Abstract
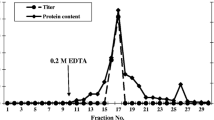
Pleurotus cornucopiae mycelial lectin (PCL-M) is a divalent cation-dependent GalNAc-specific lectin that is purified from the mycelia of the edible mushroom Pleurotus cornucopiae. PCL-M is produced only in dikaryotic mycelia growing on solid medium and is not present in the mycelia of fruiting bodies. It is a multimeric glycoprotein composed of 40 kDa subunits linked by disulfide bonds. PCL-M is localized on the surface of aggregating mycelia and may be involved in primordia formation. The procedure for PCL-M purification has been discussed herein. Additionally, an experimental method for analyzing the localization of PCL-M on mycelial surface has been described.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yoshida M, Kato S, Oguri S, Nagata Y (1994) Purification and properties of lectins from a mushroom, Pleurotus cornucopiae. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 58(3):498–501
Oguri S, Ando A, Nagata Y (1996) A novel developmental stage-specific lectin of the basidiomycete Pleurotus cornucopiae. J Bacteriol 178(19):5692–5698
Sumisa F, Ichijo N, Yamaguchi H, Nakatsumi H, Ando A, Iijima N, Oguri S, Uehara K, Nagata Y (2004) Molecular properties of mycelial aggregate-specific lectin of Pleurotus cornucopiae. J Biosci Bioeng 98(4):257–262
Sumisa F, Iijima N, Ando A, Shiga M, Kondo K, Amano K, Nagata Y (2004) Properties of mycelial aggregate-specific lectin of Pleurotus cornucopiae produced in Pichia pastoris. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 68(4):959–960. https://doi.org/10.1271/bbb.68.959
Fujimoto Z, Jackson A, Michikawa M, Maehara T, Momma M, Henrissat B, Gilbert HJ, Kaneko S (2013) The structure of a Streptomyces avermitilis alpha-L-rhamnosidase reveals a novel carbohydrate-binding module CBM67 within the six-domain arrangement. J Biol Chem 288(17):12376–12385. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M113.460097
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2020 Springer Science+Business Media, LLC, part of Springer Nature
About this protocol
Cite this protocol
Oguri, S. (2020). Pleurotus cornucopiae Mycelial Lectin (PCL-M): Purification and Detection of the Activity on Mycelial Surface. In: Hirabayashi, J. (eds) Lectin Purification and Analysis. Methods in Molecular Biology, vol 2132. Humana, New York, NY. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-0716-0430-4_43
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-0716-0430-4_43
Published:
Publisher Name: Humana, New York, NY
Print ISBN: 978-1-0716-0429-8
Online ISBN: 978-1-0716-0430-4
eBook Packages: Springer Protocols