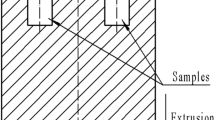
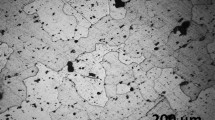
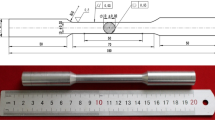
Abstract
Success of the numerical simulations depends on the accuracy of the material constitutive relations. Most of the ductile materials exhibit increased strain rate sensitivity at higher strain rates (> 103 s−1) compared to low and medium strain rates. Meanwhile, plastic deformation of any ductile material under high strain rate conditions results in heat generation due to plastic work. Hence, a reliable constitutive model should be able to predict the accurate thermo-mechanical response of the material over a wide range of strain rate loading conditions. In the present work, an enhanced constitutive model for high strain rate and elevated temperature is proposed. For calibration purpose, the stress-strain response of AA2024-T351 is studied under quasi-static and dynamic loading conditions using uniaxial compression and split Hopkinson compressive pressure bar (SHPB) respectively at various temperatures. A threshold strain rate value is identified and used to improve the prediction capabilities of the present model. Later, the proposed model is compared with Johnson-Cook (JC) and Khan-Huang-Liang (KHL) models using the different statistical parameters. This analysis revealed the improved stress-strain prediction capability of the proposed model compared to the others.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arsecularatne, J. A. and Zhang, L. C. (2004). Assessment of constitutive equations used in machining. Key Engineering Materials, 274–276, 277–282.
Bobbili, R. and Madhu, V. (2017). Constitutive modeling and fracture behavior of a biomedical Ti-13Nb-13Zr alloy. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 700, 82–91.
Børvik, T., Olovsson, L., Dey, S. and Langseth, M. (2011). Normal and oblique impact of small arms bullets on AA6082-T4 aluminium protective plates. Int. J. Impact Engineering 38, 7, 577–589.
Davies, E. D. H. and Hunter, S. C. (1963). The dynamic compression testing of solids by the method of the split Hopkinson pressure bar. J. Mechanics and Physics of Solids 11, 3, 155–179.
Djapic Oosterkamp, L., Ivankovic, A. and Venizelos, G. (2000). High strain rate properties of selected aluminium alloys. Materials Science and Engineering: A 278, 1, 225–235.
El-Magd, E. and Brodmann, M. (2001). Influence of precipitates on ductile fracture of aluminium alloy AA7075 at high strain rates. Materials Science and Engineering: A 307, 1, 143–150.
Fahad, M., Mativenga, P. T. and Sheikh, M. A. (2013). On the contribution of primary deformation zone-generated chip temperature to heat partition in machining. Int. J. Advanced Manufacturing Technology 68, 1, 99–110.
Gilat, A., Schmidt, T. E. and Walker, A. L. (2009). Full field strain measurement in compression and tensile split Hopkinson bar experiments. Experimental Mechanics 49, 2, 291–302.
Guo, Y. B., Wen, Q. and Horstemeyer, M. F. (2005). An internal state variable plasticity-based approach to determine dynamic loading history effects on material property in manufacturing processes. Int. J. Mechanical Sciences 47, 9, 1423–1441.
Hajari, A., Morakabati, M., Abbasi, S. M. and Badri, H. (2017). Constitutive modeling for high-temperature flow behavior of Ti-6242S alloy. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 681, 103–113.
Huh, H., Ahn, K., Lim, J. H., Kim, H. W. and Park, L. J. (2014). Evaluation of dynamic hardening models for BCC, FCC, and HCP metals at a wide range of strain rates. J. Materials Processing Technology 214, 7, 1326–1340.
Huh, H., Lee, H. J. and Song, J. H. (2011). Dynamic hardening equation of the auto-body steel sheet with the variation of temperature. Int. J. Automotive Technology 13, 1, 43–60.
Johnson, G. R., Hoegfeldt, J. M., Lindholm, U. S. and Nagy, A. (1983). Response of various metals to large torsional strains over a large range of strain rates — Part 2: Less ductile metals. J. Engineering Materials and Technology 105, 1, 48–53.
Kariem, M. A. (2012). Reliable Materials Performance Data from Impact Testing. Ph. D. Dissertation. Swinburne University of Technology. Melbourne, Australia.
