Abstract
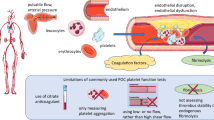
Platelets play a crucial role in primary hemostasis by forming hemostatic plugs at sites of vascular injury. There is abundant evidence that platelets also play a pivotal role in the pathogenesis of arterial thrombotic disorders, including unstable angina (UA), myocardial infarction (MI), and stroke. The underlying pathophysiological mechanism of these processes has been recognized as the disruption or erosion of a vulnerable atherosclerotic plaque, leading to local platelet adhesion and subsequent formation of partially or completely occlusive platelet thrombi. A variety of methods have been used to assess platelet aggregation, blood coagulation, and the ex vivo and/or in vitro efficacy of platelet antagonists, anticoagulants, and thrombolytics.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Konstantopoulos, K., Kukreti, S., and McIntire, L.V. (1998) Biomechanics of cell interactions in shear fields Adv drug delivery rev 33, 141–64.
Alevriadou, B.R., Moake, J.L., Turner, N.A., Ruggeri, Z.M., Folie, B.J., Phillips, M.D., Schreiber, A.B., Hrinda, M.E., and McIntire, L.V. (1993) Real-time analysis of shear-dependent thrombus formation and its blockade by inhibitors of von Willebrand factor binding to platelets Blood 81, 1263–76.
Turitto, V.T. (1982) Blood viscosity, mass transport, and thrombogenesis Prog Hemost Thromb 6, 139–77.
Palmer, R.L. (1984) Laboratory diagnosis of bleeding disorders. Basic screening tests Postgraduate Med 76, 137–42, 47–8.
Nilsson, I. Assessment of blood coagulation and general haemostasis. In: Bloom, A.L, and Thomas, D.P., eds. Haemostasis and Thrombosis, 2nd edition. Harlow: Longman Group (UK) Limited;1987:922–32
Hartert, H. (1948) Blutgerinnungsstudien mit der Thrombelastographie, einem neuen Untersuchungsverfahren Klinische Wochenschrift 26, 577–83.
Khurana, S., Mattson, J.C., Westley, S., O’Neill, W.W., Timmis, G.C., and Safian, R.D. (1997) Monitoring platelet glycoprotein IIb/IIIa-fibrin interaction with tissue factor-activated thromboelastography J Lab Clin Med 130, 401–11.
Mousa, S., Khurana, S., and Forsythe, M. (2000) Comparative in vitro efficacy of different platelet glycoprotein IIb/IIIa antagonists on platelet-mediated clot strength induced by tissue factor with use of thromboelastography: differentiation among glycoprotein IIb/IIIa antagonists Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 20, 1162–7.
Bhargava, A.S., Freihube, G., and Gunzel, P. (1980) Characterization of a new potent heparin. 3rd Communication: determinations of anticoagulant activity of a new potent heparin preparation by thrombelastography in vitro using citrated dog and human blood Arzneimittel-Forschung 30, 1256–8.
Barabas, E., Szell, E., and Bajusz, S. (1993) Screening for fibrinolysis inhibitory effect of synthetic thrombin inhibitors Blood Coagul Fibrinol 4, 243–8.
Scherer, R.U., Giebler, R.M., Schmidt, U., Paar, D., Wust, T., Spangenberg, P., Militzer, K., Hirche, H., and Kox, W.J. (1995) Short-time rabbit model of endotoxin-induced hypercoagulability Lab Animal Sci 45, 538–46.
Mousa, S.A., Bozarth, J.M., Seiffert, D., and Feuerstein, G.Z. (2005) Using thrombelastography to determine the efficacy of the platelet glycoprotein IIb/IIIa antagonist, roxifiban, on platelet/fibrin-mediated clot dynamics in humans Blood Coagul Fibrinol 16, 165–71.
Zuckerman, L., Cohen, E., Vagher, J.P., Woodward, E., and Caprini, J.A. (1981) Comparison of thrombelastography with common coagulation tests Thromb Haemost 46, 752–6.
