Abstract
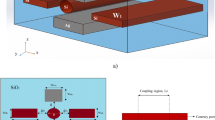
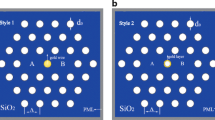
A plasmonic bidirectional/unidirectional wavelength splitter based on asymmetric metal-dielectric-metal (MDM) waveguides is proposed. In the splitter, owing to the interference effects caused by the unequal phase delays from the two asymmetric arms of MDM waveguides, surface plasmon polaritons (SPPs) will only transmit through the output port that is close to the arm where constructive interference arises. The transmission wavelengths can be linearly modulated by changing the lengths of the arms. Since two different SPP modes are obtained in two output ports, respectively, the structure can act as a bidirectional wavelength splitter. Interestingly, both SPP modes can be manipulated to transmit through the same port by adding a notch in one arm. In this case, the notch must simultaneously locate at the anti-node and at the node of the magnetic fields of two SPP modes respectively. As a result, additional phase delay for the specific mode will be produced by the notch, but without any impact on the other mode. Then, the propagation directions of both modes will turn to be identical. High transmission and high cross-talk isolation are investigated for all the cases by using the finite-difference time-domain method.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Saito K, Tanabe T, Oyama Y (2014) THz-wave generation via difference frequency mixing in strained silicon based waveguide utilizing its second order susceptibility χ(2). Opt Express 22(14):16660–16668
Yu S-P, Hood JD, Muniz JA, Martin MJ, Norte R, Hung C-L, Meenehan SM, Cohen JD, Painter O, Kimble HJ (2014) Nanowire photonic crystal waveguides for single-atom trapping and strong light-matter interactions. Appl Phys Lett 104(11):111103
Rezaei M, Jalaly S, Miri M, Khavasi A, Fard AP, Mehrany K, Rashidian B (2012) A distributed circuit model for side-coupled nanoplasmonic structures with metal–insulator–metal arrangement. IEEE J Sel Top Quant Electron 18(6):1692–1699
Wen KH, Hu YH, Chen L, Zhou JY, Lei L, Guo Z (2014) Design of an optical power and wavelength splitter based on subwavelength waveguides. J Lightwave Technol 32(17):3020–3026
Lu H, Liu XM, Wang L, Gong Y, Mao D (2011) Ultrafast all-optical switching in nanoplasmonic waveguide with Kerr nonlinear resonator. Opt Express 19(4):2910–2915
Wurtz GA, Pollard R, Zayats AV (2006) Optical bistability in nonlinear surface-plasmon polaritonic crystals. Phys Rev Lett 97(5):057402
Nikolajsen T, Leosson K, Bozhevolnyi SI (2004) Surface Plasmon polariton based modulators and switches operating at telecom wavelengths. Appl Phys Lett 85(24):5833–5835
Randhawa S, González MU, Renger J, Enoch S, Quidant R (2010) Design and properties of dielectric surface plasmon Bragg mirrors. Opt Express 18(14):14496–14510
Bozhevolnyi SI, Volkov VS, Devaux E, Laluet JY, Ebbesen TW (2006) Channel plasmon subwavelength waveguide components including interferometers and ring resonators. Nature 440(7083):508–511
Wen KH, Yan LS, Pan W, Luo B, Guo Z, Guo YH, Luo XG (2014) Electromagnetically induced transparency-like transmission in a compact side-coupled T-shaped resonator. J Lightwave Technol 32(9):1701–1707
Wen KH, Yan LS, Pan W, Luo B, Guo Z, Guo YH (2013) Design of plasmonic comb-like filters using loop-based resonators. Plasmonics 8(2):1017–1022
Enoch S, Quidant R, Badenes G (2004) Optical sensing based on plasmon coupling in nanoparticle arrays. Opt Express 12(15):3422–3427
Park J, Kim H, Lee B (2008) High order plasmonic Bragg reflection in the metal-insulator-metal waveguide Bragg grating. Opt Express 16(1):413–425
