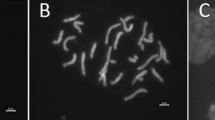
Abstract
Natural hybridization is a common phenomenon in plants and considered to be a driving force of biodiversity and evolution. In coffee spontaneous hybridization between two different species is earlier documented. Here we investigated the morphological, molecular and physiological characteristics of a natural tetraploid interspecific coffee hybrid involving allopolyploid Coffea arabica and diploid C. excelsa species. The formation of the tetraploid hybrid was postulated on account of the production of unreduced female gametes in C. excelsa. In our findings, most morphological characters of the interspecific hybrid were found to be intermediate between the putative parental species, but the young leaf colour was found to be distinctively transgressive. Sequence-related amplified polymorphism marker analysis unequivocally supported the involvement of C. excelsa and C. arabica in hybrid formation. The gas exchange parameters, chlorophyll fluorescence parameters were compared between the hybrid and parents which revealed that the interspecific hybrid had the significantly higher substomatal CO2 concentration and non-photochemical quenching compared to parents. This tetraploid interspecific hybrid encompassing the genome of two divergent species could be of ascertainable importance in arabica coffee breeding program.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arnold, M. L. (1997). Natural hybridization and evolution. New York: Oxford University Press.
Baack, E. J., & Rieseberg, L. H. (2007). A genomic view of introgression and hybrid speciation. Current Opinion in Genetics & Development, 17(6), 513–518.
Bettencourt, A. (1973). Consideraçoes gerais sobre o ‘Hibrido de Timor’ (p. 31). Campinas: Instituto Agronomico de Campinas, Circular No.
Bjorkman, W., & Demming, B. (1987). Photon yield of O2 evolution and chlorophyll fluorescence characteristics at 77 K among vascular plants of diverse origins. Planta, 170, 489–504.
Burke, J. J. (2007). Evaluation of source leaf responses to water-deficit stresses in cotton using a novel stress bioassay. Plant Physiology, 143, 108–121.
Caruso, C. M., Maherali, H., & Sherrard, M. (2006). Plasticity of physiology in Lobelia: testing for adaptation and constraint. Evolution, 60, 980–990.
Cramer, P. J. S. (1957). In F. L. Wellman (Eds.), Review of literature of coffee research in Indonesia. SIC Editorial lnternational American Institute of Agricultural Sciences, Turrialba, Costa Rica.
Das, G., Sengupta, T., Sahu, P. K., Mishra, A. K., Sen, S. K., & Saratchandra, B. (1999). Quantitative analysis of photosynthetic parameters in mulberry leaf. Indian Journal of Plant Physiology, 1(3), 171–174.
Dudley, S. A. (1996). Differing selection on plant physiological traits in response to environmental water availability: A test of adaptive hypotheses. Evolution, 50, 92–102.
Ellstrand, N. C., Whitkus, R., & Rieseberg, L. H. (1996). Distribution of spontaneous plant hybrids. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the USA, 93, 5090–5093.
Geber, M. A., & Dawson, T. E. (1990). Genetic variation in and covariation between leaf gas exchange, morphology, and development in Polygonum arenastrum, an annual plant. Oecologia, 85, 153–158.
Genty, B., Briantais, J. M., & Baker, N. R. (1989). The relationship between the quantum yield of photosynthetic electron transport and quenching of chlorophyll fluorescence. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, 990, 87–92.
Golluscio, R. A., & Oesterheld, M. (2007). Water use efficiency of twenty-five co-existing Patagonian species growing under different soil water availability. Oecologia, 154, 207–217.
Gomez, C., Batti, A., Le Pierres, D., Campa, C., Hamon, S., & de Kochko, A., et al. (2010). Favourable habitats for Coffea inter-specific hybridization in central New Caledonia: Combined genetic and spatial analyses. Journal of Applied Ecology, 47, 85–95.
Gomez, C., Despinoy, M., Hamon, S., Hamon, P., Salmon, D., & Akaffou, D. S., et al. (2016). Shift in precipitation regime promotes interspecific hybridization of introduced Coffea species. Ecology and Evolution, 6, 3240–3255. https://doi.org/10.1002/ece3.2055.
Grant, V. (1981). Plant speciation. New York: Columbia University Press.
Hamerlynck, E. P., Huxman, T. E., Nowak, R. S., Redar, S., Loik, M. E., Jordan, D. N., et al. (2000). Photosynthetic responses of Larrea tridentata to a step-increase in atmospheric CO2 at the Nevada desert FACE facility. Journal of Arid Environments, 44, 425–436.