Chandler, A.B. (1958) In vitro thrombotic coagulation of the blood; a method for producing a thrombus Lab Invest; J Tech Methods Pathol 7:110–4.
Robbie, L.A., Young, S.P., Bennett, B., and Booth, N.A. (1997) Thrombi formed in a Chandler loop mimic human arterial thrombi in structure and RAI-1 content and distribution Thromb Haemost 77, 510–5.
Stringer, H.A., van Swieten, P., Heijnen, H.F., Sixma, J.J., and Pannekoek, H. (1994) Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 released from activated platelets plays a key role in thrombolysis resistance. Studies with thrombi generated in the Chandler loop Arterioscler Thromb 14, 1452–8.
van Giezen, J.J., Nerme, V., and Abrahamsson, T. (1998) PAI-1 inhibition enhances the lysis of the platelet-rich part of arterial-like thrombi formed in vitro. A comparative study using thrombi prepared from rat and human blood Blood Coagul Fibrinol 9, 11–8.
Born, G. (1962) Quantitative investigations into the aggregation of blood platelets J Physiol (London) 162, 67P–8P.
Born, G.V. (1962) Aggregation of blood platelets by adenosine diphosphate and its reversal Nature 194, 927–9.
Haskel, E.J., and Abendschein, D.R. (1989) Deaggregation of human platelets in vitro by an RGD analog antagonist of platelet glycoprotein IIb/IIIa receptors Thromb Res 56, 687–95.
Breddin, K., Grun, H., Krzywanek, H.J., and Schremmer, W.P. (1975) Measurement of spontaneous platelet aggregation. Platelet aggregation test III (author’s transl) Klinische Wochenschrift 53, 81–9.
Klose, H.J., Rieger, H., and Schmid-Schonbein, H. (1975) A rheological method for the quantification of platelet aggregation (PA) in vitro and its kinetics under defined flow conditions Thromb Res 7, 261–72.
Marguerie, G.A., Edgington, T.S., and Plow, E.F. (1980) Interaction of fibrinogen with its platelet receptor as part of a multistep reaction in ADP-induced platelet aggregation J Biol Chem 255, 154–61.
Marguerie, G.A., Plow, E.F., and Edgington, T.S. (1979) Human platelets possess an inducible and saturable receptor specific for fibrinogen J Biol Chem 254, 5357–63.
Lumley, P., and Humphrey, P.P. (1981) A method for quantitating platelet aggregation and analyzing drug-receptor interactions on platelets in whole blood in vitro J Pharmacol Methods 6, 153–66.
Fratantoni, J.C., and Poindexter, B.J. (1990) Measuring platelet aggregation with microplate reader. A new technical approach to platelet aggregation studies Am J Clin Pathol 94, 613–7.
Ammit, A.J., and O’Neill, C. (1991) Rapid and selective measurement of platelet-activating factor using a quantitative bioassay of platelet aggregation J Pharmacol Methods 26, 7–21.
Markell, M.S., Fernandez, J., Naik, U.P., Ehrlich, Y., and Kornecki, E. (1993) Effects of cyclosporine-A and cyclosporine-G on ADP-stimulated aggregation of human platelets Ann N Y Acad Sci 696, 404–7.
Cardinal, D.C., and Flower, R.J. (1980) The electronic aggregometer: a novel device for assessing platelet behavior in blood J Pharmacol Methods 3, 135–58.
Tohgi, H., Takahashi, H., Watanabe, K., Kuki, H., and Shirasawa, Y. (1996) Development of large platelet aggregates from small aggregates as determined by laser-light scattering: effects of aggregant concentration and antiplatelet medication Thromb Haemost 75, 838–43.
Matsuo, T., Koide, M., Sakuramoto, H., Matsuo, M., and Fuji, K. (1997) Small size of platelets aggregates detected by light scattering in young habitual smokers Thromb Haemost 71(suppl), 71.
