Abstract
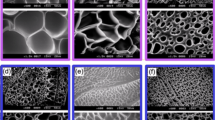
The objective of the study was to prepare neem gum polysaccharide graft copolymers of acrylamide (NGP-g-Am) using 3 factorial design. Prepared NGP-g-Am’s hydrogels were characterized using UV-visible spectroscopy, FTIR spectral analysis, SEM images, contact angle determination, biodegradability, hemocompatibility, and pH-dependent swelling ability. NGP-g-Am showed more swelling index in all the media like double distilled water, 1 N NaOH, and 0.1 N HCl than native form. Data obtained through soil burial biodegradation studies were showed t90% for neem gum polysaccharide (NGP) and NGP-g-Am (N1), 9 and 28 days, respectively. Findings of the Lee-White test for blood clotting time showed the longest clotting time (15.39 ± 0.53 min) for NGP-g-Am (N5) as compared with that for the uncoated glass surface (2.05 ± 0.93 min). Thrombus formed during studies were found to be significantly more in case of uncoated glass surface as compared with N (0.47 ± 0.23 mg), N1 (0.29 ± 0.08 mg), N2 (0.30 ± 0.13 mg), N5 (0.29 ± 0.11 mg), N7 (0.29 ± 0.07 mg), and N9 (0.28 ± 0.13 mg). Structure-based docking studies predict that binding of ligands to TLR-4 receptors is significantly more responsible for the antimicrobial effect of both NGP and NGP-g-Am.

Graphical abstract















Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. Groll, S. Smriti, A. Krystyna, M. Martin, Biocompatible and degradable nanogels via oxidation reactions of synthetic thiomers in inverse miniemulsion. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. A. Polym. Chem. 47, 5543–5549 (2009).
H. Mittal, B.S. Kaith, R. Jindal, Synthesis, characterization and swelling behaviour of poly (acrylamide-comethacrylic acid) grafted Gum ghatti based superabsorbent hydrogels. Adv. Polym. Sci. Res. 1(3), 55–66 (2010)
R. Malviya, P.K. Sharma, S.K. Dubey, Modification of polysaccharides: pharmaceutical and tissue engineering applications with commercial utility (patents). Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 68, 929–938 (2016)
R. Malviya, P.K. Sharma, S.K. Dubey, Modification and applications of polysaccharide (Lap Lambert academic publishing, Germany, 2016)
N. Bankar, P. Aggarwal, A. Singh, D. Chakraborty, R. Singh, Water availability in different soils in relation to hydrogel application. Geoderma 187–188, 94–101 (2012)
L. Wu, M. Liu, Slow-release potassium silicate fertilizer with the function of superabsorbent and water retention. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 46, 6494–6500 (2007)
R. Malviya, P.K. Sharma, S.K. Dubey, Antioxidant Potential and Emulsifying Properties of Neem (Azadirachita indica, Family Meliaceae) Gum Polysaccharide. Pharm. Anal. Acta 8, 559 (2017)
A.B. Gangurde, S.S. Malode, R.S. Bhambar, Preliminary evaluation of neem gum as tablet binder. Indian J. Pharm. Educ. Res. 42(4), 344–347 (2008)
A.T. Ogunjimi, G.A. Biowu, Flow and consolidation properties of neem gum coprocessed with two pharmaceutical excipients. Powder Technol. 246, 187–192 (2013)
R. Malviya, P.K. Sharma, S.K. Dubey, Stability facilitation of nanoparticles prepared by ultrasound assisted solvent-antisolvent method: Effect of neem gum, acrylamide grafted neem gum and carboxymethylated neem gum over size, morphology and drug release. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 91, 772–784 (2018)
Y.S. Choi, S.R. Hong, Y.M. Lee, K.W. Song, M.H. Park, Y.S. Nam, Study on gelatin-containing artificial skin: I. Preparation and characteristics of novel gelatin-alginate sponge. Biomaterials 20(5), 409–417 (1999)
K. Ulubayram, A.N. Cakar, P. Korkusuz, C. Ertan, N. Hasirci, EGF containing gelatin-based wound dressings. Biomaterials 22(11), 1345–1356 (2001)
R. Guidoin, D. Marceau, T.J. Roo, M. King, Y. Merhi, P.E. Roy, L. Martin, M. Duvel, In vitro and in vivo characterization of an impervious polyester arterial prosthesis: the Gelseal Triaxial® graft. Biomaterials 8, 433–441 (1987)
