Abstract
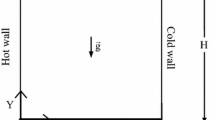
Marangoni thermocapillary convection and its contribution to heat transfer during boiling has been the subject of some debate in the open literature. Despite extensive research efforts there still remains insufficient quantitative information regarding the impact of thermocapillary flow on the heat transfer. As a result, this paper aims to present a numerical investigation of the heat transfer enhancement due to Marangoni thermocapillary convection under both earth gravity (1-g) and zero gravity (0-g) conditions. A hemispherical bubble of fixed shape is considered atop a heated top wall of a domain with variable height. The heat transfer enhancement is quantified for Marangoni numbers in the range of 100 ≤ Ma ≤ 3,000 for channel heights of 1.5 ≤ H/Rb ≤ 7.5 which, for the 1-g cases, correspond with a Raleigh number range of 51 ≤ RaH ≤ 6.5 × 104. For the most confined cases the flow and heat transfer were found to be very similar for the 0-g and 1-g cases. Also, the 0-g test cases were found to be very sensitive to increasing domain height whereas the 1-g simulations were far less sensitive.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arlabosse, P., Tadrist, L., Tadrist, H., Pantaloni, J.: Experimental analysis of the heat transfer induced by thermocapillaryconvection around a bubble. J. Heat Transfer 122, 66–73 (2000)
Bernard, H.: Tourbillons cellulaires dans une nappe liquide transportant de la chaleur par convection en regime permanent. Ann. Chem. Phys. 23, 62 (1900)
Bhunia, A., Kamotani, Y.: Flow around a bubble on a heated wall in a cross-flowing liquid under microgravity condition. Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer 44, 3895–3905 (2001)
Kassemi, M., Rashidnia, N.: Steady and oscillatory thermocapillary convection generated by a bubble. Phys. Fluids. 12(12), 3133–3122 (2000)
Koo, Y.S., Kenning, D.B.R.: Thermocapillary flow near a hemispherical bubble on a heated wall. J. Fluid Mech. 53(4), 715–735 (1972)
Larkin, B.K.: Thermocapillary flow around a hemispherical bubble. AIChE J. 16, 101–107 (1970)
Marangoni, C.G.M.: Veber die ausbreitung der tropfen einer flüssigkeit auf der oberflacke einer angerety. Tipografia Fusi, Pavia (1865)
McGrew, J.L., Bamford, F.L., Rehm, T.R.: Marangoni flow: an additional mechanism in boiling heat transfer. Science 153(3740), 1106–1107 (1966)
O’Shaughnessy, S., Robinson, A.: Numerical investigation of Marangoni convection caused by the presence of a bubble on a uniformly heated surface. In: Proceedings of ITP2007, Interdisciplinary Transport Phenomena V: Fluid, Thermal, Biological, Materials and Space Sciences, Bansko, Bulgaria, 14–19 October (2007)
Pearson, J.R.A.: On convection cells. J. Fluid Mech. 4, 489 (1958)
Petrovic, S., Robinson, A., Judd, R.L.: Marangoni heat transfer in subcooled nucleate pool boiling. Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer 47, 5115–5128 (2004)
Raake, D., Siekman, J.: Temperature and velocity fields due to syrface tension driven flow. Exp. Fluids 7, 164–172 (1989)
Radulescu, C., Robinson, A.: Numerical study of Marangoni-thermocapillary convection influence during boiling heat transfer in minichannels. Proceedings of the 6th ASME Conference on Nanochannels, Microchannels and Minichannels, ICNMM2008-62244 (2008)
Reynard, C., Santini, S., Tadrist, L.: Experimental study on the gravity influence on the periodic thermocapillary convection around a bubble. Exp. Fluids 31, 440–446 (2001)
Sefiane, K., Ward, C.A.: Recent advances on thermocapillary flows and interfacial conditions during the evaporation of liquids. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 134–125, 201–223 (2007)
Straub, J.: The role of surface tension for two-phase heat and mass transfer in the absence of gravity. Exp. Therm. Fluid Sci. 9, 253–273 (1994)
Thomson, J.: Capillary action, summarized in J.C. Maxwell’s article. Encyclopedia Britannica, 9th edn. (Samuel L. Hall, New York, 1878). Phil. Mag. 10(4), 330 (1855)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Radulescu, C., Robinson, A.J. The Influence of Gravity and Confinement on Marangoni Flow and Heat Transfer Around a Bubble in a Cavity: A Numerical Study. Microgravity Sci. Technol 20, 253–259 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12217-008-9034-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12217-008-9034-3