Khan, A. S. and Huang, S. (1992). Experimental and theoretical study of mechanical behavior of 1100 aluminum in the strain rate range 10−5 — 104 s−1. Int. J. Plasticity, 8, 397–424.
Khan, A. S. and Liang, R. (1999). Behaviors of three BCC metal over a wide range of strain rates and temperatures: Experiments and modeling. Int. J. Plasticity 15, 10, 1089–1109.
Khan, A. S. and Liang, R. (2000). Behaviors of three BCC metals during non-proportional multi-axial loadings: Experiments and modeling. Int. J. Plasticity 16, 12, 1443–1458.
Khan, A. S. and Liu, H. (2012). Variable strain rate sensitivity in an aluminum alloy: Response and constitutive modeling. Int. J. Plasticity, 36, 1–14.
Kotkunde, N., Deole, A. D., Gupta, A. K. and Singh, S. K. (2014). Comparative study of constitutive modeling for Ti-6Al-4V alloy at low strain rates and elevated temperatures. Materials & Design, 55, 999–1005.
Lee, W.-S. and Chen, C.-W. (2013). High temperature impact properties and dislocation substructure of Ti-6Al-7Nb biomedical alloy. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 576, 91–100.
Lindholm, U. S. and Yeakley, L. M. (1968). High strain-rate testing: Tension and compression. Experimental Mechanics 8, 1, 1–9.
Lou, Y. and Yoon, J. W. (2018). A stress based model for shear ductole fracture. Proc. AEPA2018, Jeju, Korea.
Ludwik, P. (1909). Elemente der Technologischen Mechanik. 1st edn. Spriger-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg. Heidelberg, Germany.
Nguyen, D. T., Banh, T.-L., Kim, Y. S. and Jung, D. W. (2011). A modified Johnson-Cook model for sheet metal forming at elevated temperatures and its application for cooled stress-strain curve and spring-back prediction. AIP Conf. Proc. 1383, 1, 626–633.
Regazzoni, G., Kocks, U. F. and Follansbee, P. S. (1987). Dislocation kinetics at high strain rates. Acta Metallurgica 35, 12, 2865–2875.
Rodríguez, J., Navarro, C. and Sánchez-Gálvez (1994). Some corrections to the data analysis of the dynamic tensile tests in the Hopkinson bar. 04, C8, C8–83–C8–88.
Seidt, J. D. and Gilat, A. (2013). Plastic deformation of 2024-T351 aluminum plate over a wide range of loading conditions. Int. J. Solids and Structures 50, 10, 1781–1790.
Sima, M. and Özel, T. (2010). Modified material constitutive models for serrated chip formation simulations and experimental validation in machining of titanium alloy Ti-6Al-4V. Int. J. Machine Tools and Manufacture 50, 11, 943–960.
Smerd, R., Winkler, S., Salisbury, C., Worswick, M., Lloyd, D. and Finn, M. (2005). High strain rate tensile testing of automotive aluminum alloy sheet. Int. J. Impact Engineering 32, 1, 541–560.
Tanaka, K. and Nojima, T. (1975). Strain rate change tests of aluminum alloys under high strain rate. Proc. 19th Japan Cong. Materials Research, Tokyo, Japan, 48–51.
Wang, R., Zhang, H., Tang, L., Shao, J., Xiao, Z., Chen, Z., Liu, C. and Tang, J. (2019). Adiabatic shear deformation behaviors of cold-rolled copper under different impact loading directions. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 754, 330–338.
Xu, Z., He, X., Hu, H., Tan, P. J., Liu, Y. and Huang, F. (2019). Plastic behavior and failure mechanism of Ti-6Al-4V under quasi-static and dynamic shear loading. Int. J. Impact Engineering, 130, 281–291.
Zhang, X., Shivpuri, R. and Srivastava, A. K. (2016). Chip fracture behavior in the high speed machining of titanium alloys. J. Manufacturing Science and Engineering 138, 8, 081001.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This paper was significantly extended and modified from the original paper presented in Asia-Pacific Symposium on Engineering Plasticity and its Applications 2018, and recommended by the Scientific & Technical Committee for journal publication.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Paresi, P.R., Lou, Y., Narayanan, A. et al. Enhanced Constitutive Model for Aeronautic Aluminium Alloy (AA2024-T351) under High Strain Rates and Elevated Temperatures. Int.J Automot. Technol. 20 (Suppl 1), 79–87 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12239-019-0130-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12239-019-0130-8