Harrison, R. G. (1993). Hybrid zones and the evolutionary process. New York: Oxford University Press.
Hegarty, M. J., & Hiscock, S. J. (2004). Hybrid speciation in plants: New insights from molecular studies. New Phytologist, 165, 411–423.
Herrera, J. C., D’Hont, A., & Lashermes, P. (2007). Use of fluorescence in situ hybridization as a tool for introgression analysis and chromosome identification in coffee (Coffea arabica L.). Genome, 50, 619–626.
Heschel, M. S., & Riginos, C. (2005). Mechanisms of selection for drought stress tolerance and avoidance in Impatiens capensis (Balsaminaceae). American Journal of Botany, 92, 37–44.
Kumar, A., Ganesh, S., & Mishra, M. K. (2014). Confirmation of genome introgression in the interspecific hybrid progenies of Coffea species through SRAP marker technique. Scholars Academic Journal of Biosciences, 2(3), 224–235.
Kumar, A., & Mishra, M. K. (2014). A new spontaneous interspecific hybrid in coffee (Coffea sp.). Scholars Academic Journal of Biosciences, 2(2), 168–171.
Lanaud, C. (1979). Etude de problèmes génétiques posés chez le caféier par l’introgression de caractères d’une espèce sauvage C. kianjavatensis Mascarocoffea dans Iespece cultivee C. canephora Eucoffea. Café Cacao The, 23, 3–28.
Li, G., & Quiros, C. F. (2001). Sequence-related amplified polymorphism (SRAP), a new marker system based on a simple PCR reaction: Its application to mapping and gene tagging in Brassica. Theoretical and Appied Genetics, 103, 455–461.
Liu, L., Liu, G., Gong, Y., Dai, W., Wang, Y., Yu, F., et al. (2007). Evaluation of genetic purity of F1 hybrid seeds in cabbage with RAPD, ISSR, SRAP and SSR markers. HortScience, 42, 724–727.
Mahé, L., Varzea, V. M. P., Le Pierrès, D., Combes, M. C., & Lashermes, P. (2007). A new source of resistance against coffee leaf rust from New-Caledonian natural interspecific hybrids between Coffea arabica and C. canephora. Plant Breeding, 126, 638–641.
McKay, J. K., Richards, J. H., & Mitchell-Olds, T. (2003). Genetics of drought adaptation in Arabidopsis thaliana: Pleiotropy contributes to genetic correlations among ecological traits. Molecular Ecology, 12, 1137–1151.
Mishra, M. K. (1997). Stomatal characteristics at different ploidy levels of Coffea L. Annals of Botany, 80, 689–692.
Mishra, M. K., Bhat, A. M., Suresh, N., Satheesh Kumar, S., Padmajyothi, D., Prakash, N. S., et al. (2011a). Molecular genetic analysis of arabica coffee hybrids using SRAP marker approach. Journal of Plantation Crops, 39(1), 41–47.
Mishra, M. K., Nishani, S., & Jayarama, (2011b). Molecular identification and genetic relationships among coffee species (Coffea L.) inferred from ISSR and SRAP marker analyses. Archives of Biological Sciences, 63(3), 667–679.
Mishra, M. K., Ram, A. S., Jyothi, D. P., Prakash, N. S., & Srinivasan, C. S. (2003). Stomatal characteristics of different species of Coffea L. Journal of Plantation Crops, 31, 35–39.
Mishra, M. K., & Slater, A. (2012). Recent advances in the genetic transformation of coffee. Biotechnology Research International. https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/580857.
Mishra, M. K., Suresh, N., Bhat, A. M., Prakash, N. S., Satheesh Kumar, S., Kumar, A., et al. (2011c). Genetic molecular analysis of Coffea arabica (Rubiaceae) hybrids using SRAP markers. Revista Biologia Tropical, 59(2), 607–617.
Müller, P., Li, X.-P., & Niyogi, K. K. (2001). Non-photochemical quenching. A response to excess light energy. Plant Physiology, 125, 1558–1566.
Oxborongh, K., & Baker, N. R. (1997). Resolving chlorophyll a fluorescence images of photosynthetic efficience into photochemical and non-photochemical components-calculation of qP and Fv-/Fm-without measuring Fo. Photosynthesis Research, 54, 135–142.
Petite, M. A., Moro, G. B., Murua, G. C., Lacuesta, M., & Rueda, M. A. (2000). Sequential effects of acidic precipitation and drought on photosynthesis and chlorophyll fluorescence parameters of Pinus radiata D. Don seedlings. Journal of Plant Physiology, 156, 84–92.
