Abstract
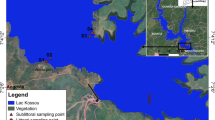
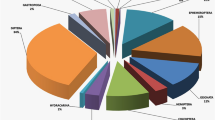
The purpose of this study is to evaluate the seasonal variations in the density and diversity of macroinvertebrates in relation to the dynamics of physicochemical parameters of water quality and study factors which influence the lake ecosystem of Prashar lake of Himachal Pradesh. Monthly sampling from November 2014 to October 2015 at three sites was undertaken to evaluate the community structure of macroinvertebrates in relation to the dynamics of water quality parameters. All three sites (S1, S2, and S3) were identified keeping in view the accessibility, type of substrate and other influencing factors. A total of 25 genera of nine macroinvertebrates groups were identified during the study period. The highest macroinvertebrates abundance was observed in winter and the lowest in monsoon season. Maximum Shannon–Wiener diversity index was recorded at site S3 in winter season as compared to the sites S1 and S2. Water temperature, dissolved oxygen (DO), pH, electrical conductivity (EC), turbidity, total dissolved solids (TDS), and nitrates were important water quality variables that affected the macroinvertebrates diversity of the Prashar lake. The stable and healthy environmental condition of Prashar lake was recorded which was indicated by the presence of Ephemeroptera, Plecoptera, Trichoptera (EPT) during winter season. Factors which disturb the diversity and ecosystem of the lake are attributed to the natural and anthropogenic pressures such as, soil erosion, overgrazing, tourism load and solid waste. The density of macroinvertebrates was further influenced by the growth of riparian vegetation, suitable bottom substrates, and water level fluctuations. A strategy for conservation and management is proposed i.e., ex-situ and in-situ conservation, regular environmental monitoring, restoration of the riparian zone, afforestation in the catchment area, raising awareness, solid waste management and research programmes that will be helpful for sustainable management of Prashar lake.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anthony EO (2001) Composition and diversity of Diptera in temporary pond in Southern Nigeria. Trop Ecol 42(2):259–268
APHA (2005) Standard methods for the examination of water and waste water. American Public Health Association, Washington, pp 1–1368
Balachandran C, Ramachandra TV (2010) Aquatic macroinvertebrate diversity and water quality of bangalore lakes. Wetl Biodivers Clim Change. https://doi.org/10.13140/2.1.4732.0966
Beauger A, Lair N, Reyes-Marchant P, Peiry JL (2006) The distribution of macroinvertebrate assemblages in areach of the River Allier (France) in relation to riverbed characteristics. Hydrobiologia 571:63–76
Belal AAM, El-Sawy MA, Dar MA (2016) The effect of water quality on the distribution of macro-benthic fauna in Western Lagoon and Timsah Lake, Egypt. I. Egypt J Aquat Res 42:437–448
Blettler MCM, Amsler ML, Ezcurra de Drago I, Drago E, Paira A, Espinola LA, Eberle E, Szupiany R (2016) Fine sediment input and benthic fauna interactions at the confluence of two large rivers. Int J Environ Res 10(1):65–76
Chang H (2002) Spatial and temporal variations of water quality in the river and its tributaries, Seoul, Korea. Water Air Soil Pollut 161:267–284
Death RG, Winterbourn MJ (1995) Diversity patterns in stream benthic invertebrate communities: the influence of habitat stability. Ecology 76:1446–1460
Dhanalakshmi V, Shanthi K, Remia KM (2013) Physicochemical study of Eutrophic pond in Pollachi town, Tamilnadu, India. Int J Curr Microbiol Appl Sci 2(12):219–227
Dolis D, Dohet A (2003) The use of Ephemeroptera to assess aquatic biodiversity in the rhithral part of the Luxembourgish rivers. In: Gaino E (ed) Research update on ephemeroptera and plecoptera. Università di Perugia, Perugia, pp 299–303