Xiao, Z., and Theroux, P. (1998) Platelet activation with unfractionated heparin at therapeutic concentrations and comparisons with a low-molecular-weight heparin and with a direct thrombin inhibitor Circulation 97, 251–6.
Bennett, J.S., and Vilaire, G. (1979) Exposure of platelet fibrinogen receptors by ADP and epinephrine J Clin Invest 64, 1393–401.
Mendelsohn, M.E., O’Neill, S., George, D., and Loscalzo, J. (1990) Inhibition of fibrinogen binding to human platelets by S-nitroso-N-acetylcysteine J Biol Chem 265, 19028–34.
Gallimore, M.J., Tyler, H.M., and Shaw, J.T. (1971) The measurement of fibrinolysis in the rat Thromb Diath Haemorrh 26, 295–310.
Teitel, P. (1977) Basic principles of the ‘Filterability test’ (FT) and analysis of erythrocyte flow behavior Blood Cells 3, 55–70.
Kiesewetter, H., Dauer, U., Teitel, P., Schmid-Schonbein, H., and Trapp, R. (1982) The single erythrocyte rigidometer (SER) as a reference for RBC deformability Biorheology 19, 737–53.
Roggenkamp, H.G., Jung, F., and Kiesewetter, H. (1983) A device for the electrical measurement of the deformability of red blood cells Biomedizinische Technik 28, 100–4.
Seiffge, D., and Behr, S. (1986) Passage of red blood cells in the SER: their distribution and influences of various extrinsic and intrinsic factors Clin Hemorheol 6, 1510164.
Schmid-Schonbein, H., von Gosen, J., Heinich, L., Klose, H.J., and Volger, E. (1973) A counter-rotating "rheoscope chamber" for the study of the microrheology of blood cell aggregation by microscopic observation and microphotometry Microvasc Res 6, 366–76.
Jen, C.J., and McIntire, L.V. (1984) Characteristics of shear-induced aggregation in whole blood J Lab Clin Med 103, 115–24.
Sweeney, J.D., Labuzzetta, J.W., Michielson, C.E., and Fitzpatrick, J.E. (1989) Whole blood aggregation using impedance and particle counter methods Am J Clin Pathol 92, 794–7.
Konstantopoulos, K., Kamat, S.G., Schafer, A.I., Banez, E.I., Jordan, R., Kleiman, N.S., and Hellums, J.D. (1995) Shear-induced platelet aggregation is inhibited by in vivo infusion of an anti-glycoprotein IIb/IIIa antibody fragment, c7E3 Fab, in patients undergoing coronary angioplasty Circulation 91, 1427–31.
Mousa, S.A., Abulencia, J.P., McCarty, O.J., Turner, N.A., and Konstantopoulos, K. (2002) Comparative efficacy between the glycoprotein IIb/IIIa antagonists roxifiban and orbofiban in inhibiting platelet responses in flow models of thrombosis J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 39, 552–60.
Abulencia, J.P., Tien, N., McCarty, O.J., Plymire, D., Mousa, S.A., and Konstantopoulos, K. (2001) Comparative antiplatelet efficacy of a novel, nonpeptide GPIIb/IIIa antagonist (XV454) and abciximab (c7E3) in flow models of thrombosis Arterioscl Thromb Vasc Biol 21, 149–56.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2010 Springer Science+Business Media, LLC
About this protocol
Cite this protocol
Mousa, S.A. (2010). In Vitro Methods of Evaluating Antithrombotics and Thrombolytics. In: Mousa, S. (eds) Anticoagulants, Antiplatelets, and Thrombolytics. Methods in Molecular Biology, vol 663. Humana Press, Totowa, NJ. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-60761-803-4_1
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-60761-803-4_1
Published:
Publisher Name: Humana Press, Totowa, NJ
Print ISBN: 978-1-60761-802-7
Online ISBN: 978-1-60761-803-4
eBook Packages: Springer Protocols