Abstract
Aim
This study performed a systematic review of the laparoscopic approach to intestinal malrotation and compare the outcomes to the open approach in children.
Method
Medline/PubMed databases were reviewed and studies in patients < 18 years published in English/Spanish were included and selected by two independent reviewers. Demographics (age, weight, type of malrotation, type of surgery, conversions, comorbidity and complications) were collected. Descriptive statistics were used to analyze the quantities portion of the study, with results presented as percentages, means and medians.
Results
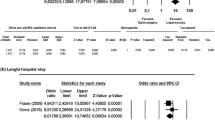
Between 1996 and 2019, 26 papers with 1828 patients from newborns to 13 years (median 7 years, mean 6.5 years) met the inclusion criteria. N = 457 (25%) patients were treated laparoscopic, n = 1055 (57.7%) open and no data on n = 316 (17.3%). The rate of laparoscopic conversion was 16.8% (n = 77). 14/26 articles described appendectomy as a part of Ladd’s procedure. 1/26 article (laparoscopy group) described cecopexy as a part of the procedure. There were 82 redo procedures (4.5%), 34 (7.4%) in the laparoscopy group and 41 (3.8%) in the open group (data not available n = 7). Complications were reported in n = 259 (14.2%), n = 62 (13.6%) in the laparoscopy group and n = 148 (14.0%) (n = 49 not specified). There were n = 4 lethal outcomes (0.4%) in the open cohort and none in the laparoscopic group.
Conclusions
Laparoscopic approach to malrotation in the pediatric age group is associated with a conversion rate of 16.8%. Poor reporting about the type of malrotation, co-mobidities and exact procedures performed needs to be improved to better evaluate outcomes both in laparoscopic and open procedures.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Millar AJ, Rode H, Cywes S (2003) Malrotation and volvulus in infancy and childhood. Semin Pediatr Surg 12:229–236
Martinez Ferro M, Cannizzaro C, Rodriguez S, et al. Intestinal malrotation Gaston E. In: Surgical neonatology, 2004, 1st edn. Grupo Guia, Buenos Aires (in press)
Zellos A, Zarganis D, Ypsiladis S et al (2012) Malrotation of the intestine and chronic volvulus as a cause of protein-losing enteropathy in infancy. Pediatrics 129:e515–e518
Adams SD, Stanton MP (2014) Malrotation and intestinal atresias. Early Hum Dev 90:921–925
Dekonenko C, Sujka J, Weaver K et al (2019) The identification and treatment of intestinal malrotation in older children. Pediatr Surg Int 35:665–671
Vural V, Türkoğlu M, Karatasb G (2015) Incidental midgut malrotation detected during second laparotomy: case report and literature review. Int J Surg Case Rep 7:134–136
Warner B (1997) Malrotation. In: Oldham KT, Colombani PM, Foglia RP (eds) Surgery of infants and children: scientific principles and practice. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Philadelphia, p 1229
Dilley AV, Pereira J, Shi EC (2000) The radiologist says malrotation: does the surgeon operate? Pediatr Surg Int 16:45
Berseth CL (1998) Disorders of the intestines and pancreas. In: Taeusch WH, Ballard RA (eds) Avery’s diseases of the newborn, 7th edn. WB Saunders, Philadelphia, p 918
Coste AH, Waheed A, Ahmad H (2019) Midgut volvulus. Stat Pearls Publishing, Treasure Island
Bill AH (1979) Malrotation of the intestine. In: Ravitch MM, Welch KJ, Benson CD et al (eds) Pediatric surgery. Year Book Medical, Chicago, pp 912–923
Wanjari AK, Deshmukh AJ, Tayde PS et al (2012) Midgut malrotation with chronic abdominal pain. N Am J Med Sci 4:196–198
Ezer SS, Oguzkurt P, Temiz A et al (2016) Intestinal malrotation needs immediate consideration and investigation. Pediatr Int 58:1200–1204
El-Gohary Y, Alagtal M, Gillick J (2010) Long-term complications following operative intervention for intestinal malrotation: a 10-year review. Pediatr Surg Int 26:203–206
Millar AJW, Rode H, Brown RA et al (1987) The deadly vomit: malrotation and midgut volvulus. Pediatr Surg Int 2:172–176
Malek MM, Burd RS (2005) Surgical treatment of malrotation after infancy: a population-based study. J Pediatr Surg 40:285–289
Nehra D, Goldstein AM (2011) Intestinal malrotation: varied clinical presentation from infancy through adulthood. Surgery 149:386–393
Yoon JR, You SJ (2012) A case of midgut malrotation presenting as multiple afebrile seizures. Brain Dev 34:244–247
Lee HC, Pickard SS, Sridhar S et al (2012) Intestinal malrotation and catastrophic volvulus in infancy. J Emerg Med 43:e49–e51
Messineo A, MacMillan JH, Palder SB et al (1992) Clinical factors affecting mortality in children with malrotation of the intestine. J Pediatr Surg 27:1343–1345
Langer J (2017) Intestinal rotation abnormalities and midgut volvulus. Surg Clin N Am 97:147–159. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.suc.2016.08.011
Carrol AG, Kavanagh RG, Leifhin N et al (2016) Comparative effectiveness of imaging modalities for the diagnosis of intestinal obstruction in neonates and infants: a critically appraised topic. Acad Radiol 23:559–568
