Abstract
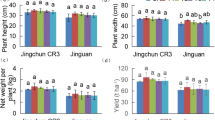
A new kind of liquid fertilizer, contained essential elements for plant growth and some nonessential elements like Ti, was used as foliar fertilizer on Chinese cabbage. Yields, quality, and safety of Chinese cabbage were investigated. The results illustrated that contrasted to control, yield and quality of Chinese cabbage cultivated with fertilizer for 42 days were promoted remarkably. Under the optimal fertilizer dilution multiple of 3,000 the height and yield increased by 226.5 and 489.2 %, respectively. Additionally, the content of chlorophyll and vitamin C increased by 55.1 and 30 %, respectively. Utilization of this liquid fertilizer could achieve a decrease in nitrate and nitrite content by 6.2–17.2 % and 24.1–46.9 %, respectively. The results indicated that this new kind of fertilizer has a prospect in practical utilization.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anna K, Tomas C, Daniel M (2007) Elemental analysis of instant soups and seasoning mixtures by ICP–OES. Food Chem 105:242–247
Arnon DI, McSwain BD, Tsujimoto HY, Wada K (1974) Photochemical activity and components of membrane preparations from blue-green algae I. Biochem Biophys Acta 357:231–245
Bao BJ (2001) The useful element for plant growth-Ti. Phosphate Compd Fertil 16:67 (in Chinese)
Carter GA (1998) Reflectance wavebands and indices for remote estimation of photosynthesis and stomatal conductance in pine canopies. Remote Sens Environ 63:61–72
Chen J, Wang QH, Zou DX, Yamagata K, Zheng J, Li FS (2008) Study on effects of a new kind of plant growth regulator on vegetable growth. J Heilongjiang univ 25:1–5
Fang SP (2002) MS Zhe Jiang University, p 59
Filella L, Serrano L, Serra J, Penuelas J (1995) Evaluation of wheat crop nitrogen status by remote sensing: reflectance indices and discriminant analysis. Crop Sci 35:1400–1405
Fine D (1980). Advances in environmental Science and Technology In: Pitts J, Metcalf R (eds), Wiley, New York, pp 39–123
Guo LN, Liu XZ, Zhao XJ (2005) Effects of Fertilization and Environmental Factors on Nitrate Accumulation in Vegetables. J Shanxi Agric Univ 25:416–420 (in Chinese)
Guo RD, Ming JL, Feng WM, Dong L (2009) Antioxidant capacity and the relationship with polyphenol and Vitamin C in Actinidia fruits. Food Chem 113:557–562
Hotchnkiss J (1989) Food toxicology (Taylor-Scanlan, Ed.), Institute of Food Technologist, 221N. La Salle St, Chicago
IARC (1993) IARC monographs on the evaluation of carcinogenic risks to humans. International Agency for Research on Cancer, Lyon, pp 119–237
Järup L (2003) Hazards of heavy metal contamination. Br Med Bull 68:167–182
Kaur C, Kapoor HC (2001) Antioxidants in fruits and vegetables—the millennium’s health. Int J Food Sci Technol 36:703–725
Liang XM, Huang XW, Rong K (2002) Studies on the application of microecological fertilizer in hulunber. J Nat Sci Heilongjiang Univ 19(2):109–115
Lin SQ, Xu L (1992) 981 Plant promote long-group research collaboration, pp 208–211
Menzer RE, Nelson JO (1991) Water and soil pollutants. In: Casarett and doulls toxicology: the basic science of poisons, 4th ed. McGraw-Hill, New York
National Academy of Sciences (1981) The health effects of nitrate, nitrite, and N-nitroso compounds. National Academy Press, Washington
Nriagu J, Pacyna J (1988) Quantitative assessment of world wide contamination of air, water and soils by trace metals. Nature 333:134–139
Oskarsson A, Widell A, Olsson IM, Petersson GK (2004) Cadmium in food chain and health effects in sensitive population groups. Biometals 17:531–534
Reuveni R, Reuveni M (1998) Foliar-fertilizer therapy—a concept in integrated pest management. Crop Prot 17:111–118
Steenland K, Boffetta P (2000) Lead and cancer in humans: where are we now? Am J Ind Med 38:295–299
Sun B, Zhou SL, Zhao QG (2003) Combined pollution of heavy metal in soil based on spatial variation analysis. J Agro-Environ Sci 22:248–251
Tavarini S, Degl’Innocenti E, Remorini D, Massai R, Guidi L (2008) Polygalacturonase and β-galactosidase activities in Hayward kiwifruit as affected by light exposure, maturity stage and storage time. Food Chem 107:282–288
Wan CH (2001) Ti and the growth of plant Agric. Inputs Sci Technol 6:18–19 (in Chinese)
Wang CH, Li SX, Tian XH (1998) Influence of Nitrogen Rates on Nitrate Accumulation in Vegetables. Plant Nutr Fertil Sci 4:22–88 (in Chinese)
WHO (1992) In: Environmental Health Criteria, Geneva, p 134
WHO (1995) In: Environmental Health Criteria, Geneva, p 165
Xu YM, Li JX (2003) Inactivation of Pb, Hg and Cd in-Situ in contaminated soil by a functionalized monolayer material. J Agro-Environ Sci 22(1):86–89 (in Chinese)
Zhang LZ, Wan CH (1995) Effect of Ti-chelator on the expansion, synthesis of chlorophyll and carotenoid of excised cucumber cotyledons. Plant Nutr Fertil Sci 1:48–52 (in Chinese)
Zhang ZH, Liu S (2006) International comparison of vegetable industry in Chinese. China Veg 3:1–5 (in Chinese)
Zhao XY. (2002) Thesis, M. S. Hunan agriculture university Master, p 36
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Song, N., Wang, J., Wang, Q. et al. Effect of a New Kind of Liquid Fertilizer on Yield, Quality and Safety of Greenhouse Chinese Cabbage. Agric Res 4, 57–62 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40003-014-0145-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40003-014-0145-3