Abstract
Purpose
Insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF1) gene single nucleotide polymorphism (rs5742612) has been associated with adolescent idiopathic scoliosis (AIS) in several studies with limited sample size and inconsistent outcomes. So we perform this meta-analysis to assess the precise association between IGF1 gene single nucleotide polymorphism (rs5742612) and AIS.
Methods
We systematically searched Pubmed, Embase, Web of Science and Cochrane Library up to January 19, 2016 to obtain relevant studies using our research strategy. Four articles all belonging to case–control studies were included in our meta-analysis.
Results
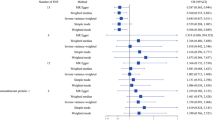
A total of four studies containing 763 cases and 559 controls satisfied the inclusion criteria after judgment by two reviewers. No significant associations were detected between IGF1 gene single nucleotide polymorphism (rs5742612) and AIS (T vs. C, OR = 1.10, 95 % CI 0.91–1.34, p = 0.32; TT vs. CC: OR = 1.28, 95 % CI 0.82–2.02, p = 0.28; TC vs. CC: OR = 1.29, 95 % CI 0.82–2.06, p = 0.27; TT/TC vs. CC: OR = 1.28, 95 % CI 0.83–1.98, p = 0.27; TT vs. TC/CC: OR = 1.06, 95 % CI 0.82–1.36, p = 0.66).
Conclusions
IGF1 gene single nucleotide polymorphism (rs5742612) is not significant associated with susceptibility to AIS in either Asian or Caucasian populations. However, IGF1 gene rs5742612 may be associated with severity of AIS. Further studies with larger sample size and different population groups involving the relationship are required to confirm the potential association.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yagi M MM, Asazuma T (2014) Pathogenesis of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. JBJS Rev 2(1). doi:10.2106/JBJS.REV.M.00037
Kane WJ (1977) Scoliosis prevalence: a call for a statement of terms. Clin Orthop Relat Res (126):43–46
Suh SW, Modi HN, Yang JH, Hong JY (2011) Idiopathic scoliosis in Korean schoolchildren: a prospective screening study of over 1 million children. Eur Spine J 20:1087–1094. doi:10.1007/s00586-011-1695-8
Weinstein SL (1999) Natural history. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 24:2592–2600
Negrini S, Aulisa AG, Aulisa L, Circo AB, de Mauroy JC, Durmala J, Grivas TB, Knott P, Kotwicki T, Maruyama T, Minozzi S, O’Brien JP, Papadopoulos D, Rigo M, Rivard CH, Romano M, Wynne JH, Villagrasa M, Weiss HR, Zaina F (2012) 2011 SOSORT guidelines: orthopaedic and Rehabilitation treatment of idiopathic scoliosis during growth. Scoliosis 7:3. doi:10.1186/1748-7161-7-3
Chen S, Zhao L, Roffey DM, Phan P, Wai EK (2014) Association of rs11190870 near LBX1 with adolescent idiopathic scoliosis in East Asians: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Spine J Off J N Am Spine Soc 14:2968–2975. doi:10.1016/j.spinee.2014.05.019
Chan V, Fong GC, Luk KD, Yip B, Lee MK, Wong MS, Lu DD, Chan TK (2002) A genetic locus for adolescent idiopathic scoliosis linked to chromosome 19p13.3. Am J Hum Genet 71:401–406. doi:10.1086/341607
Miller NH, Justice CM, Marosy B, Swindle K, Kim Y, Roy-Gagnon MH, Sung H, Behneman D, Doheny KF, Pugh E, Wilson AF (2012) Intra-familial tests of association between familial idiopathic scoliosis and linked regions on 9q31.3–q34.3 and 16p12.3–q22.2. Hum Hered 74:36–44. doi:10.1159/000343751
Ji XR, Yang ZD, Yang XH, Liu DD, Ni HJ, Li M (2013) Change of selenium in environment and risk of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: a retrospective cohort study. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 17:2499–2503
Zhang Y, Gu Z, Qiu G (2014) The association study of calmodulin 1 gene polymorphisms with susceptibility to adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Biomed Res Int 2014:168106. doi:10.1155/2014/168106
Lowe TG, Edgar M, Margulies JY, Miller NH, Raso VJ, Reinker KA, Rivard CH (2000) Etiology of idiopathic scoliosis: current trends in research. J Bone Jt Surg Am 82-A:1157–1168
Gorman KF, Julien C, Moreau A (2012) The genetic epidemiology of idiopathic scoliosis. Eur Spine J 21:1905–1919. doi:10.1007/s00586-012-2389-6
Chen S, Zhao L, Roffey DM, Phan P, Wai EK (2014) Association between the ESR1 -351A > G single nucleotide polymorphism (rs9340799) and adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur Spine J 23:2586–2593. doi:10.1007/s00586-014-3481-x
