Abstract
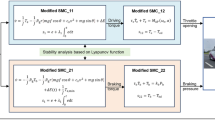
A driver’s intention is recognized accurately by employing fuzzy identification and a logic threshold including acceleration intention and steering intention. Different torque distribution control strategies are developed for different intentions and the driver’s torque demand is amended by fuzzy identification so that the response of the vehicle is more consistent with the driver’s intention of operation. Finally, a simulation model is built using MATLAB/Simulink to validate the control strategy. Simulation results show that the system accurately identifies the driver’s intention and improves the acceleration performance and steering stability of the vehicle.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hasan, M.M.A.E., Ektesabi, M., Kapoor, A.: Pollution control and sustainable urban transport system-electric vehicle. World Acad. Sci. Eng. Technol. 78, 970–975 (2011)
Papelis, Y.E., Watson, G.S., Brown, T.L.: An empirical study of the effectiveness of electronic stability control system in reducing loss of vehicle control. Accid. Anal. Prev. 42, 929–934 (2010)
Wang, B.: Study on Experiment Platform of Four-Wheel-Independent-Drive EV and its Driving Force control System. Tsinghua University, Beijing (2009)
Chen, Y.X.: Study of Direct Yaw Moment Control for in-Wheel Motor Electric Vehicles. Jilin University, Changchun (2013)
He, P., Hori, Y.: Improvement of EV maneuverability and safety by disturbance observer based dynamic force distribution. In: The 22nd International Battery, Hybrid and Fuel Cell Electric Vehicle Symposium and Exposition. Yokohama, Japan, pp. 1818–1827 (2006)
Yu, Z.P., Jiang, W., Zhang, L.J.: Torque distribution control for four wheel in-wheel-motor electric vehicle. J. Tongji Univ. (Nat. Sci.) 36(8), 1115–1119 (2008)
Wang, B., Luo, Y.G., Fan, J.J., et al.: A study on driving force distribution of four-wheel-independent drive electric vehicle based on control allocation. Automot. Eng. 32(2), 128–132 (2010)
Lin, J.G., Gu, J.A.: A study on PHEV output torque control based on fuzzy recognition of driver’s intention. Automot. Eng. 11(34), 984–989 (2012)
Wang, Q.N., Tang, X.Z., Wang, P.Y.: Control strategy of hybrid electric vehicle based on driving intention identification. J. Jilin Univ. (Eng. Sci.) 4(42), 789–795 (2012)
Raksincharoensak, P., Mizushima, T., Nagai, M.: Direct yaw moment control system based on driver behaviour recognition. Veh. Syst. Dyn. 9(56), 911–921 (2008)
Yang, W.F.: Automotive Theory. South China University of Technology Press, Guangzhou (2010)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Peng, B., Zhang, H., Xuan, F. et al. Torque Distribution Strategy of Electric Vehicle with In-wheel Motors Based on the Identification of Driving Intention. Automot. Innov. 1, 140–146 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42154-018-0024-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42154-018-0024-x