Hu FF, Yi HX, Zhou ZP (2011) Wavelength demultiplexing structure based on arrayed plasmonic slot cavities. Opt Lett 36(8):1500–1502
Ma FS, Lee C (2013) Optical nanofilters based on meta-atom side-coupled plasmonics metal-insulator-metal waveguides. J Lightwave Technol 31(17):2876–2880
Chen J, Li Z, Zou Y, Deng Z, Xiao J, Gong QH (2013) Coupled-resonator-induced fano resonances for plasmonic sensing with ultra-high figure of merits. Plasmonics 8(4):1627–1631
Guo YH, Yan LS, Pan W, Luo B, Wen KH, Guo Z, Luo XG (2013) Characteristics of plasmonic filters with a notch located along rectangular resonators. Plasmonics 8(2):167–171
Noual A, Akjouj A, Pennec Y, Gillet J-N, Djafari-Rouhani B (2009) Modeling of two-dimensional nanoscale Y-bent plasmonic waveguides with cavities for demultiplexing of the telecommunication wavelengths. N J Phys 11(10):103020
Tian J, Yang R, Song L, Xue W (2014) Optical properties of a Y-splitter based on hybrid multilayer plasmonic waveguide. IEEE J Quant Electron 50(11):898–903
Xu T, Zhao YH, Gan DC, Wang CT, Du CL, Luo XG (2008) Directional excitation of surface plasmons with subwavelength slits. Appl Phys Lett 9(10):101501
Wen KH, Yan LS, Pan W, Luo B, Guo Z, Guo YH (2012) A four-port plasmonic quasi-circulator based on metal-insulator-metal waveguides. Opt Express 20(27):28025–28032
Bavil MA, Zhou Z, Deng Q (2013) Active unidirectional propagation of surface plasmons at subwavelength slits. Opt Express 21(14):17066–17076
Pu MB, Yao N, Hu CG, Xin XC, Zhao ZY, Wang CT, Luo XG (2010) Directional coupler and nonlinear Mach-Zehnder interferometer based on metal-insulator-metal plasmonic waveguide. Opt Express 18(20):21030–21037
Raghunathan SB, Gan CH, Dijk TV, Kim BE, Schouten HF, Ubachs W, Lalanne P, Visser TD (2012) Plasmon switching: observation of dynamic surface plasmon steering by selective mode excitation in a sub-wavelength slit. Opt Express 20(14):15326–15335
Miroshnichenko AE, Kivshar YS (2013) Polarization traffic control for surface plasmons. Science 340(6130):283–284
Lin J, Mueller JB, Wang Q, Yuan G, Antoniou N, Yuan XC, Capasso F (2013) Polarization-controlled tunable directional coupling of surface plasmon polaritons. Science 340(6130):331–334
Dionne JA, Sweatlock LA, Atwater HA, Polman A (2006) Plasmon slot waveguides: towards chip-scale propagation with subwavelength-scale localization. Phys Rev B 73(3):035407
Johnson PB, Christy RW (1972) Optical constants of the noble metals. Phys Rev B 6(12):4370–4379
Acknowledgments
The work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grants No. 61405039 and No. 61475037, Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province, China under Grant No. 2014A030310300, the State Key Lab of Optical Technologies for Micro-Engineering and Nano-Fabrication of China, the Foundation for Distinguished Young Talents in Higher Education of Guangdong, China under Grant No. 2014KQNCX066, the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation under Grant No. 2014M552173, and the Research Fund of Guangdong University of Technology under Grant No. 13ZK0387.
Compliance with Ethical Standards
The content of this manuscript does not have any potential conflict of interest with anyone. This research does not involve in any human participant or animal. No part of this manuscript has been published or submitted elsewhere. Also, all the authors have given their approvals to the submission of this paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wen, K., Hu, Y., Chen, L. et al. Plasmonic Bidirectional/Unidirectional Wavelength Splitter Based on Metal-Dielectric-Metal Waveguides. Plasmonics 11, 71–77 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-015-0021-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-015-0021-4