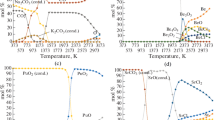
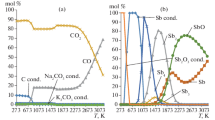
Abstract—Graphite is used as a neutron moderator and reflector. Moreover, graphite can be used as sealants and bearings in reactors. The graphite mass in a reactor is 1–2 ths t. A large amount of radioactive graphite wastes forms when graphite reactors are taken out of service. The existing methods of processing radioactive graphite are based on its isolation from the environment. These methods cannot substantially decrease the volume of radioactive graphite wastes. As a result, the processing of irradiated reactor graphite by oxidation in molten salts can be considered as an alternative reclamation method, which can decrease the volume of radioactive graphite wastes. The oxidation of radioactive graphite in the Na2CO3–K2CO3–Sb2O3 melt in an argon atmosphere is thermodynamically simulated using the TERRA software package. The data obtained are used to analyze the distribution of elements over condensed and gas phases. Heating of the system to 1073 K is found to cause the evaporation of the condensed compounds of antimony and cesium. Upon heating to 1273 K, the condensed compounds of potassium, sodium, and chlorine evaporate. Heating to 1373 K leads to the evaporation of the condensed compounds of nickel. Heating to 1673 K brings about the evaporation of the condensed compounds of uranium, calcium, and strontium. Heating to 1773 K causes the evaporation of the condensed compounds of plutonium, beryllium, americium, and europium. At temperatures above 1773 K, only a vapor–gas phase exists in the system.







Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
V. M. Kuznetsov, H. D. Chechenov, and V. S. Nikitin, Removal of Nuclear Engineering Objects from Service (NIPKTs Voshod-A, Moscow, 2009).
G. V. Belov and B. G. Trusov, “Thermodynamic Simulation of Chemically Reacting Systems (MGTU, Moscow, 2013).
B. G. Trusov, in Proceedings of III International Conference on Theoretical and Applied Plasmachemistry (Ivanovo, 2002), p. 487.
N. M. Barbin, I. A. Sidash, D. I. Terent’ev, and S. G. Alekseev, “Thermodynamic simulation of the behavior of radionuclides upon heating (burning) of radioactive graphite in a carbon dioxide atmosphere,” Pozharovzryivobezopasnost 23 (11), 52–60 (2014).
N. M. Barbin, I. A. Sidash, D. I. Terent’ev, and S. G. Alekseev, “Behavior of uranium, plutonium, and americium upon heating of radioactive graphite in a carbon dioxide atmosphere,” Tehnosfernaya Bezopasnost, No. 1(2), 72–75 (2014).
N. M. Barbin, I. A. Sidash, D. I. Terent’ev, and S. G. Alekseev, “Computer simulation of thermal processes with the participation of calcium, strontium, and cesium radionuclides upon heating of radioactive graphite in a carbon dioxide atmosphere,” Izv. Vyssh. Uchebn. Zaved., Yadern. Energetika, No. 1, 73–82 (2017).
N. M. Barbin, I. A. Sidash, D. I. Terent’ev, and S. G. Alekseev, “Thermodynamic analysis of thermal processes with the participation of U, Am, and Pu radionuclides upon heating of radioactive graphite in a carbon dioxide atmosphere,” Inzh. Fiz., No. 10, 27–32 (2016).
D. I. Terent’ev, N. M. Barbin, A. V. Borisenko, and S. G. Alekseev, “Thermodynamic study of the gas phase composition over Pb + Bi melts,” Perspektivnye Materialy, No. 13, 858–864 (2011).
D. I. Terent’ev, N. M. Barbin, A. V. Borisenko, and S. G. Alekseev, “Composition and thermophysical properties of the (Pb + Bi)–vapor system under various conditions,” Prikl. Fiz., No. 3, 22–28 (2012).
D. I. Terent’ev, N. M. Barbin, A. V. Borisenko, S. G. Alekseev, and P. S. Popel’, “Thermodynamic simulation of the evaporation of Pb + Bi melts at various pressures,” Khim. Fiz. Mezoskopiya, No. 13, 350–355 (2011).
N. M. Barbin, A. M. Kobelev, D. I. Terent’ev, and S. G. Alekseev, “Thermodynamic simulation of the behavior of radionuclides upon heating (burning) of radioactive graphite in water vapors,” Pozharo-vzryvobezopasnost, No. 10, 38–47 (2014).
N. M. Barbin, “Thermodynamic simulation of the thermal behavior of Li2CO3 + Na2CO3 and CaCO3 + Na2CO3 melts,” Khim. Fiz. Mezoskopiya, No. 3, 354–360 (2008).
N. M. Barbin, D. I. Terent’ev, A. V. Peshkov, and S. G. Alekseev, “Thermodynamic simulation of the behavior of radionuclides upon heating (burning) of radioactive graphite in an air atmosphere,” Pozharovzryvobezopasnost, No. 3, 58–67 (2014).
N. M. Barbin, I. V. Tikina, D. I. Terent’ev, and S. G. Alekseev, “Thermodynamic simulation of the vapor phase during the evaporation of the molten Wood alloy at various pressures,” Prikl. Fiz., No. 3, 12–16 (2014).
N. Barbin, D. Terentiev, S. Alexeev, and T. Barbina, “Thermodynamic modeling of the Pb + Bi melt evaporation under various pressures and temperatures,” Comput. Mater. Sci. 66, 28–33 (2013).
N. M. Barbin, D. I. Terentiev, and S. G. Alexeev, “Computer calculations for thermal behavior of Na2CO3–Li2CO3 melt,” J. Eng. Thermophys., No. 3, 308–314 (2011).
N. M. Barbin, I. V. Ovchinnikova, D. I. Terent’ev, and S. G. Alekseev, “Thermodynamic simulation of the thermal processes that take place in the molten Wood alloy under various conditions,” Prikl. Fiz., No. 3, 8–11 (2014).
N. M. Barbin, D. I. Terentiev, S. G. Alexeev, and T. M. Barbina, “Thermodynamic analysis of radioactive graphite reprocessing by incineration in air and oxidation in molten salt,” J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem., No. 3, 1747–1757 (2014).
N. M. Barbin, D. I. Terent’ev, A. V. Peshkov, and S. G. Alekseev, “Comparative thermodynamic analysis of the burning of radioactive graphite in an air atmosphere and its oxidation in a molten salt,” Rasplavy, No. 4, 25–35 (2013).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated by K. Shakhlevich
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Barbin, N.M., Sidash, I.A., Terent’ev, D.I. et al. Thermodynamic Analysis of the Oxidation of Radioactive Graphite in the Na2CO3–K2CO3–Sb2O3 Melt in an Argon Atmosphere. Russ. Metall. 2018, 716–721 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0036029518080037
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0036029518080037