Abstract
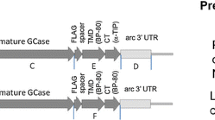
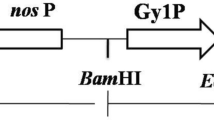
Genetic deficiency of acid alpha glucosidase (GAA) results in glycogen storage disease type II (GSDII) or Pompe’s disease. To investigate whether we could generate a functional recombinant human GAA enzyme (tobrhGAA) in tobacco seeds for future enzyme replacement therapy, we subcloned the human GAA cDNA into the plant expression plasmid-pBI101 under the control of the soybean β-conglycinin seed-specific promoter and biochemically analyzed the tobrhGAA. Tobacco seeds contain the metabolic machinery that is more compatible with mammalian glycosylation−phosphorylation and processing. We found the tobrhGAA to be enzymatically active was readily taken up by GSDII fibroblasts and in white blood cells from whole blood to reverse the defect. The tobrhGAA corrected the enzyme defect in tissues at 7 days after a single dose following intraperitoneal (IP) administration in GAA knockout (GAA−/−) mice. Additionally, we could purify the tobrhGAA since it bound tightly to the matrix of Sephadex G100 and can be eluted by competition with maltose. These data demonstrate indirectly that the tobrhGAA is fully functional, predominantly proteolytically cleaved and contains the minimal phosphorylation and mannose-6-phosphate residues essential for biological activity.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- IP:
-
intraperitoneal
- AMD:
-
acid maltase deficiency
- GSDII:
-
glycogen storage disease type II
- exon 6 neo:
-
exon 6 neomycin resistent
- rhGAA:
-
recombinant GAA
- tobrhGAA:
-
recombinant GAA produced in tobacco seeds
- GAA:
-
acid maltase
- ERT:
-
enzyme replacement therapy
References
Fischer, R., Schillberg, S., Hellwig, S., Twyman, R. M., & Drossard, J. (2012). GMP issues for recombinant plant-derived pharmaceutical proteins. Biotechnology Advances, 30, 434–439.
Lico, C., Santi, L., Twyman, R. M., Pezzotti, M., & Avesani, L. (2012). The use of plants for the production of therapeutic human peptides. Plant Cell Reports, 31, 439–451.
Twyman, R. M., Stoger, E., Schillberg, S., Christou, P., & Fischer, R. (2003). Molecular farming in plants: host systems and expression technology. Trends in Biotechnology, 21, 570–578.
Twyman, R. M., Ramessar, K., Quemada, H., Capell, T., & Christou, P. (2009). Plant biotechnology: the importance of being accurate. Trends in Biotechnology, 27, 609–612.
Kusnadi, A. R., Evangelista, R. L., Hood, E. E., Howard, J. A., & Nikolov, Z. L. (1998). Processing of transgenic corn seed and its effect on the recovery of recombinant beta-glucuronidase. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 60, 44–52.
Reggi, S., Marchetti, S., Patti, T., De Amicis, F., Cariati, R., Bembi, B., & Fogher, C. (2005). Recombinant human acid β-glucosidase stored in tobacco seed is stable, active and taken up by human fibroblasts. Plant Molecular Biology, 57, 101–113.
Stoeger, E., Vaquero, C., Torres, E., Sack, M., Nicholson, L., Drossard, J., Williams, S., Keen, D., Perrin, Y., Christou, P., & Fischer, R. (2000). Cereal crops as viable production and storage systems for pharmaceutical scFv antibodies. Plant Molecular Biology, 42, 583–590.
Kermode, A. R. (2006). Plants as factories for production of biopharmaceutical and bioindustrial proteins: lessons from cell biology. Canadian Journal of Botany, 84, 679–694.
Kermode, A. R. (2012). Seed Expression Systems for Molecular Farming. In A. Wang & S. Ma (Eds.), Molecular farming in plants: recent advances and future prospects (pp. 89–123). New York: Springer.
Lau, O. S., & Sun, S. S. M. (2009). Plant seeds as bioreactors for recombinant protein production. Biotechnology Advances, 27, 1015–1022.
Boothe, J., Nykiforuk, C., Shen, Y., Zaplachinski, S., Szarka, S., Kuhlman, P., Murray, E., Morck, D., & Moloney, M. M. (2010). Seed-based expression system for plant molecular farming. Plant Biotechnology Journal, 8, 588–606.
Stoger, E., & Ma, J. K. (2005). Sowing the seeds of success: Pharmaceutical proteins from plants. Current Opinion in Biotechnology, 16, 167–173.3.
Gomord, V., Fischette, A. C., Menu-Bouaouiche, L., Saint-Jore-Dupas, C., Plasson, C., Michaud, D., & Faye, L. (2010). Plant-specific glycosylation patterns in the context of therapeutic protein production. Plant Biotechnology Journal, 8, 564–587.
