Abstract
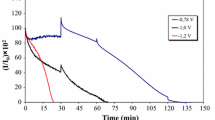
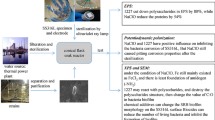
Scale formation in heat exchanger tube reduces heat transfer efficiency and enhances corrosion. Scale formation in cooling water is due to many factors including pH, temperature, salt etc. In this study, microbiological aspects of scale formation and their role on corrosion are presented. The calcium precipitating bacteria (CPB) were isolated from the scales collected from heat exchanger tube in a gas turbine power station using B4 medium. The dominant CPB was isolated and identified using 16s rRNA sequencing, and the phylogenetic analysis reveals that the predominant bacteria were Serratia sp. (FJ973548), Enterobacter sp. (FJ973549, FJ973550), and Enterococcus sp. (FJ973551). The nature of crystal deposits of bacteria has been explained. The corrosion behavior of CPB on mild steel was studied by the electrochemical method (polarization and impedance), and the biogenic calcium scale formations in CPB were analyzed by XRD method. The scale formation by bacteria reduced the cathodic corrosion current, where resistance was lower in the presence of bacteria. It is claimed that the CPB is one of the causative factor for scale formation and corrosion in cooling water system.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Castanier, S., LeMetayer-Levrel, G., Perthuisot, J.P.: Ca-carbonates precipitation and limestone genesis—the microbiogeologist point of view. Sedim. Geol. 126, 9–23 (1999)
Erlich, H.L.: Geomicrobiology: its significance for geology. Earth Sci. Rev 45, 45–60 (1998)
Kile, D.E., Eberl, D.D., Hoch, A.R.V., Reddy, M.M.: An assessment of calcite crystal growth mechanisms based on crystal size distributions. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 64, 2937–2950 (2000)
Beveridge, T.J., Meloche, J.D., Fyfe, W.S., Murray, R.G.E.: Diagenesis of metals chemically complexed to bacteria: laboratory formation of metal phosphates, sulfides, and organic condensates in artificial sediments. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 45, 1094–1108 (1983)
Ghiorse, W.C.: Biology of iron- and manganese-depositing bacteria. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 38, 515–550 (1984)
Knoll, A.H., Swett, K.: Calcareous deposition during the late Proterozoic era: an example from Spitsbergen. Am. J. Sci. 141, 104–132 (1990)
Ruiz, C., Monteoliva-Sanches, M., Huertas, F., Ramos-Cormenzana, A.: Calcium carbonate precipitation by several species of Myxococcus. Chemosphere 17, 835–838 (1988)
Rivadeneyra, M.A., Delgado, R., Del Moral, A., Ferrer, R.M., Ramos-Cormenzana, A.: Precipitation of calcium carbonate by Vibrio spp. from an inland saltern. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol 13, 197–204 (1994)
Kajander, E.O., Ciftcioglu, N.: Nanobacteria : an alternative mechanism for pathogenic intra and extracellular calcification and stone formation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 95, 8274–8279 (1998)
Folk, R.: SEM imaging of bacteria and nanobacteria in carbonate sediments and rocks. J. Sedim. Petrol. 63, 990–999 (1993)
Liu, T., Li, X., Wang, H., Sun, X.: Formation process of mixed fouling of microbe and CaCO3 in water systems. Chem. Eng. J. 88, 249–254 (2002)
Gollapudi, U.K., Knutson, C.L., Bang, S.S., Islam, M.R.: A new method for controlling leaching through permeable channels. Chemosphere 30, 695–705 (1995)
Douglas, S., Beveridge, T.J.: Mineral formation by bacteria in natural microbial communities. FEMS. Microbiol. Ecol. 26, 79–88 (1998)
Yates, K.K., Robbins, L.L.: Radioisotope tracer studies of inorganic carbon and Ca in microbiologically derived CaCO3. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 63, 129–136 (1999)
Ferrer, R.M., Quevedo-Sarmiento, J., Rivadeneyra, M.A., Bejar, V., Delgado, R., Ramos-Cormenzana, A.: Calcium carbonate precipitation by two groups of moderately halophilic microorganisms at different temperatures and salt concentrations. Curr. Microbiol. 17, 221–227 (1988)
Stocks-Fischer, S., Galinat, J.K., Bang, S.S.: Microbiological precipitation of CaCO3. Soil Biol. Biochem. 31, 1563–1571 (1999)
