Abstract
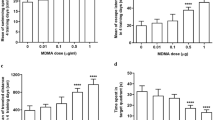
Repeated methamphetamine (METH) exposure can cause severe neurotoxicity to the central nervous system, and lead to memory deficits. L-Stepholidine (L-SPD) is a structurally identified alkaloid extract of the Chinese herb Stephania intermedia, which elicits dopamine (DA) D1-type receptors partial agonistic activity and D2-type receptors antagonistic activity. In this study, we investigated the effect of L-SPD on METH-induced memory deficits in mice and its underlying mechanisms. We found that repeated exposure to METH (10 mg/kg, i.p., once per day for 7 consecutive days) impaired memory functions in the novel object recognition experiment. Pretreatment of L-SPD (10 mg/kg, i.p.) significantly improved METH-induced memory deficits in mice. Meanwhile, the protein expression of dopaminergic D2 receptors in hippocampus area was significantly increased by repeated METH exposure, while the protein expression of dopamine transporter (DAT) was significantly reduced. Additionally, the protein expression of phospho-protein kinase A (p-PKA) was significantly increased by repeated METH exposure. The hyperpolarization-activated cyclic-nucleotide-gated non-selective cation 1 (HCN1) channel, which was a key regulator of memory functions and could be regulated by p-PKA, was also significantly increased by repeated METH exposure. These changes caused by METH could be prevented by L-SPD pretreatment. Therefore, our data firstly showed that pretreatment of L-SPD exhibited the protective effect against METH-induced memory deficits, possibly through reducing METH-induced upregulation of dopaminergic pathway and HCN1 channels.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abiraman K, Sah M, Walikonis RS, Lykotrafitis G, Tzingounis AV (2016) Tonic PKA activity regulates SK channel nanoclustering and somatodendritic distribution. J Mol Biol 428:2521–2537
Anneken JH, Angoa-Perez M, Sati GC, Crich D, Kuhn DM (2018) Assessing the role of dopamine in the differential neurotoxicity patterns of methamphetamine, mephedrone, methcathinone and 4-methylmethamphetamine. Neuropharmacology 134:46–56
Antunes M, Biala G (2012) The novel object recognition memory: neurobiology, test procedure, and its modifications. Cogn Process 13:93–110
Ares-Santos S, Granado N, Moratalla R (2013) The role of dopamine receptors in the neurotoxicity of methamphetamine. J Intern Med 273:437–453
Benarroch EE (2013) HCN channels: function and clinical implications. Neurology 80:304–310
Bender RA, Baram TZ (2008) Hyperpolarization activated cyclic-nucleotide gated (HCN) channels in developing neuronal networks. Prog Neurobiol 86:129–140
Berke JD, Hyman SE (2000) Addiction, dopamine, and the molecular mechanisms of memory. Neuron 25:515–532
Biel M, Wahl-Schott C, Michalakis S, Zong X (2009) Hyperpolarization-activated cation channels: from genes to function. Physiol Rev 89:847–885
Brewster AL, Bernard JA, Gall CM, Baram TZ (2005) Formation of heteromeric hyperpolarization-activated cyclic nucleotide-gated (HCN) channels in the hippocampus is regulated by developmental seizures. Neurobiol Dis 19:200–207
Cadet JL, Bisagno V (2015) Neuropsychological consequences of chronic drug use: relevance to treatment approaches. Front Psychiatry 6:189
Cadet JL, Bisagno V, Milroy CM (2014) Neuropathology of substance use disorders. Acta Neuropathol 127:91–107
Cantero Mdel R, Velazquez IF, Streets AJ, Ong AC, Cantiello HF (2015) The cAMP signaling pathway and direct protein kinase A phosphorylation regulate polycystin-2 (TRPP2) channel function. J Biol Chem 290:23888–23896
Chen YJ, Liu YL, Zhong Q, Yu YF, Su HL, Toque HA, Dang YH, Chen F, Xu M, Chen T (2012) Tetrahydropalmatine protects against methamphetamine-induced spatial learning and memory impairment in mice. Neurosci Bull 28:222–232
