Abstract
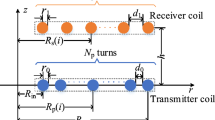
In case of misalignment, variation in the coupling coefficient between transmitting and receiving coils employed for wireless power transfer is obvious. During the design process of coil system, assurance of least affected coupling coefficient during misalignment is an important issue and can be addressed through appropriate coil structure. Asymmetrical circular spiral coils with unequal outer diameter and fixed self-inductance exhibits better tolerance to misalignment with the limitation of smaller averaged coupling coefficient. The present paper considers the analytical model of asymmetrical circular spiral coils to investigate the dependency of the coil system dimensions on mutual inductance and coupling coefficient with equal outer diameter. Based on the observations from analytical expressions, simulations are performed through finite element method approach using ANSYS MAXWELL. Outcome of the investigations has been used for the design consideration of coil system, which is less sensitive to the misalignment. Based on the proposed design considerations, experimental setup is developed and tested for the case study of E-Rickshaw with 400 mm outer diameter and 120-mm air gap.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Madawala, U.K.; Thrimawithana, D.J.: A bidirectional inductive power interface for electric vehicles in V2G systems. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 58(10), 4789–4796 (2011)
Villa, J.L.; Sallan, J.; Sanz Osorio, J.F.; Llombart, A.: High-misalignment tolerant compensation topology for ICPT systems. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 59(2), 945–951 (2012)
Khaligh, A.; Dusmez, S.: Comprehensive topological analysis of conductive and inductive charging solutions for plug-in EVs. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 61(8), 3475–3489 (2012)
Covic, G.A.; Boys, J.T.: Inductive power transfer. Proc. IEEE 101(6), 1276–1289 (2013)
Miller, J.M.; Onar, O.C.; Chinthavali, M.: Primary-side power flow control of wireless power transfer for electric vehicle charging. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Topics Power Electron. 3(1), 147–162 (2015)
Vilathgamuwa, D.; Sampath, J.: Wireless power transfer (WPT) for electric vehicles (EVs) present and future trends. In: Plug in Electric Vehicles in Smart Grids, chap 2. Springer, Berlin, pp. 3360 (2015)
Samanta, S.; Rathore, A.K.: A new current-fed CLC transmitter and LC receiver topology for inductive wireless power transfer application: analysis, design, and experimental results. IEEE Trans. Transport. Electrif. 1(4), 357–368 (2015)
Buja, G.; Bertoluzzo, M.; Mude, K.N.: Design and experimentation of WPT charger for electric city car. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electon. 62(12), 7436–7447 (2015)
Kim, H.; et al.: Coil design and measurements of automotive magnetic resonant wireless charging system for high-efficiency and low magnetic field leakage. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 64(2), 383–400 (2016)
Zhang, W.; Mi, C.C.: Compensation topologies of high-power wireless power transfer systems. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 65(6), 4768–4778 (2016)
Li, W.; Zhao, H.; Deng, J.; Li, S.; Mi, C.C.: Comparison study on SS and double-sided LCC compensation topologies for EV/PHEV wireless chargers. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 65(6), 4429–4439 (2016)
Vaka, R.; Keshri, R.K.: Review on contactless power transfer for electric vehicle charging. Energies 10(5), 636 (2017)
Ravikiran, V.; Keshri, R.K.; Santos, M.M.: Inductive characteristics of asymmetrical coils for wireless power transfer. In: Eighteenth annual IEEE international conference on industrial technology, ICIT, Toronto, ON, pp. 538–542 (2017)
Aditya, K.; Williamson, S.S.: A review of optimal conditions for achieving maximum power output and maximum efficiency for a seriesseries resonant inductive link. IEEE Trans. Transport. Electrif. 3(2), 303–311 (2017)
Samanta, S.; Rathore, A.K.; Thrimawithana, D.J.: Bidirectional Current-Fed Half-Bridge (C) (LC)(LC ) configuration for inductive wireless power transfer system. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 53(4), 4053–4062 (2017)
Wang, Y.; Yao, Y.; Liu, X.; Xu, D.: S/CLC compensation topology analysis and circular coil design for wireless power transfer. IEEE Trans. Transport. Electrif. 3(2), 496–507 (2017)
Tejeda, A.; Carretero, C.; Boys, J.T.; Covic, G.A.: Ferrite-less circular pad with controlled flux cancelation for EV wireless charging. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 32(11), 8349–8359 (2017)
Zaheer, A.; Hao, H.; Covic, G.A.; Kacprzak, D.: Investigation of multiple decoupled coil primary pad topologies in lumped IPT systems for interoperable electric vehicle charging. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 30(4), 1937–1955 (2015)
Kim, S.; Covic, G.A.; Boys, J.T.: Tripolar pad for inductive power transfer systems for EV charging. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 32(7), 5045–5057 (2017)