Saint-Jore-Dupas, C., Faye, L., & Gomord, V. (2007). From planta to pharma with glycosylation in the toolbox. Trends in Biotechnology, 25, 317–323.
Lerouge, P., Cabanes-Macheteau, M., Rayon, C., Fischette-Lainé, A. C., Gomord, V., & Faye, L. (1998). N-glycosylation of recombinant pharmaceutical glycoproteins produced in transgenic plants: towards an humanisation of plant N-glycans. Plant Molecular Biology, 38, 31–48.
Gomord, V., & Faye, L. (2004). Posttranslational modification of therapeutic proteins in plants. Current Opinion in Plant Biology, 7, 171–181.
Kermode, A. R. (1996). Mechanisms of intracellular protein transport and targeting. Critical Reviews in Plant Sciences, 15, 285–423.
He, X., Galpin, J. D., Tropak, M. B., Mahuran, D., Haselhorst, T., von Itzstein, M., Kolarich, D., Packer, N. H., Miao, Y., Jiang, L., Grabowski, G. A., Clarke, L. A., & Kermode, A. R. (2012). Production of active human glucocerebrosidase in seeds of Arabidopsis thaliana complex-glycan-deficient (cgl) plants. Glycobiology, 22, 492–503.
Hers, H. G. (1963). Alpha-glucosidase deficiency in generalized glycogen storage disease (Pompe's Disease). Biochemical Journal, 86, 11–16.
Kornfeld, S. (1986). Trafficking of lysosomal enzymes in normal and disease states. The Journal of Clinical Investigation, 77, 1–6.
Rosenfeld, M. G., Kreibich, G., Popov, D., Kato, K., & Sabatini, D. D. (1982). Biosynthesis of lysosomal hydrolases: their synthesis in bound polysomes and the role of co- and post-translational processing in determining their subcellular distribution. The Journal of Cell Biology, 93, 135–141.
Oude Elferink, R.P.J. (1985) Biosynthesis, transport and processing of lysosomal alpha glucosidase. PhD Thesis, University of Amsterdam.
Slonim, A., Bulone, L., Ritz, S., Goldberg, T., Chen, A., & Martiniuk, F. (2000). Identification of two subtypes of infantile acid maltase deficiency: Evaluation of twenty-two patients and review of the literature. Journal of Pediatrics, 137, 283–285.
Horsch, R. B., Fry, J. E., Hoffmann, N. L., Eichholtz, D., Roger, S. D., & Fraley, R. T. (1985). A simple and general method for transferring genes into plants. Science, 227, 1229–1231.
Doyle, J. J., & Doyle, J. L. (1997). A rapid DNA isolation procedure for small quantities of fresh leaf tissue. Phytochemical Bulletin, 19, 11–15.
Martiniuk, F., Honig, J., & Hirschhorn, R. (1984). Further studies of the structure of human placental acid alpha-glucosidase. Archives of Biochemistry and Biophysics, 231, 454–460.
Martiniuk, F., & Hirschhorn, R. (1981). Characterization of neutral isozymes of human alpha-glucosidase. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, 658, 248–261.
Martiniuk, F., Chen, A., Donnabella, V., Arvanitopoulos, E., Slonim, A., Raben, N., Plotz, P., & Rom, W. N. (2000). Correction of glycogen storage disease type II by enzyme replacement with a recombinant human acid maltase produced by over-expression in a CHO DHFRneg cell line. Biochem Biophys Res Comm., 276, 917–923.
Raben, N., Nagaraju, K., Lee, E., Kessler, P., Byrne, B., Lee, L., LaMaurex, M., King, J., Sauer, B., & Plotz, P. (1998). Targeted disruption of the acid alpha glucosidase gene in mice causes an illness with critical features of both infantile and adult human glycogen storage disease type II. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 273, 19086–19092.
Bijvoet, A. G., Kroos, M. A., Pieper, F. R., Van der Vliet, M., De Boer, H. A., Van der Ploeg, A. T., Verbeet, M. P., & Reuser, A. J. (1998). Recombinant human acid alpha-glucosidase: high level production in mouse milk, biochemical characteristics, correction of enzyme deficiency in GSDII KO mice. Human Molecular Genetics, 1815–24.
Maga, J. A., Zhou, J., Kambampati, R., Peng, S., Wang, X., Bohnsack, R. N., Thomm, A., Golata, S., Tom, P., Dahms, N. M., Byrne, B. J., & Lebowitz, J. H. (2013). Glycosylation-independent lysosomal targeting of acid α-glucosidase enhances muscle glycogen clearance in Pompe mice. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 288, 1428–1438.