Hammes, F., Verstraete, W.: Key roles of pH and calcium metabolism in microbial carbonate precipitation. Rev. Environ. Sci. Biotechnol. 1, 3–7 (2002)
Baskar, S., Baskar, R., Mauclaire, L., Mckenzie, A.J.: Microbially induced calcite precipitation in culture experiments: possible origin for stalactites in Sahastradhara caves, Dehradun, India. Curr. Sci. 90, 58–64 (2006)
Chen, L., Shen, Y., Xie, A., Huang, B., Jia, R., Guo, R., Tang, W.: Bacteria-mediated synthesis of metal carbonate minerals with unusual morphologies and structures. Cryst. Growth Des. 9, 743–754 (2009)
Ercole, C., Cacchio, P., Botta, A.L., Centi, V., Lepidi, A.: Bacterially induced mineralization of calcium carbonate: the role of exopolysaccharides and capsular polysaccharides. Microsc. Microanal. 13, 42–50 (2007)
Sone Eli, D., Weiner, S., Addadi, L.: Biomineralization of limpet teeth: a cryo-TEM study of the organic matrix and the onset of mineral deposition. J. Struct. Biol. 158, 428–444 (2007)
Holt, J.G., Kreig, N.R., Sneath, P.H.A., Stanely, J.T.: In: Williams, S.T. (ed.) Bergey’s Manual of Determinative Bacteriology. Williams and Wilkins, Baltimore (1994)
Marmur, J.: A procedure for the isolation of deoxyribonucleic acid from micro-organisms. J. Mol. Biol. 3, 208 (1961)
Reddy, G.S.N., Aggarwal, R.K., Matsumoto, G.I., Shivaji, S.: Arthrobacter flavus sp. nov., a psychrophilic bacterium isolated from a pond in McMurdo Dry Valley, Antarctica. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 50, 1553 (2000)
Kimura, M.: A simple method for estimating evolutionary rates of base substitutions through comparative studies of nucleotide sequences. J. Mol. Evol. 16, 111 (1980)
Felsentein, J.: PHYLIP (Phylogeny Inference Package) Version 3.5c. Department of Genetics, University of Washington, Seattle, USA (1993)
Morita, R.Y.: Calcite precipitation by marine bacteria. Geomicrobiol. J. 2, 63–82 (1980)
Boquet, E., Boronat, A., Ramos-Cormenzana, A.: Production of calcite (calcium carbonate) crystals by soil bacteria is a general phenomenon. Nature (London) 246, 527–529 (1973)
Kramer, G., Klingler, H.C., Steiner, G.E.: Role of bacteria in the development of kidney stones. Curr. Opin. Urol. 10, 35–38 (2000)
McKay, D.S., Gibson, E.K., Thomas-Keprta, K.L., Vali, H., Romanek, C.S., Clemett, S.J., Chillier, X.D., Maechling, C.R., Zare, R.N.: Search for past life on Mars: possible relic biogenic activity in Martian meteorite ALH84001. Science 273, 924–930 (1996)
Vali, H., McKee, M.D., Çiftçioglu, N., Sears, K., Plows, F., Chevet, E., Ghiabi, P., Plavsic, M., Kajander, E.O., Zare, R.N.: Nanoforms: a new type of protein-associated mineralization. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 65, 63–74 (2001)
Fujita, Y., Ferris, E.G., Lawson, R.D., Colwell, F.S., Smith, R.W.: Calcium carbonate precipitation by ureolytic subsurface bacteria. Geomicrobiol. J. 17, 305–318 (2000)
Braissant, O., Verrecchia, E.P., Aragno, M.: Is the contribution of bacteria to terrestrial carbon budget grately understimated? Nat. Sci. (Naturwissenschaften) 89, 366–370 (2002). German
Knorre, H., Krumbein, W.: Bacterial calcification. In: Riding, R.R., Awramik, S.M. (eds.) Microbial Sediments, pp. 25–31. Springer-Verlag, Berlin (2000)
McConnaughey, T.A., Whelan, F.F.: Calcification generates protons for nutrient an bicarbonate uptake. Earth Sci. Rev. 42, 95–117 (1997)
Lian, B., Hu, Q., Chen, J., Ji, J., Teng, H.H.: Carbonate biomineralization induced by soil bacterium Bacillus megaterium. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 70, 5522–5535 (2006)
Tourney, J., Ngwenya, B.T.: Bacterial extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) mediate CaCO3 morphology and polymorphism. Chem. Geol. 262, 138–146 (2009)
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thank Mr. R. Ravishanker and Miss. S. Krithika of Instrumentation Division, CECRI, for their assistance in the utilization of SEM and XRD facility.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Maruthamuthu, S., Dhandapani, P., Ponmariappan, S. et al. Scale Formation by Calcium-Precipitating Bacteria in Cooling Water System. J Fail. Anal. and Preven. 10, 416–426 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11668-010-9377-0
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11668-010-9377-0