Chu HY, Zhen X (2010) Hyperpolarization-activated, cyclic nucleotide-gated (HCN) channels in the regulation of midbrain dopamine systems. Acta Pharmacol Sin 31:1036–1043
Chuang JY, Chang WT, Cherng CG, Kao GS, Yu L (2011) Repeated co-administrations of alcohol- and methamphetamine-produced anxiogenic effect could be associated with the neurotoxicity in the dentate gyrus. J Neural Transm (Vienna) 118:1559–1569
Cordeiro Matos S, Zhang Z, Seguela P (2015) Peripheral neuropathy induces HCN channel dysfunction in pyramidal neurons of the medial prefrontal cortex. J Neurosci 35:13244–13256
Fortuna JTS, Gralle M, Beckman D, Neves FS, Diniz LP, Frost PS, Barros-Aragao F, Santos LE, Goncalves RA, Romao L, Zamberlan DC, Soares FAA, Braga C, Foguel D, Gomes FCA, De Felice FG, Ferreira ST, Clarke JR, Figueiredo CP (2017) Brain infusion of alpha-synuclein oligomers induces motor and non-motor Parkinson’s disease-like symptoms in mice. Behav Brain Res 333:150–160
Fricks-Gleason AN, German CL, Hoonakker AJ, Friend DM, Ganesh KK, Carver AS, Hanson GR, Fleckenstein AE, Keefe KA (2016) An acute, epitope-specific modification in the dopamine transporter associated with methamphetamine-induced neurotoxicity. Synapse 70:139–146
Gonzalez B, Jayanthi S, Gomez N, Torres OV, Sosa MH, Bernardi A, Urbano FJ, Garcia-Rill E, Cadet JL, Bisagno V (2018) Repeated methamphetamine and modafinil induce differential cognitive effects and specific histone acetylation and DNA methylation profiles in the mouse medial prefrontal cortex. Prog Neuro-Psychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 82:1–11
Gonzalez B, Raineri M, Cadet JL, Garcia-Rill E, Urbano FJ, Bisagno V (2014) Modafinil improves methamphetamine-induced object recognition deficits and restores prefrontal cortex ERK signaling in mice. Neuropharmacology 87:188–197
Gonzalez B, Rivero-Echeto C, Muniz JA, Cadet JL, Garcia-Rill E, Urbano FJ, Bisagno V (2016) Methamphetamine blunts Ca(2+) currents and excitatory synaptic transmission through D1/5 receptor-mediated mechanisms in the mouse medial prefrontal cortex. Addict Biol 21:589–602
Gutierrez A, Jablonski SA, Amos-Kroohs RM, Barnes AC, Williams MT, Vorhees CV (2017) Effects of housing on methamphetamine-induced neurotoxicity and spatial learning and memory. ACS Chem Neurosci 8:1479–1489
Hanson JE, Birdsall E, Seferian KS, Crosby MA, Keefe KA, Gibb JW, Hanson GR, Fleckenstein AE (2009) Methamphetamine-induced dopaminergic deficits and refractoriness to subsequent treatment. Eur J Pharmacol 607:68–73
Hao JR, Sun N, Lei L, Li XY, Yao B, Sun K, Hu R, Zhang X, Shi XD, Gao C (2015) L-Stepholidine rescues memory deficit and synaptic plasticity in models of Alzheimer’s disease via activating dopamine D1 receptor/PKA signaling pathway. Cell Death Dis 6:e1965
He C, Chen F, Li B, Hu Z (2014) Neurophysiology of HCN channels: from cellular functions to multiple regulations. Prog Neurobiol 112:1–23
Ishikawa R, Kim R, Namba T, Kohsaka S, Uchino S, Kida S (2014) Time-dependent enhancement of hippocampus-dependent memory after treatment with memantine: implications for enhanced hippocampal adult neurogenesis. Hippocampus 24:784–793
Jablonski SA, Williams MT, Vorhees CV (2016) Mechanisms involved in the neurotoxic and cognitive effects of developmental methamphetamine exposure. Birth Defects Res C Embryo Today 108:131–141
Jiang H, Zhang X, Wang Y, Zhang H, Li J, Yang X, Zhao B, Zhang C, Yu M, Xu M, Yu Q, Liang X, Li X, Shi P, Bao T (2017) Mechanisms underlying the antidepressant response of acupuncture via PKA/CREB signaling pathway. Neural Plast 2017:4135164
Kelley AE, Berridge KC (2002) The neuroscience of natural rewards: relevance to addictive drugs. J Neurosci 22:3306–3311