Orzech N, Navarro OM, Langer JC (2006) Is ultrasonography a good screening test for intestinal malrotation? J Pediatr Surg 41:1005–1009
Pumberger W, Kargl S (2012) Malposition of the intestine malposition malrotation volvulus “midgut volvulus”. Eur Surg 44(4):237–247. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10353-012-0102-y
Ladd WE (1936) Surgical diseases of the alimentary tract in infants. N Engl J Med 215:705–708
Van der Zee DC, Bax NM (1995) Laparoscopic repair of acute volvulus in a neonate with malrotation. Surg Endosc 9:1123–1124
Hsiao M, Langer JC (2012) Surgery for suspected rotation abnormality: selection of open vs laparoscopic surgery using a rational approach. J Pediatr Surg 47:904–910
Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG, PRISMA Group (2009) Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. BMJ 339:b2535
Zhu H, Zheng S, Alganabi M et al (2019) Reoperation after Ladd’s procedure in the neonatal period. Pediatr Surg Int 35:117–120
Isani M, Schlieve C, Jackson J et al (2018) Is less more? Laparoscopic versus open Ladd’s procedure in children with malrotation. J Surg Res 229:351–356
Reddy A, Shah R, Kulkarni D (2018) Laparoscopic Ladd’s procedure in children: challenges, results, and problems. J Indian Assoc Pediatr Surg 23:61–65
Kisku S (2017) Orbit technique in malrotation with non-obstructive volvulus: a novel technique of devolvulation. Asian J Endosc Surg 10:213–215
Huntington J, Lopez J, Mahida J et al (2017) Comparing laparoscopic versus open Ladd’s procedure in pediatric patients. J Pediatr Surg 52:1128–1131
Ooms N, Matthyssens L, Draaisma J et al (2016) Laparoscopic treatment of intestinal malrotation in children. Eur J Pediatr Surg 26:376–381
Miyano G, Fukuzawa H, Morita K et al (2015) Laparoscopic repair of malrotation: what are the indications in neonates and children? J Laparoendosc Adv Surg Tech A 25:155–158
Fernandez EM, Favre Rizzo J, Arteaga González I et al (2014) Left-sided appendicitis: diagnosis and minimally invasive treatment. Acta Gastroenterol Latinoam 44:62–66
Hsiao M, Langer JC (2011) Value of laparoscopy in children with a suspected rotation abnormality on imaging. J Pediatr Surg 46:1347–1352
Nasir A, Abdur-Rahman L, Adeniran J (2011) Outcomes of surgical treatment of malrotation in children. Afr J Paediatr Surg 8:8–11
Hagendoorn J, Vieira-Travassos D, van der Zee D (2011) Laparoscopic treatment of intestinal malrotation in neonates and infants: retrospective study. Surg Endosc 25:217–220
Stanfill A, Pearl R, Kalvakuri K et al (2010) Laparoscopic Ladd’s procedure: treatment of choice for midgut malrotation in infants and children. J Laparoendosc Adv Surg Tech A 20:369–372
Fraser J, Aguayo P, Sharp SW et al (2009) The role of laparoscopy in the management of malrotation. J Surg Res 156:80–82
Adikibi B, Strachan C, MacKinlay G (2009) Neonatal laparoscopic Ladd’s procedure can safely be performed even if the bowel shows signs of ischemia. J Laparoendosc Adv Surg Tech A 19(Suppl 1):S167–S170
McVay M, Kokoska E, Jackson R et al (2007) Jack Barney Award. The changing spectrum of intestinal malrotation: diagnosis and management. Am J Surg 194:712–717
Palanivelu C, Rangarajan M, Shetty A et al (2007) Intestinal malrotation with midgut volvulus presenting as acute abdomen in children: value of diagnostic and therapeutic laparoscopy. J Laparoendosc Adv Surg Tech A 17:490–492
Draus J, Foley D, Bond S (2007) Laparoscopic Ladd procedure: a minimally invasive approach to malrotation without midgut volvulus. Am Surg 73:693–696
Ten B, Tolboom J, Boetes C et al (2006) Surgical intervention of intestinal malrotations in paediatric patients without other congenital anatomical abnormalities: overview from a single center. Eur J Radiol 59:20–24
Wu M, Hsu W, Lin W et al (2002) Laparoscopic Ladd’s procedure for intestinal malrotation: report of three cases. J Formos Med Assoc 101:152–155
Yamashita H, Kato H, Uyama S et al (1999) Laparoscopic repair of intestinal malrotation complicated by midgut volvulus. Surg Endosc 13:1160–1162
Fernández M, Vila J, Ibáñez V et al (1999) Laparoscopic transsection of Ladd’s bands: a new indication for therapeutic laparoscopy in neonates. Cir Pediatr 12:41–43
Bax N, van der Zee D (1998) Laparoscopic treatment of intestinal malrotation in children. Surg Endosc 12:1314–1316
Lessin M, Luks F (1998) Laparoscopic appendectomy and duodenocolonic dissociation (LADD) procedure for malrotation. Pediatr Surg Int 13:184–185
Mazziotti M, Strasberg S, Langer J (1997) Intestinal rotation abnormalities without volvulus: the role of laparoscopy. J Am Coll Surg 185:172–176
Waldhausen J, Sawin R (1996) Laparoscopic Ladd’s procedure and assessment of malrotation. J Laparoendosc Surg 6(Suppl 1):S103–S105
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chacon, C.S., Saxena, A.K. Approach to intestinal malrotation in children in the laparoscopic era. J Ped Endosc Surg 1, 137–142 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42804-019-00036-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42804-019-00036-7