Abstract
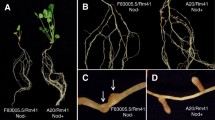
The contributions of various nod genes from Rhizobium leguminosarum biovar viceae to host-specific nodulation have been assessed by transferring specific genes and groups of genes to R. leguminosarum bv. trifolii and testing the levels of nodulation on Pisum sativum (peas) and Vicia hirsuta. Many of the nod genes are important in determination of host-specificity; the nodE gene plays a key (but not essential) role and the efficiency of transfer of host specific nodulation increased with additional genes such that nodFE < nodFEL < nodFELMN. In addition the nodD gene was shown to play an important role in host-specific nodulation of peas and Vicia whilst other genes in the nodABCIJ gene region also appeared to be important. In a reciprocal series of experiments involving nod genes cloned from R. leguminosarum bv. trifolii it was found that the nodD gene enabled bv. viciae to nodulate Trifolium pratense (red clover) but the nodFEL gene region did not. The bv. trifolii nodD or nodFEL genes did significantly increase nodulation of Trifolium subterraneum (sub-clover) by R. leguminosarum bv. viciae. It is concluded that host specificity determinants are encoded by several different nod genes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baddasarian M, Lurz R, Rückert B, Franklin FCH, Bagdasarian MM, Frey J, Timmis KT: Specific-purpose plasmid cloning vectors. II. Broad host range, high copy RSF1010-derived vectors and a host-vector system for gene cloning in Pseudomonas. Gene 16: 237–247 (1981).
Beringer JE: R factor transfer in Rhizobium leguminosarum. J Gen Microbiol 84: 188–198 (1974).
Beringer JE, Beynon JL, Buchanan-Wollaston AV, Hirsch PR, Johnston AWB: Transfer of the drug resistance transposon Tn5 to Rhizobium. Nature 276: 633–634 (1978).
Beynon JL, Beringer JE, Johnston AWB: Plasmids and host range in Rhizobium leguminosarum and Rhizobium phaseoli. J Gen Microbiol 120: 421–429 (1980).
Burn JE, Rossen L, Johnston AWB: Four classes of mutation in the nodD gene of Rhizobium leguminosarum biovar viciae which affect its ability to autoregulate and/or to activate other nod genes in the presence of flavonoid inducers. Genes and Dev 1: 456–464 (1987).
Debellé F, Rosenberg C, Vasse J, Maillet F, Martinez E, Denarie J, Truchet G: Assignment of symbiotic developmental phenotypes to common and specific nodulation (nod) genetic loci of Rhizobium meliloti. J Bact 168: 1075–1086 (1986).
Debellé F, Sharma SB: Nucleotide sequence of Rhizobium meliloti RCR2011 genes involved in host specificity of nodulation. Nucl Acids Res 14: 7453–7472 (1986).
Djordjevic MA, Gabriel DW, Rolfe BG: Rhizobium, the refined parasite of legumes. Ann Rev Phytopath 25: 145–168 (1987).
Djordjevic MA, Innes RW, Wijffelman CA, Schofield PR, Rolfe BG: Nodulation of specific legumes is controlled by several distinct loci in Rhizobium trifolii. Plant Mol Biol 6: 389–401 (1986).
Djordjevic MA, Schofield PR, Rolfe BG: Tn5 mutagenesis of Rhizobium trifolii host-specific nodulation genes result in mutants with altered host-range ability. Mol Gen Genet 200: 463–471 (1985).
Downie JA, Hombrecher G, Ma Q-S, Knight CD, Wells B, Johnston AWB: Cloned nodulation genes of Rhizobium leguminosarum determine host-range specificity. Mol Gen Genet 190: 359–365 (1983).
Downie JA, Knight CD, Johnston AWB, Rossen L: Identification of genes and gene products involved in the nodulation of peas by Rhizobium leguminosarum. Mol Gen Genet 198: 255–262 (1985).
Downie JA, Ma Q-S, Knight CD, Hombrecher G, Johnston AWB: Cloning of the symbiotic region of Rhizobium leguminosarum: the nodulation genes are between the nitrogenase genes and a nifA-like gene. EMBO J 2: 947–952 (1983).
Evans IJ, Downie JA: The nodI gene product of Rhizobium leguminosarum is closely related to ATP-binding bacterial transport proteins; nucleotide sequence analysis of the nodI and nodJ genes. Gene 43: 95–101 (1986).
Figurski DH, Helinski DR: Replication of an origincontaining derivative of plasmid RK2 dependent on a plasmid function provided in trans. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 76: 1648–1652 (1979).
Firmin JL, Wilson KE, Rossen L, Johnston AWB: Flavonoid activation of nodulation genes in Rhizobium reversed by other compounds present in plants. Nature 324: 90–92 (1986).
Fisher RF, Swanson JA, Mulligan JT, Long SR: Extended region of nodulation genes in Rhizobium meliloti 1021. II. Nucleotide sequence transcription start sites and protein products. Genetics 117: 191–201 (1987).
Fisher RF, Tu JF, Long SR: Conserved nodulation genes in Rhizobium meliloti and Rhizobium trifolii. Appl Environ Microbiol 39: 1432–1435 (1985).
Friedman AM, Long SR, Brown SE, Buikema WJ, Ausubel FM: Construction of a broad host range cosmid cloning vector and its use in the genetic analysis of Rhizobium mutants. Gene 18: 289–296 (1982).
Higashi ST: Transfer of clover infectivity of Rhizobium trifolii to Rhizobium phaseoli as mediated by an episomic factor. J Gen Appl Microbiol 13: 391–403 (1967).