Kutlu MG, Gould TJ (2016) Effects of drugs of abuse on hippocampal plasticity and hippocampus-dependent learning and memory: contributions to development and maintenance of addiction. Learn Mem 23:515–533
Li CJ, Lu Y, Zhou M, Zong XG, Li C, Xu XL, Guo LJ, Lu Q (2014) Activation of GABAB receptors ameliorates cognitive impairment via restoring the balance of HCN1/HCN2 surface expression in the hippocampal CA1 area in rats with chronic cerebral hypoperfusion. Mol Neurobiol 50:704–720
Long JD, Liu Y, Jiao DL, Wang YJ, Zan GY, Ju YY, Zhao M, Liu JG (2017) The neuroprotective effect of memantine on methamphetamine-induced cognitive deficits. Behav Brain Res 323:133–140
Ma BM, Yue K, Xing JQ, Gong XK, Ru Q, Chen L, Xiong Q, Tian X, Liu L, Gan YQ, Wang DS, Jin GZ, Li CY (2014) L-Stepholidine blocks methamphetamine-induced locomotor sensitization in mice. Adv Mater Res 998:156–159
Maroso M, Szabo GG, Kim HK, Alexander A, Bui AD, Lee SH, Lutz B, Soltesz I (2016) Cannabinoid control of learning and memory through HCN channels. Neuron 89:1059–1073
Moore TL, Schettler SP, Killiany RJ, Herndon JG, Luebke JI, Moss MB, Rosene DL (2005) Cognitive impairment in aged rhesus monkeys associated with monoamine receptors in the prefrontal cortex. Behav Brain Res 160:208–221
Moszczynska A, Callan SP (2017) Molecular, behavioral, and physiological consequences of methamphetamine neurotoxicity: implications for treatment. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 362:474–488
Natesan S, Reckless GE, Barlow KB, Odontiadis J, Nobrega JN, Baker GB, George SR, Mamo D, Kapur S (2008) The antipsychotic potential of l-stepholidine--a naturally occurring dopamine receptor D1 agonist and D2 antagonist. Psychopharmacology 199:275–289
Nolan MF, Malleret G, Dudman JT, Buhl DL, Santoro B, Gibbs E, Vronskaya S, Buzsaki G, Siegelbaum SA, Kandel ER, Morozov A (2004) A behavioral role for dendritic integration: HCN1 channels constrain spatial memory and plasticity at inputs to distal dendrites of CA1 pyramidal neurons. Cell 119:719–732
Nordahl TE, Salo R, Leamon M (2003) Neuropsychological effects of chronic methamphetamine use on neurotransmitters and cognition: a review. J Neuropsychiatr Clin Neurosci 15:317–325
O’Dell SJ, Feinberg LM, Marshall JF (2011) A neurotoxic regimen of methamphetamine impairs novelty recognition as measured by a social odor-based task. Behav Brain Res 216:396–401
Okita K, Morales AM, Dean AC, Johnson MC, Lu V, Farahi J, Mandelkern MA, London ED (2018) Striatal dopamine D1-type receptor availability: no difference from control but association with cortical thickness in methamphetamine users. Mol Psychiatry 23:1320–1327
Plattner F, Hayashi K, Hernandez A, Benavides DR, Tassin TC, Tan C, Day J, Fina MW, Yuen EY, Yan Z, Goldberg MS, Nairn AC, Greengard P, Nestler EJ, Taussig R, Nishi A, Houslay MD, Bibb JA (2015) The role of ventral striatal cAMP signaling in stress-induced behaviors. Nat Neurosci 18:1094–1100
Ramirez E, Mendieta L, Flores G, Limon ID (2018) Neurogenesis and morphological-neural alterations closely related to amyloid beta-peptide (25-35)-induced memory impairment in male rats. Neuropeptides 67:9–19
Reichel CM, Chan CH, Ghee SM, See RE (2012) Sex differences in escalation of methamphetamine self-administration: cognitive and motivational consequences in rats. Psychopharmacology 223:371–380
Reichel CM, Schwendt M, McGinty JF, Olive MF, See RE (2011) Loss of object recognition memory produced by extended access to methamphetamine self-administration is reversed by positive allosteric modulation of metabotropic glutamate receptor 5. Neuropsychopharmacology 36:782–792