Xu L, Sun W, Qin X, Qiu Y, Zhu Z (2016) The TGFB1 gene is associated with curve severity but not with the development of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: a replication study in the Chinese population. BMC Musculoskelet Disord 17:15. doi:10.1186/s12891-016-0863-8
Yang Y, Wu Z, Zhao T, Wang H, Zhao D, Zhang J, Wang Y, Ding Y, Qiu G (2009) Adolescent idiopathic scoliosis and the single-nucleotide polymorphism of the growth hormone receptor and IGF-1 genes. Orthopedics 32:411. doi:10.3928/01477447-20090511-08
Yeung HY, Tang NL, Lee KM, Ng BK, Hung VW, Kwok R, Guo X, Qin L, Cheng JC (2006) Genetic association study of insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-I) gene with curve severity and osteopenia in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Stud Health Technol Inform 123:18–24
Rubin K (2000) Pubertal development and bone. Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes 7:65–70
McCarthy TL, Centrella M, Canalis E (1989) Regulatory effects of insulin-like growth factors I and II on bone collagen synthesis in rat calvarial cultures. Endocrinology 124:301–309. doi:10.1210/endo-124-1-301
Kim JG, Roh KR, Lee JY (2002) The relationship among serum insulin-like growth factor-I, insulin-like growth factor-I gene polymorphism, and bone mineral density in postmenopausal women in Korea. Am J Obstet Gynecol 186:345–350
Rietveld I, Janssen JA, Hofman A, Pols HA, van Duijn CM, Lamberts SW (2003) A polymorphism in the IGF-I gene influences the age-related decline in circulating total IGF-I levels. Eur J Endocrinol Eur Fed Endocr Soc 148:171–175
Takahashi Y, Matsumoto M, Karasugi T, Watanabe K, Chiba K, Kawakami N, Tsuji T, Uno K, Suzuki T, Ito M, Sudo H, Minami S, Kotani T, Kono K, Yanagida H, Taneichi H, Takahashi A, Toyama Y, Ikegawa S (2011) Lack of association between adolescent idiopathic scoliosis and previously reported single nucleotide polymorphisms in MATN1, MTNR1B, TPH1, and IGF1 in a Japanese population. J Orthop Res 29:1055–1058. doi:10.1002/jor.21347
Nikolova S, Yablanski V, Vlaev E, Stokov L, Savov AS, Kremensky IM (2015) Association study between idiopathic scoliosis and polymorphic variants of VDR, IGF-1, and AMPD1 genes. Genet Res Int 2015:852196. doi:10.1155/2015/852196
Moon ES, Kim HS, Sharma V, Park JO, Lee HM, Moon SH, Chong HS (2013) Analysis of single nucleotide polymorphism in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis in Korea: for personalized treatment. Yonsei Med J 54:500–509. doi:10.3349/ymj.2013.54.2.500
Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG, Group P (2009) Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. BMJ 339:2535. doi:10.1136/bmj.b2535
Higgins JP, Thompson SG, Deeks JJ, Altman DG (2003) Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. BMJ 327:557–560. doi:10.1136/bmj.327.7414.557
Ioannidis JP, Trikalinos TA (2007) The appropriateness of asymmetry tests for publication bias in meta-analyses: a large survey. CMAJ 176:1091–1096. doi:10.1503/cmaj.060410
Noshchenko A, Hoffecker L, Lindley EM, Burger EL, Cain CM, Patel VV, Bradford AP (2015) Predictors of spine deformity progression in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: a systematic review with meta-analysis. World J Orthop 6:537–558. doi:10.5312/wjo.v6.i7.537
Zhu F, Qiao J, Qiu X, Xu L, Liu Z, Zhu Z, Qian B, Sun X, Qiu Y (2014) Lack of association between suppressor of cytokine signaling-3 gene polymorphism and susceptibility and curve severity of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Eur Spine J 23:2432–2436. doi:10.1007/s00586-014-3452-2
Acknowledgments
This work is supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81271347).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declared that they have no conflicts of interest to this work. No benefits in any form have been or wiil be received from a commercial party related directly or indirectly to the subject of this manuscript.
Additional information
M. Guan and H. Wang contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guan, M., Wang, H., Fang, H. et al. Association between IGF1 gene single nucleotide polymorphism (rs5742612) and adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: a meta-analysis. Eur Spine J 26, 1624–1630 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-016-4742-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-016-4742-7