Van der Ploeg, A. T., Bolhuis, P. A., Wolterman, R. A., Visser, J. W., Loonen, M. C., Busch, H. F., & Reuser, A. J. (1988). Prospect for enzyme therapy in glycogenosis II variants: a study on cultured muscle cells. Journal of Neurology, 235, 392–396.
Van der Ploeg, A. T., Kroos, M. A., Willemsen, R., Brons, N. H., & Reuser, A. J. (1991). Intravenous administration of phosphorylated acid alpha-glucosidase leads to uptake of enzyme in heart and skeletal muscle of mice. The Journal of Clinical Investigation, 87, 513–518.
Van den Hout, J., Kamphoven, J., Winkel, L. P., Arts, W. F., De Klerk, J. B., Loonen, M. C., Vulto, A. G., Cromme-Dijkhuis, A., Weisglas-Kuperus, N., Hop, W., Van Hirtum, H., Van Diggelen, O. P., Boer, M., Kroos, M. A., Van Doorn, P. A., Van der Voort, E., Sibbles, B., Van Corven, E. J., Brakenhoff, J. P., Van Hove, J., Smeitink, J. A., de Jong, G., Reuser, A. J., & Van der Ploeg, A. T. (2004). Long-term intravenous treatment of Pompe disease with recombinant human α-glucosidase from milk. Pediatrics, 113, 448–457.
Kikuchi, T., Yang, H. W., Pennybacher, M., Ichihara, N., Mizutani, M., van Hove, J. L. K., & Chen, Y. T. (1998). Clinical and metabolic correction of Pompe disease by enzyme therapy in acid maltase-deficient quail. Journal of Clinical Laboratory, 101, 827–833.
Xu, X., Gan, Q., Clough, R. C., Pappu, K. M., Howard, J. A., Baez, J. A., & Wang, K. (2011). Hydroxylation of recombinant human collagen type I alpha 1 in transgenic maize co-expressed with a recombinant human prolyl 4-hydroxylase. BMC Biotechnology, 11, 69–80.
De Marchis, F., Balducci, C., Pompa, A., Riise Stensland, H. M., Guaragno, M., Pagiotti, R., Menghini, A. R., Persichetti, E., Beccari, T., & Bellucci, M. (2011). Human α-mannosidase produced in transgenic tobacco plants is processed in human α-mannosidosis cell lines. Plant Biotechnology Journal, 9, 1061–1073.
Nozoye, T., Takaiwa, F., Tsuji, N., Yamakawa, T., Arakawa, T., Hayashi, Y., & Matsumoto, Y. (2009). Production of Ascaris suum As14 protein and its fusion protein with cholera toxin B subunit in rice seeds. Journal of Veterinary Medical Science, 71, 995–1000.
Oszvald, M., Kang, T. J., Tomoskozi, S., Jenes, B., Kim, T. G., Cha, Y. S., Tamas, L., & Yang, M. S. (2008). Expression of cholera toxin B subunit in transgenic rice endosperm. Molecular Biotechnology, 40, 261–268.
Blais, D. R., & Altosaar, I. (2006). Human CD14 expressed in seeds of transgenic tobacco displays similar proteolytic resistance and bioactivity with its mammalian-produced counterpart. Transgenic Research, 15, 151–164.
Samyn-Petit, B., Wajda Dubos, J. P., Chirat, F., Coddeville, B., Demaizieres, G., Farrer, S., Slomianny, M. C., Theisen, M., & Delannoy, P. (2003). Comparative analysis of the site-specific N-glycosylation of human lactoferrin produced in maize and tobacco plants. European Journal of Biochemistry, 270, 3235–3242.
Woodard, S. L., Mayor, J. M., Bailey, M. R., Barker, D. K., Love, R. T., Lane, J. R., Delaney, D. E., McComas-Wagner, J. M., Mallubhotla, H. D., Hood, E. E., Dangott, L. J., Tichy, S. E., & Howard, J. A. (2003). Maize (Zea mays)-derived bovine trypsin: characterization of the first large-scale, commercial protein product from transgenic plants. Biotechnology and Applied Biochemistry, 38, 123–130.
Martiniuk, F., Tzall, S., & Chen, A. (1992). Recombinant human acid alpha-glucosidase generated in bacteria: antigenic, but enzymatically inactive. DNA and Cell Biology, 11, 701–706.
Acknowledgements
This research was supported in part by a grant UL1 TR000038 from the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences, National Institutes of Health.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Reprints should be directed to Frank Martiniuk.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Martiniuk, F., Reggi, S., Tchou-Wong, KM. et al. Production of a Functional Human Acid Maltase in Tobacco Seeds: Biochemical Analysis, Uptake by Human GSDII Cells, and In Vivo Studies in GAA Knockout Mice. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 171, 916–926 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-013-0367-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-013-0367-z