorie der Differentialgleichungen. Springer, Heidelberg (1979)
Bouzas, A.O.: Addition theorems for spin spherical harmonics: I. Preliminaries. J. Phys. A Math. Theor. 44(16), 165301 (2011)
Bouzas, A.O.: Addition theorems for spin spherical harmonics: II. Results. J. Phys. A Math. Theor. 44(16), 165302 (2011)
Burridge, R.: Spherically symmetric differential equations, the rotation group, and tensor spherical functions. Math. Proc. Camb. Philos. Soc. 65(1), 157–175 (1969)
Campbell, W.B.: Tensor and spinor spherical harmonics and the spin-s harmonics sYlm(θ, ϕ)∗. J. Math. Phys. 12(8), 1763–1770 (1971)
Dahlen, F.A., Tromp, J.: Theoretical Global Seismology. Princeton University Press, Princeton (1998)
Dhurandhar, S.V., Tinto, M.: Astronomical observations with a network of detectors of gravitational waves – I. Mathematical framework and solution of the five detector problem. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 234(3), 663–676 (1988)
Dray, T.: The relationship between monopole harmonics and spin-weighted spherical harmonics. J. Math. Phys. 26(5), 1030–1033 (1985)
Eastwood, M., Tod, P.: Edth – a differential operator on the sphere. Math. Proc. Camb. Philos. Soc. 92(2), 317–330 (1982)
Edmonds, A.R.: Angular Momentum in Quantum Mechanics. Princeton University Press, Princeton (1957)
Fengler, M.J., Freeden, W.: A nonlinear Galerkin scheme involving vector and tensor spherical harmonics for solving the incompressible Navier-Stokes equation on the sphere. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 27(3), 967–994 (2005)
Freeden, W., Gervens, T.: Vector spherical spline interpolation – basic theory and computational aspects. Math. Methods Appl. Sci. 16(3), 151–183 (1993)
Freeden, W., Gervens, T., Schreiner, M.: Tensor spherical harmonics and tensor spherical splines. Manuscr. Geodaet. 19, 70–100 (1994)
Freeden, W., Gervens, T., Schreiner, M.: Constructive Approximation on the Sphere with Applications to Geomathematics. Oxford University Press, Oxford (1998)
Freeden, W., Schreiner, M.: Spherical Functions of Mathematical Geosciences. Springer, Heidelberg (2009)
Goldberg, J.N., Macfarlane, A.J., Newman, E.T., Rohrlich, F., Sudarshan, E.C.G.: Spin-s spherical harmonics and
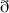 . J. Math. Phys. 8(11), 2155–2161 (1967)
. J. Math. Phys. 8(11), 2155–2161 (1967)Hill, E.L.: The theory of vector spherical harmonics. Am. J. Phys. 22(4), 211–214 (1954)
Hu, W., White, M.: CMB anisotropies: total angular momentum method. Phys. Rev. D 56(2), 596–615 (1997)
Kostelec, P.J., Maslen, D.K., Healy, D.M., Rockmore, D.N.: Computational harmonic analysis for tensor fields on the two-sphere. J. Comput. Phys. 162(2), 514–535 (2000)
Lewis, A., Challinor, A., Turok, N.: Analysis of CMB polarization on an incomplete sky. Phys. Rev. D 65(2), 023505 (2002)
Michel, V.: Lectures on Constructive Approximation. Fourier, Spline, and Wavelet Methods on the Real Line, the Sphere, and the Ball. Birkhäuser Verlag, New York (2013)
Newman, E.T., Penrose, R.: Note on the Bondi-Metzner-Sachs group. J. Math. Phys. 7(5), 863–870 (1966)
Penrose, R., Rindler, W.: Spinors and Space-Time Volume 1: Two-Spinor Calculus and Relativistic Fields. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (1984)
Penrose, R., Rindler, W.: Spinors and Space-Time Volume 2: Spinor and Twistor Methods in Space-Time Geometry. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (1986)
Phinney, R.A., Burridge, R.: Representation of the elastic-gravitational excitation of a spherical Earth model by generalized spherical harmonics. Geophys. J. Int. 34(4), 451–487 (1973)
Schreiner, M.: Tensor Spherical Harmonics and Their Application in Satellite Gradiometry. Ph.D. thesis, Geomathematics Group, Department of Mathematics, University of Kaiserslautern (1994)
Seibert, K.: Spin-Weighted Spherical Harmonics and Their Application for the Construction of Tensor Slepian Functions on the Spherical Cap. Ph.D. thesis, Geomathematics Group, Department of Mathematics, University of Siegen (2018)
Sharma, S.K., Khanal, U.: Perturbation of FRW spacetime in NP formalism. Int. J. Mod. Phys. D 23(2), 1450017 (2014)
Tamm, I.: Die verallgemeinerten Kugelfunktionen und die Wellenfunktionen eines Elektrons im Felde eines Magnetpoles. Z. Phys. 71(3–4), 141–150 (1931)
Thorne, K.S.: Multipole expansions of gravitational radiation. Rev. Mod. Phys. 52(2), 299–339 (1980)
Torres del Castillo, G.F.: Spin-weighted spherical harmonics and their applications. Rev. Mex. Fis. 53(2), 125–134 (2007)
Varshalovich, D.A., Moskalev, A., Khersonskii, V.: Quantum Theory of Angular Momentum. World Scientific Publishing Co Pte Ltd, Singapore (1988)
Voigt, A., Wloka, J.: Hilberträume und elliptische Differentialoperatoren. Bibliographisches Institut, Mannheim (1975)
Wiaux, Y., Jacques, L., Vielva, P., Vandergheynst, P.: Fast directional correlation on the sphere with steerable filters. Astrophys. J. 652(1), 820–832 (2006)
Wiaux, Y., Jacques, L., Vandergheynst, P.: Fast spin ± 2 spherical harmonics transforms and application in cosmology. J. Comput. Phys. 226(2), 2359–2371 (2007)
Wu, T.T., Yang, C.N.: Some properties of monopole harmonics. Phys. Rev. D 16(4), 1018–1021 (1977)
Zaldarriaga, M., Seljak, U.: All-sky analysis of polarization in the microwave background. Phys. Rev. D 55(4), 1830–1840 (1997)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Section Editor information
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2018 Springer-Verlag GmbH Deutschland, ein Teil von Springer Nature
About this entry
Cite this entry
Michel, V., Seibert, K. (2018). A Mathematical View on Spin-Weighted Spherical Harmonics and Their Applications in Geodesy. In: Freeden, W., Rummel, R. (eds) Handbuch der Geodäsie. Springer Reference Naturwissenschaften . Springer Spektrum, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-662-46900-2_102-1
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-662-46900-2_102-1
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer Spektrum, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-662-46900-2
Online ISBN: 978-3-662-46900-2
eBook Packages: Springer Referenz Naturwissenschaften


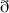 . J. Math. Phys. 8(11), 2155–2161 (1967)
. J. Math. Phys. 8(11), 2155–2161 (1967)