Quick, W. P., Chaves, M. M., Wendler, R., David, M., Rodrigues, M. L., Passaharinho, J. A., et al. (1992). The effect of water stress on photosynthetic carbon metabolism in four species grown under field conditions. Plant, Cell and Environment, 15, 25–35.
Ren, X., Huang, J., Liao, B., Zhang, X. H., & Jiang, H. (2010). Genomic affinities of Arachis genus and inter-specific hybrids were revealed by SRAP markers. Genetic Resources and Crop Evolution, 57, 903–913.
Rieseberg, L. H., & Carney, S. E. (1998). Plant hybridization (Tansley review no. 102). New Phytologist, 140, 599–624.
Rohácek, K., & Barták, M. (1999). Technique of the modulated chlorophyll fluorescence: Basic concepts, useful parameters, and some applications. Photosynthetica, 37(3), 339–363.
Rohlf, F. J. (2000). NTSYS pc: Numerical taxonomy and multivariate analysis system version 2.10. Setauket, NY: Exeterior Software.
Ruban, A. V., Berera, R., Ilioaia, C., van Stokkum, I. H., Kennis, J. T., Pascal, A. A., et al. (2007). Identification of a mechanism of photoprotective energy dissipation in higher plants. Nature, 450(7169), 575–578.
Schreiber, U., Schliwa, U., & Bilger, W. (1986). Continuous recording of photochemical and non-photochemical chlorophyll fluorescence quenching with a new type of modulation fluorometer. Photosynthesis Research, 10, 51–61.
Seiler, G. J., Qi, L. L., & Marek, L. (2017). Utilization of sunflower crop wild relatives for cultivated sunflower improvement. Crop Science, 57, 1–19.
Setotaw, T. A., Pena, G. F., Zambolin, E. M., Pereira, A. A., & Sakiyama, N. S. (2010). Breeding potential and genetic diversity of “Híbrido do Timor” coffee evaluated by molecular markers. Crop Breeding and Applied Biotechnology, 10, 298–304.
Shasany, A. K., Darokar, M. P., Dhawan, S., Gupta, A. K., Gupta, S., Shukla, A. K., et al. (2005). Use of RAPD and AFLP markers to identify inter- and intraspecific hybrids of Mentha. Journal of Heredity, 96(5), 542–549.
Sheng, X., Wen, G., Guo, Y., Yan, H., Zhao, H., & Liu, F. (2012). A semi-fertile interspecific hybrid of Brassica rapa and B. nigra and the cytogenetic analysis of its progeny. Genetic Resources and Crop Evolution, 59,(1), 73–81. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10722-011-9669-6.
Sneath, P. H., & Sokal, R. R. (1973). Numerical taxonomy: The principal and practice of numerical classification. San Francisco: W. H. Freeman and Company.
Sreenivasan, M. S., & Govindappa, D. A. (1984). Cytology of polyploids in robusta arabica hybrids of coffee. Journal of Coffee Research, 14, 75–84.
Sreenivasan, M. S., Prakash, N. S., & Mishra, M. K. (1992). Evaluation of some indirect ploidy indicators in Coffea L. Café Cacao The, 36, 199–205.
Venkataramanan, D. (1985). Physiological studies in coffee. Ph.D. thesis, University of Mysore, India.
Wolf, J. B., Brodie, E. D., Cheverud, J. M., Moore, A. J., & Wade, M. J. (1998). Evolutionary consequences of indirect genetic effects. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 13, 64–69.
Xuan, C., Hailin, G., Dandan, X., & Jianxiu, L. (2008). Identification of Zyosia hybrids by SRAP analysis. Molecular Plant Breeding, 6, 1233–1238.
Zhu, X. F., Li, Y., Wu, G. L., Fang, Z. D., Li, Q. J., & Liu, J. Q. (2009). Molecular and morphological evidence for natural hybridization between primula secundiflora franchet and p. poissonii franchet (primulaceae). Acta Biologica Cracoviensia Series Botanica, 51(2), 29–36.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
40502_2018_410_MOESM2_ESM.tif
Fig. S1: Scatter plot of the first and second principal coordinate analysis (PCoA) of parents and interspecific hybrid based on the SRAP marker analysis (TIFF 45 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mishra, M.K., Awati, M., Anand, C. et al. Molecular and physiological characterization of a natural interspecific coffee hybrid. Ind J Plant Physiol. 23, 810–821 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40502-018-0410-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40502-018-0410-8