Ricotta D, Conner SD, Schmid SL, von Figura K, Honing S (2002) Phosphorylation of the AP2 mu subunit by AAK1 mediates high affinity binding to membrane protein sorting signals. J Cell Biol 156:791–795
Rusyniak DE (2013) Neurologic manifestations of chronic methamphetamine abuse. Psychiatr Clin North Am 36:261–275
Seiden LS, Lew R, Malberg JE (2001) Neurotoxicity of methamphetamine and methylenedioxymethamphetamine. Neurotox Res 3:101–116
Shah MM (2016) Hyperpolarization-activated cyclic nucleotide-gated channel currents in neurons. Cold Spring Harb Protoc 2016:pdb top087346
St Clair JR, Larson ED, Sharpe EJ, Liao Z, Proenza C (2017) Phosphodiesterases 3 and 4 differentially regulate the funny current, If, in Mouse Sinoatrial Node Myocytes. J Cardiovasc Dev Dis 4:10. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcdd4030010
St Clair JR, Liao Z, Larson ED, Proenza C (2013) PKA-independent activation of I(f) by cAMP in mouse sinoatrial myocytes. Channels (Austin) 7:318–321
Thurm F, Schuck NW, Fauser M, Doeller CF, Stankevich Y, Evens R, Riedel O, Storch A, Lueken U, Li SC (2016) Dopamine modulation of spatial navigation memory in Parkinson’s disease. Neurobiol Aging 38:93–103
Tsay D, Dudman JT, Siegelbaum SA (2007) HCN1 channels constrain synaptically evoked Ca2+ spikes in distal dendrites of CA1 pyramidal neurons. Neuron 56:1076–1089
Wang M, Gamo NJ, Yang Y, Jin LE, Wang XJ, Laubach M, Mazer JA, Lee D, Arnsten AF (2011) Neuronal basis of age-related working memory decline. Nature 476:210–213
Wang W, Zhou Y, Sun J, Pan L, Kang L, Dai Z, Yu R, Jin G, Ma L (2007) The effect of L-stepholidine, a novel extract of Chinese herb, on the acquisition, expression, maintenance, and re-acquisition of morphine conditioned place preference in rats. Neuropharmacology 52:355–361
Xu J, Yu L, Minobe E, Lu L, Lei M, Kameyama M (2016) PKA and phosphatases attached to the Ca(V)1.2 channel regulate channel activity in cell-free patches. Am J Phys Cell Phys 310:C136–C141
Yuan J, Darvas M, Sotak B, Hatzidimitriou G, McCann UD, Palmiter RD, Ricaurte GA (2010) Dopamine is not essential for the development of methamphetamine-induced neurotoxicity. J Neurochem 114:1135–1142
Yue K, Ma BM, Chen L, Tian X, Ru Q, Gan YQ, Wang D, Jin GZ, Li CY (2014a) L-Stepholidine, a naturally occurring dopamine D1 receptor agonist and D2 receptor antagonist, attenuates heroin self-administration and cue-induced reinstatement in rats. Neuroreport 25:7–11
Yue K, Ma BM, Xing JQ, Gong XK, Ru Q, Chen L, Xiong Q, Tian X, Liu L, Gan YQ, Wang DS, Jin GZ, Li CY (2014b) L-stepholidine, a naturally occurring dopamine D1 receptor agonist and D2 receptor antagonist, attenuates methamphetamine self-administration in rats. Adv Mater Res 998:169–172
Zhao W, Huang Y, Liu Z, Cao BB, Peng YP, Qiu YH (2013) Dopamine receptors modulate cytotoxicity of natural killer cells via cAMP-PKA-CREB signaling pathway. PLoS One 8:e65860
Zhou M, Lin K, Si Y, Ru Q, Chen L, Xiao H, Li C (2019) Downregulation of HCN1 channels in hippocampus and prefrontal cortex in methamphetamine re-exposed mice with enhanced working memory. Physiol Res 68:107–117
Zhu JP, Xu W, Angulo JA (2006) Methamphetamine-induced cell death: selective vulnerability in neuronal subpopulations of the striatum in mice. Neuroscience 140:607–622
Funding
This study was performed with the financial support of grants from the Science and Technology Research Project of Hubei Provincial Department of Education (no. B2016294).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, M., Gong, X., Ru, Q. et al. The Neuroprotective Effect of L-Stepholidine on Methamphetamine-Induced Memory Deficits in Mice. Neurotox Res 36, 376–386 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-019-00069-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-019-00069-z