Hong GF, Burn JE, Johnston AWB: Evidence that DNA involved in the expression of the nodulation (nod) genes in Rhizobium binds to the product of the regulatory gene nodD. Nucl Acids Res 15: 9677–9690 (1987).
Horvath B, Bachem CWB, Schell J, Kondorosi A: Host-specific regulation of nodulation genes in Rhizobium is mediated by a plant-signal, interacting with the nodD gene product. EMBO J 6: 841–848 (1987).
Horvath B, Kondorosi E, John M, Schmidt J, Torok I, Gyorgypal Z, Barabas I, Wieneke U, Schell J, Kondorosi A: Organization, structure and symbiotic function of Rhizobium meliloti nodulation genes determining host specificity for alfalfa. Cell 46: 335–343 (1986).
Johnston AWB, Beynon JL, Buchanan-Wollaston AV, Setchell SM, Hirsch PR, Beringer JE: High frequency transfer of nodulation ability between strains and species of Rhizobium. Nature 276: 634–636 (1978).
Knight CD, Rossen L, Robertson JG, Wells B, Downie JA: Nodulation inhibition by Rhizobium leguminosarum multicopy nodABC genes and analysis of early stages of plant infection. J Bact 166: 552–558 (1986).
Kosslak RM, Brookland R, Barkei J, Paaren HE, Appelbaum ER: Induction of Bradyrhizobium japonicum common nod genes by isoflavones isolated from Glycine max. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 84: 7428–7432 (1987).
Long SR: Genetics of Rhizobium nodulation. In: Kosuge T, Nester EW (eds) Plant Microbe Interactions, Vol. 1: Molecular and Genetic Perspectives, pp. 265–306. Academic Press, New York (1984).
Lamb JW, Hombrecher G, Johnston AWB: Plasmid-determinated nodulation and nitrogen fixation abilities in Rhizobium phaseoli. Mol Gen Genet 186: 449–452 (1982).
Maniatis T, Fritsch EF, Sambrook J: Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, Cold Spring Harbor, NY (1982).
Nieuwkoop AJ, Banfalvi Z, Oeshmane N, Gerhold D, Schell MG, Sirotkin KM, Stacey G: A locus encoding host range is linked to the common nodulation genes of Bradyrhizobium japonicum. J Bact 169: 2631–2638 (1987).
Peters NK, Frost JW, Long SR: A plant flavone, luteolin, induces expression of Rhizobium meliloti nodulation genes. Science 233: 977–980 (1986).
Putnoky P, Kondorosi A: Two gene clusters of Rhizobium meliloti code for early essential nodulation functions and a third influences nodulation efficiency. J Bact 167: 881–887 (1986).
Redmond JW, Batley M, Djordjevic MA, Innes RW, Kuempel PL, Rolfe BG: Flavones induce expression of nodulation genes in Rhizobium, Nature 323: 632–635 (1986).
Rolfe BG, Gresshoff PM, Shine J: Rapid screening for symbiotic mutants of Rhizobium and white clover. Plant Sci Lett 19: 277–284 (1980).
Rossen L, Davis EO, Johston AWB: Plant-induced expression of Rhizobium genes involved in host specificity and early stages of nodulation. TIBS 12: 430–434 (1987).
Rossen L, Johnston AWB, Downie JA: DNA sequence of the Rhizobium leguminosarum genes nodAB and C required for root hair curling. Nucl Acids Res 12: 9497–9508 (1984).
Schofield PR, Ridge RW, Rolfe BG, Shine J, Watson JM: Host-specific nodulation in encoded on a 14 kb DNA fragment in Rhizobium trifolii. Plant Mol Biol 3: 3–11 (1984).
Schofield PR, Watson JM: DNA sequence of Rhizobium trifolii nodulation genes reveals a reiterated and potentially regulatory sequence preceding nodABC and nodFE. Nucl Acids Res 14: 2891–2903 (1986).
Schwinghamer EA: Studies on induced variation in the rhizobia. III. Host range modification of Rhizobium trifolii by spontaneous and radiation-induced mutation. Am J Bot 49: 269–277 (1962).
Scott KF: Conserved nodulation genes from the non-legume symbiont Bradyrhizobium sp. parasponia. Nucl Acids Res 14: 2905–2919 (1986).
Shearman CA, Rossen L, Johnston AWB, Downie JA: The Rhizobium leguminosarum nodulation gene nodF encodes a polypeptide similar to acyl-carrier protein and is regulated by nodD plus a factor in pea root exudate. EMBO J 5: 647–652 (1986).
Spaink HP, Wijffelman CA, Pees E, Okker RJH, Lugtenberg BJJ: Rhizobium nodulation gene nodD as a determinant of host specificity. Nature 328: 337–339 (1987).
Surin BP, Downie JA: Characterisation of the Rhizobium leguminosarum genes nodLMN involved in efficient host-specific nodulation. Mol Microbiol 2: 173–183 (1988).
Swanson JA, Tu J, Ogawa J, Sanga R, Fisher RF, Long SR: Extended region of nodulation genes in Rhizobium meliloti. I. Phenotypes of Tn5 insertion mutants. Genetics 117: 181–189 (1987).
Wood WB: Host specificity of DNA produced by E. coli mutations affecting the restriction and modification of DNA. J Mol Biol 16: 118–133 (1966).
Zaat SAJ, Wijffelman CA, Spaink HP, VanBrussel AAN, Okker RJH, Lugtenberg BJJ: Induction of the nodA promoter of Rhizobium leguminosarum sym plasmid pRL1JI by plant flavonones and flavones. J Bact 169: 198–204 (1987).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Surin, B.P., Downie, J.A. Rhizobium leguminosarum genes required for expression and transfer of host specific nodulation. Plant Mol Biol 12, 19–29 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00017444
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00017444