Duan H, Ma R, Xu X, Kong F, Zhang S, Kong W (2009) 2-decade reconstruction of algal blooms in China’s Lake Taihu. Environ Sci Technol 43(10):3522–3528
Edington JM, Hilldrew AG (1995) Caseless Caddis Larvae of the British Isles: a key with ecological notes. Freshw Biol Assoc, Ambleside, pp 1–134
Edmondson WT (1965) Reproductive rate of planktonic rotifers as related to food and temperature in nature. Ecol Monit 35:61–111
Elliott JM, Humpesch UH, Macan TT (1988) Larvae of the British Ephemeroptera: a key with ecological notes. Freshwater Biological Association, Ambleside, pp 1–145
Emere MC, Nasiru CE (2009) Macro invertebrates as indicators of the water quality of an urbanized stream, Kaduna Nigeria. Nat Sci 7(1):1–7
Fore LS, Karr JR, Wisseman RW (1996) Assessing invertebrate responses to human activities: evaluating alternative approaches. J N Am Benthol Soc 15(2):212–231
Ghosh D, Biswas JK (2015) Macroinvertebrate diversity indices: a quantitative bioassessment of ecological health status of an oxbow lake in Eastern India. J Adv Environ Health Res 3(2):78–90
Gopal B (1994) The role of ecotones (transition zones) in the conservation and management of tropical inland waters. Inland Waters of tropical Asia and Australia: conservation and management. Schweizerbart Verl, Stuttgart, pp 17–25
Graf W, Grasser U, Waringer J (2002) Trichoptera—part III. In: Moog O (ed) Fauna Aquatica Austriaca, edition—Wasserwirtschaftskataster, Bundesministerium für Land- und Fortwirtschaft. Umwelt und Wasserwirtschaft, Wien, p 42
Gupta S (2013) Surface water quality monitoring of some selected fresh water environments in Durgapur, West Bengal, India in relation to macroinvertebrate diversity and ecological health status. Asian Acad Res J Multidiscip 1(14):342–363
Hynes HBN (1971) The ecology of running waters. Liverpool University Press, Liverpool, pp 1–555
Ishaq F, Khan A (2013) Diversity pattern of macrozoobenthos and their relation with qualitative characteristics of River Yamuna in Doon Valley Uttarakhand. American-Eurasian J Toxicol Sci 5(1):20–29
Johnson RK, Goedkoop W, Sandin L (2004) Spatial scale and ecological relationships between the macroinvertebrate communities of stony habitats of streams and lakes. Freshw Biol 49:1179–1194
Khan MAG, Chowdhury SH (1994) Physical and chemical limnology of lake Kaptai, Bangladesh. Trop Ecol 35:35–51
Krull JN (1970) Aquatic plants, macro-invertebrates association and waterfowls. J Wildl Manag 34:707–718
Kumari R, Sharma RC (2018) Assessment of water quality index and multivariate analysis of high altitude sacred lake Prashar, Himachal Pradesh, India. Int J Environ Sci Technol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-018-2007-1
Lancaster J, Hildrew AG (1993) Flow refugia and the microdistribution of lotic macroinvertebrates. J N Am Benthol Soc 12:385–393
Mabidi A, Bird MS, Perissinotto R (2017) Distribution and diversity of aquatic macroinverbrate assemblages in a semi-arid region earmarked for shale exploration (Eastern Cape Karoo, South Africa). PLoS One. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0178559
Macan TT (1974) Freshwater Ecology. Longman Group Ltd., London
Masese FO, Omukoto JO, Nyakeya K (2013) Biomonitoring as a prerequisite for sustainable water resources: a review of current status, opportunities and challenges to scaling up in East Africa. Ecohydrol Hydrobiol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecohyd.2013.06.004
Needham JG, Needham PR (1962) A guide to the study of freshwater biology, 5th edn. Hl3lden-Day, Inc, San Francisco, p 108
Ntislidou C, Lazaridou M, Tsiaoussi V, Bobori DC (2018) A new multimetric macroinvertebrate index for the ecological assessment of Mediterranean lakes. Ecol Ind 93:1020–1033