R.A. Jones, G. Ziemer, F.J. Schoen, L. Britton, A.R. Castaneda, A new sealant for knitted Dacron prostheses: minimally cross-linked gelatin. J. Vasc. Surg. 7, 414–419 (1998)
K.S.C.R. dos Santos, J.F.J. Coelho, P. Ferreira, I. Pinto, S.G. Lorenzetti, E.I. Ferreira, O.Z. Higa, M.H. Gil, Synthesis and characterization of membranes obtained by graft copolymerization of 2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate and acrylic acid onto chitosan. Int. J. Pharm. 310, 37–45 (2006)
K. Sharma, B.S. Kaith, V. Kumar, S. Som, S. Kalia, H.C. Swart, Synthesis and properties of poly(acrylamide-aniline)-grafted gum ghatti based nanospikes. RSC Adv. 3, 25830–25839 (2013)
B.S. Kaith, R. Jindal, H. Mittal, K. Kumar, Synthesis, characterization, and swelling behavior evaluation of hydrogels based on gum ghatti and acrylamide for selective absorption of saline from different petroleum fraction-saline emulsions. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 124, 2037–2047 (2012)
H. Mittal, A. Maity, S.S. Ray, J. Phys, The adsorption of Pb2+ and Cu2+ onto gum ghatti-grafted poly(acrylamide-co-acrylonitrile) biodegradable hydrogel: isotherms and kinetic models. Chem. B. 119(5), 2026–2039 (2015)
T.K. Giri, S. Pure, D.K. Tripathi, Synthesis of graft copolymers of acrylamide for locust bean gum using microwave energy: swelling behavior, flocculation characteristics and acute toxicity study. Polimeros 25(2), 168–174 (2015)
K. Sharma, V. Kumar, B.S. Kaith, V. Kumar, S. Som, S. Kalia, H.C. Swart, A study of the biodegradation behaviour of poly(methacrylic acid/aniline)-grafted gum ghatti by a soil burial method. RSC Adv. 4, 25637–25649 (2014)
I.M. Thakore, S. Desai, B.D. Sarawade, S. Devi, Studies on biodegradability, morphology and thermo-mechanical properties of LDPE/modified starch blends. Eur. Polym. J. 37, 151–160 (2001)
A. Maghchiche, A. Haouam, B. Immirzi, Use of polymers and biopolymers for water retaining and soil stabilization in arid and semiarid regions. J. Taibah Univ. Sci. 4, 9–16 (2010)
L. Wu, M. Liu, R. Liang, Preparation and properties of a double-coated slow-release NPK compound fertilizer with superabsorbent and water-retention. Bioresour. Technol. 99(3), 547–554 (2008)
H. Marsh, F. Rodriguez-Reinoso, in Activated carbon, 1st edn. Elsevier Sci Technol. Books, (2006), pp. 401–462
G. Newcombe, R. Hayes, M. Drikas, Granular activated carbon: Importance of surface properties in the adsorption of naturally occurring organics. Colloid Surf. A. 78, 65–71 (1993)
M.V. Lopez-Ramon, F. Stoeckli, C. Moreno-Castilla, F. Carrasco-Marin, On the characterization of acidic and basic surface sites on carbons by various techniques. Carbon 37, 1215–1221 (1999)
S.L. Goertzen, K.D. Theriault, A.M. Oickle, A.C. Tarasuk, H.A. Andreas, Standardization of the Boehm titration. Part I. CO 2 expulsion and endpoint determination. Carbon 48, 1252–1261 (2010)
K. Ishihara, H. Oshida, Y. Endo, T. Ueda, A. Watanabe, N. Nakabayashi, Hemocompatibility of human whole blood on polymers with a phospholipid polar group and its mechanism. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A. 26, 1543–1552 (1992)
N.N. Reddy, K. Varaprasad, S. Ravindra, G.V.S. Reddy, K.M.S. Reddy, K.M.M. Reddy, K.M. Reddy, Evaluation of blood compatibility and drug release studies of gelatin based magnetic hydrogel nanocomposites. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 385, 20–27 (2011)
J.P. Singhal, A.R. Raya, Synthesis of blood compatible polyamide block copolymers. Biomaterials 23, 1139–1145 (2002)
General chapter (11) USP reference standards United States Pharmacopoeia-27-National Formulary 22, (US Pharmacopoeial Convention Inc., Rockville, 2004), pp. 2111–2139
R. Aravindhan, T. Sreelatha, P.T. Perumal, A. Gnanamani, Synthesis, characterization and biological profile of metal and azo-metal complexes of embelin. Complex Met. 1, 69–79 (2014)
P.J. Manna, T. Mitra, N. Pramanik, V. Kavitha, A. Gnanamani, P.P. Kundu, Potential use of curcumin loaded carboxymethylated guar gum grafted gelatin film for biomedical applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromolec. 75, 437–446 (2015)
