Abstract
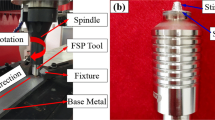
Friction stir processing (FSP) was applied to plates of cast aluminum A206 alloy. The focus of the work was on the evolution of microstructure during processing, which yielded dramatic decrease in the local grain size of the processed material. Reduction in pore morphology features, as well as intermetallic particle size, was also observed. Friction-stir-processed metal is characterized by a high ratio of high-angle grain boundaries to low-angle boundaries compared to what is observed in the as-cast alloy. Consistent with findings of other investigators, FSP generates a product nugget which has a portion of its structure having an onion skin-type structure that is characterized by a preferred crystallographic texture within individual bands in the nugget.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Z.Y. Ma, S.R. Sharma, R.S. Mishra, M.W. Mahoney, Microstructural modification of cast aluminum alloys via friction stir processing. Mater. Sci. Forum 426–432, 2891–2896 (2003)
Z.Y. Ma, S.R. Sharma, R.S. Mishra, Microstructural modification of as-cast Al–Si–Mg alloy by friction stir processing. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 37, 3323–3336 (2006)
M.L. Santella, T. Engstrom, D. Storjohann, Effects of friction stir processing on mechanical properties of the cast aluminum alloys A319 and A356. Scripta Mater. 53, 201–206 (2005)
Z.Y. Ma, A.L. Pilchak, M.C. Juhas, J.C. Williams, Microstructural refinement and property enhancement of cast light alloys via friction stir processing. Scripta Mater. 58, 361–366 (2008)
D. Zhang, M. Suzuki, K. Maruyama, Microstructural evolution of a heat-resistant magnesium alloy due to friction stir welding. Scripta Mater. 52, 899–903 (2005)
W.M. Thomas, E.D. Nicholas, J.C. Needham, M.G. Murch, P. Templesmith, C.J. Dawes, G.B. Patent Application No. 9125978.8 (1991)
K.V. Jata, S.L. Semiatin, Continuous dynamic recrystallization during friction stir welding of high strength aluminum alloys. Scripta Mater. 43, 743–749 (2000)
J.-Q. Su, T.W. Nelson, R. Mishra, M. Mahoney, Microstructural investigation of friction stir welded 7075-T651 aluminum. Acta Materialia 51, 713–729 (2003)
M. Karlsen, Ø. Frigaard, J. Hjelen, Ø. Grong, H. Norum, SEM-EBSD characterisation of the deformation microstructure in friction stir welded 2024 T351 aluminium alloy. Mater. Sci. Forum 426–432, 2861–2866 (2003)
C.G. Rhodes, M.W. Mahoney, W.H. Bingel, M. Calabrese, Fine-grain evolution in friction-stir processed 7075 aluminum. Scripta Mater. 48, 1451–1455 (2003)
J.-Q. Su, T.W. Nelson, C.J. Sterling, Grain refinement of aluminum alloys by friction stir processing. Philos. Mag. 86, 1–26 (2006)
T.R. McNelley, S. Swwaminathan, J.-Q. Su, Recrystallization mechanism during friction stir welding/processing of aluminum alloys. Scripta Mater. 58, 349–354 (2008)
Y.J. Kwon, N. Saito, I. Shigematsu, Friction stir process as a new manufacturing technique of ultrafine grained aluminum alloy. J. Mater. Sci. Lett. 21, 1473–1476 (2002)
D.C. Hofmann, K.S. Vecchio, Submerged friction stir processing (SFSP): an improved method for creating ultra-fine-grained bulk materials. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 234, 234–241 (2005)
Z.Y. Ma, R.S. Mishra, Development of ultrafine-grained microstructure and low temperature (0.48 Tm) superplasiticity in friction stir processed Al–Mg–Zr. Scripta Mater. 53, 75–80 (2005)
P. Cavaliere, P.P. De Marco, Friction stir processing of a Zr-modified 2014 alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 462, 206–210 (2007)
P. Cavaliere, A. Squillace, High temperature deformation of friction stir processed 7075 aluminium alloy. Mater. Charact. 55, 136–142 (2005)
P. Cavaliere, Effects of friction stir processing on the fatigue properties of a Zr-modified 2014 alloy. Mater. Charact. 57, 100–104 (2006)
D.C. Hofmann, K.S. Vecchio, Thermal history analysis of friction stir processed and submerged friction stir processed aluminum. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 465, 165–175 (2007)
K.N. Krishnan, On the formation of onion rings in friction stir welds. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 327, 246–251 (2002)
G.R. Cui, Z.Y. Ma, S.X. Li, Periodical plastic flow pattern in friction stir processed Al–Mg alloy. Scripta Mater. 58, 1082–1085 (2008)
Z.W. Chen, S. Cui, On the forming mechanism of banded structures in aluminum alloy friction stir welds. Scripta Mater. 58, 417–420 (2008)
B. Yang, J. Yan, M.A. Sutton, A.P. Reynolds, Banded microstructure in AA2024-T351 and AA2524-T351 aluminum friction stir welds: part I. Metallurgical studies. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 364, 55–65 (2004)
P.B. Prangenell, C.P. Heason, Grain structure formation during friction stir welding observed by the ‘stop action technique’. Acta Mater. 53, 3179–3192 (2005)
Y.S. Sato, H. Kokawa, K. Ikeda, M. Enomoto, S. Jogan, T. Hashimoto, Microtexture in the friction-stir weld of an aluminum alloy. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 32, 941–948 (2001)
D.P. Field, T.W. Nelson, Y. Hovanski, K.V. Jata, Heterogeneity of crystallographic texture in friction stir welds of aluminum. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 32, 2869–2877 (2001)
J.A. Schneider, A.C. Nunes Jr., Charaterization of plastic flow and resulting microstextures in a friction stir weld. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 35, 777–783 (2004)
R.W. Fonda, J.F. Bingert, K.J. Colligan, Development of grain structure during friction stir welding. Scripta Mater. 51, 243–248 (2004)
R.W. Fonda, K.E. Knipling, J.F. Bingert, Microstructure evolution ahead of the tool in aluminum friction stir welds. Scripta Mater. 58, 343–348 (2008)
C.I. Chang, C.J. Lee, J.C. Huang, Relationship between grain size and Zener–Holloman parameter during friction stir processing in AZ31 Mg alloys. Scripta Mater. 51, 509–514 (2004)
R.W. Fonda, J.F. Bingert, Texture variations in an aluminum friction stir weld. Scripta Mater. 57, 1052–1055 (2007)
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge the member companies of the Advanced Casting Research Center (ACRC) for their support of this work, and for their continued support of research focused on the science and technology of metal casting at Worcester Polytechnic Institute.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, N., Apelian, D. Friction Stir Processing of Aluminum Alloy A206: Part I—Microstructure Evolution. Inter Metalcast 13, 234–243 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40962-018-0263-y
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40962-018-0263-y