Peeters ETHM, Dewittev A, Koelmans AA, Velden JA, Besten PJ (2001) Evaluation of bioassays versus contaminant concentrations in explaning the macroinvertebrate community structure in the Rhine-Meuse delta, The Netherlands. Environ Toxicol Chem 20:2883–2891
Petr T (1972) Benthic fauna of a tropical man-made lake (Volta Lake, Ghana, 1965-1968). Archiv fürHydrobiologie 70:484–533
Rawat MS, Sharma RC (2005) Phytoplankton population of Garhwal Himalayam Lake Deoria Tal, Uttranchal. J Ecophysiol Occupat Health 5:73–76
Rempel LL, Richardson JS, Healey MC (1999) Flow refugia for benthic macroinvertebrates during flooding of a large river. J N Am Benthol Soc 18:34–48
Scarsbrook MR, Townsend CR (1993) Stream community structure in relation to spatial and temporal variation: a habitat templet study of two contrasting New Zealand streams. Freshw Biol 29:395–410
Shanthala M, Shanker PH, Basaling BH (2008) Diversity of phytoplanktons in a waste stabilization pond at Shimoga town, Karnataka State, India. Environ Monit Assess 151:437–443
Sharma I, Dhanze R (2012) Evaluation of macrobenthic fauna in hill stream environment of Western Himalaya, India. J Threat Taxa 4(9):2875–2882
Sharma RC, Rawat JS (2009) Monitoring of aquatic macro-invertebrates as bioindicator for assessing the health of wetlands: a case study in the Central Himalayas, India. Ecol Ind 9:118–128
Sharma V, Walia YK (2015) Water quality assessment using physico-chemical parameters and heavy metals of Gobind Sagar lake, Himachal Pradesh (India). Curr World Environ 10(3):161–166
Shekhar STR, Kiran BR, Puttaiah ET, Shivaraj Y, Mahadevan KM (2008) Phytoplankton as index of water quality with reference to industrial pollution. J Environ Biol 29(2):233–236
Stewart PM, Butcher JT, Swinford TO (2000) Land use, habitat, and water quality effects on macroinvertebrate communities in three watersheds of a Lake Michigan associated marsh system. Aquat Ecosyst Health Manag 3:179–189
Tara JS, Kour R, Sharma S (2011) Studies on the occurrence and seasonal abundance of aquatic coleopteran in relation to some physicochemical parameters of water of Gharana wetland Wetland Reserve Jammu. Bioscan 6(2):257–261
Tolonen KT, Hamalain H, Holopainen IJ, Karjalainen J (2001) Influences of habitat type and environmental variables on littoral macroinvertebrate communities in a large lake system. Archiv für Hydrobiologie 152:39–67
Tonapi GT (1980) Fresh water animals of India-an ecological approach. Oxford and IBH Publishing Co, New Delhi, p 341
Wallace ID, Wallace B, Philipson GN (1990) A key to the case bearing Caddis Larvae of Britain and Ireland. Freshw Biol Assoc, Ambleside, p 237
Ward HB, Whipple GC (1992) Freshwater Biology, 2nd edn. Wiley, New York, pp 1–1248
Washington HG (1984) Diversity, biotic and similarity indices: a review with special relevance to aquatic ecosystems. Water Res 18(6):653–694
Welcome RI (1979) Fisheries ecology of flood plain rivers. Longman Ltd, New York, p 317
Winkelmann C, Worischka S, Koop JHE, Benndorf J (2007) Predation effects of benthivorous fish on grazing and shredding macroinvertebrates in a detritus-based stream food web. Limnologica 37:121–128
Ziglio G, Flaim G, Siligardi M (2006) Biological monitoring of rivers. Water quality measurements, vol 2. Wiley, New Jersey, pp 5–490
Acknowledgements
The corresponding author is thankful to University Grants Commission and H.N.B. Garhwal (A Central University) for providing Central University fellowship for undertaking the present work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kumari, R., Sharma, R.C. Seasonal effects on diversity of macroinvertebrates in Himalayan Lake Prashar, Himachal Pradesh, India. Environmental Sustainability 1, 449–459 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42398-018-00041-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42398-018-00041-1