W. Fang, D. Bi, R. Zheng, N. Cai, H. Xu, R. Zhou, Identification and activation of TLR4-mediated signalling pathways by alginate-derived guluronate oligosaccharide in RAW264.7 macrophages. Sci. Rep. 7(1), 1663 (2017)
C. Susan, A.J. Luke, O’Neill, How important are Toll-like receptors for antimicrobial responses? Cellular Microbiology, 9(8), 1891–1901 (2007)
L. Lundin, A.M. Hermansson, Supermolecular aspects of xanthan-locust bean gum gels based on rheology and electron microscopy. Carbohydr. Polym. 26, 129–140 (1995)
S. Kaity, J. Issac, P.M. Kumar, A. Bose, T.W. Wong, A. Ghosh, Microwave assisted synthesis of acrylamide grafted locust bean gum and its application in drug delivery. Carbohydr. Polym. 98, 1083–1094 (2013)
A.V. Singh, L.K. Nath, M. Guha, Microwave assisted synthesis and characterization of Phaseolus aconitifolius starch-g-acrylamide. Carbohydr. Polym. 86, 872–876 (2011)
S. Saber-Samandari, M. Gazi, E. Yilmaz, UV-induced synthesis of chitosan-g-polyacrylamide semi-IPN superabsorbent hydrogels. Polym. Bull. 68, 1623–1639 (2012)
W. Wang, A. Wang, Synthesis and swelling properties of pH-sensitive semi-IPN superabsorbent hydrogels based on sodium alginate-g-poly(sodium acrylate) and polyvinylpyrrolidone. Carbohydr. Polym. 80(4), 1028–1036 (2010)
B.S. Saruchi, R. Kaith, G.S. Jindal, Kapur, Enzyme-based green approach for the synthesis of gum tragacanth and acrylic acid cross-linked hydrogel: its utilization in controlled fertilizer release and enhancement of water-holding capacity of soil. Iran Polym. J. I. 22, 561–570 (2013)
K. Erdener, B.U. Omer, S. Dursun, Swelling equilibria and dye adsorption studies of chemically crosslinked superabsorbent acrylamide/maleic acid hydrogels. Eur. Polym. J. 38, 2133–2141 (2000)
A. Pourjavadi, A.M. Harzandi, H. Hosseinzaden, Modified carrageenan 3. Synthesis of a novel polysaccharide-based superabsorbent hydrogel via graft copolymerization of acrylic acid onto kappa-carrageenan in air. Eur. Polym. J. 40, 1363–1370 (2004)
K. Sharma, B.S. Kaith, V. Kumar, S. Kalia, V. Kumar, H.C. Swart, Water retention and dye adsorption behavior of Gg-cl-poly(acrylic acid-aniline) based conductive hydrogels. Geoderma 232-234, 45–55 (2014)
P. Deepika, K.S. Avjeet, I.S. Michael, Recyclability of poly (N-isopropylacrylamide) microgel-based assemblies for organic dye removal from water. Colloid Polym. Sci. 291, 1795–1802 (2013)
G. Azzulia, R. Barbucci, M. Benvenuti, P. Ferriti, M. Nocentini, Chemical and biological evaluation of heparinized poly(amido-amine) grafted polyurethane. Biomaterials 8, 61–66 (1987)
M.C. Tanzi, C. Barozzi, G. Teighi, R. Ferrara, G. Casini, F. Tempesti, Heparinizable graft copolymers from chlorosulphonated polyethylene with poly(amido-amine) segments. Biomaterials 6, 273–276 (1985)
K. Ishihara, H. Oshida, Y. Endo, T. Ueda, A. Watanable, N. Nakabayashi, Hemocompatibility of human whole blood on polymers with a phospholipid polar group and its mechanism. J. Biomed. Res. 26 1543–1552 (1992)
T. Ueda, A. Watanable, K. Ishihara, N. Nakabayashi, J. Biomaterial Sci, Polym. Ed. 3, 185–194 (1991)
M. Mrlik, P. Sobolciak, I. Krupa, P. Kasak, Light-controllable viscoelastic properties of a photolabile carboxybetaine ester-based polymer with mucus and cellulose sulfate. Emerg. Mater. 1, 35–45 (2018)
Acknowledgments
The authors are highly thankful to Mr. Mukesh Roy, Asst. Professor, Amity University, to carry out contact angle measurement and their help in SEM analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Malviya, R., Sharma, P.K. & Dubey, S.K. Microwave-assisted preparation of biodegradable, hemocompatible, and antimicrobial neem gum–grafted poly (acrylamide) hydrogel using (3)2 factorial design. emergent mater. 2, 95–112 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42247-019-00022-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42247-019-00022-y