Zhao, F.; Wei, G.; Zhu, C.; Song, K.: Design and optimizations of asymmetric solenoid type magnetic coupler in wireless charging system for electric vehicles. In: IEEE PELS Workshop on Emerging Technologies: Wireless Power Transfer (WoW), Chongqing, pp. 157–162 (2017)
Fujita, T.; Yasuda, T.; Akagi, H.: A moving wireless power transfer system applicable to a stationary system. In: IEEE Energy Conversion Congress and Exposition (ECCE), Montreal, QC, pp. 4943–4950 (2015)
Boys, J.T.; Covic, G.A.: Inductive power transfer systems (IPT) fact sheet: No. 1 basic concepts. In: Qualcomm (2012)
Budhia, M.; Boys, J.T.; Covic, G.A.; Huang, C.Y.: Development of a single-sided flux magnetic coupler for electric vehicle IPT charging systems. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 60(1), 318–328 (2013)
Liu, N.; Habetler, T.G.: Design of a universal inductive charger for multiple electric vehicle models. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 30(11), 6378–6390 (2015)
Ni, W.; et al.: Radio alignment for inductive charging of electric vehicles. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inf. 11(2), 427–440 (2015)
Budhia, M.; Covic, G.A.; Boys, J.T.: Design and optimization of circular magnetic structures for lumped inductive power transfer systems. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 26(11), 3096–3108 (2011)
Covic, G.A.; Boys, J.T.: Modern trends in inductive power transfer for transportation applications. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Topics Power Electr. 1(1), 28–41 (2013)
Wu, H.H.; Gilchrist, A.; Sealy, K.D.; Bronson, D.: A high efficiency 5 kW inductive charger for EVs using dual side control. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inf. 8(3), 585–595 (2012)
Bosshard, R.; Kolar, J.W.; Wunsch, B.: Accurate finite-element modeling and experimental verification of inductive power transfer coil design. In: IEEE Applied Power Electronics Conference and Exposition, APEC, Fort Worth, TX, pp. 1648–1653 (2014)
Diekhans, T.; De Doncker, R.W.: A dual-side controlled inductive power transfer system optimized for large coupling factor variations and partial load. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 30(11), 6320–6328 (2015)
Esteban, B.; Stojakovic, N.; Sid-Ahmed, M.; Kar, N.C.: Development of mutual inductance formula for misaligned planar circular spiral coils. In: IEEE Energy Conversion Congress and Exposition (ECCE), Montreal, QC, pp. 1306–1313 (2015)
Zheng, C.; Ma, H.; Lai, J.S.; Zhang, L.: Design considerations to reduce gap variation and misalignment effects for the inductive power transfer system. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 30(11), 6108–6119 (2015)
Conway, J.T.: Inductance calculations for circular coils of rectangular cross section and parallel axes using bessel and struve functions. IEEE Trans. Magn. 46(1), 75–81 (2010)
Babic, S.I.; Akyel, C.: Calculating mutual inductance between circular coils with inclined axes in air. IEEE Trans. Magn. 44(7), 1743–1750 (2008)
Fotopoulou, K.; Flynn, B.W.: Wireless power transfer in loosely coupled links: coil misalignment model. IEEE Trans. Magn. 47(2), 416–430 (2011)
Wheeler, H.A.: Simple inductance formulas for radio coils. Proc. Inst. Radio Eng. 16(10), 13981400 (1928)
Wheeler, H.A.: Inductance formulas for circular and square coils. Proc. IEEE 70(12), 1449–1450 (1982)
SAE TIR J2954 Wireless Power Transfer for Light-Duty Plug-In/Electric Vehicles (2016)
Chopra, S.; Bauer, P.: Analysis and design considerations for a contactless power transfer system. In: IEEE 33rd International Telecommunications Energy Conference (INTELEC), Amsterdam, pp. 1–6 (2011)
Niu, W.Q.; Chu, J.X.; Gu, W.; Shen, A.D.: Exact analysis of frequency splitting phenomena of contactless power transfer systems. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 60(6), 1670–1677 (2013)
Mude, K.N.; Bertoluzzo, M.; Buja, G.; Pinto, R.: Design and experimentation of two-coil coupling for electric city-car WPT charging. J. Electromagn. Waves Appl. 30(1), 70–78 (2016)
Palandoken, M.; Aksoy, M.; Tumay, M.: A fuzzy-controlled single-phase active power filter operating with fixed switching frequency for reactive power and current harmonics compensation. Electr. Eng. 86(1), 9–16 (2003)
Palandoken, M.; Aksoy, M.; Tumay, M.: Application of fuzzy logic controller to active power filters. Electr. Eng. 86(4), 191–198 (2004)
Palandoken, M.; Tumay, M.; Aksoy, M.: A novel approach to active power filter control. Electr. Eng. 87(1), 33–39 (2005)
Acknowledgements
Authors are grateful to Department of Science and Technology SERB and Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology, Government of India for financial support under projects DST/ECR/2016/002029 and MLA/MUM/GA/10(37)B respectively.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vaka, R., Keshri, R.K. Design Considerations for Enhanced Coupling Coefficient and Misalignment tolerance Using Asymmetrical Circular Coils for WPT System. Arab J Sci Eng 44, 1949–1959 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-018-3219-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-018-3219-x