Abstract
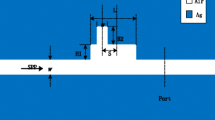
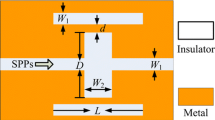
Fano resonances are numerically predicted in an ultracompact plasmonic structure, comprising a metal-isolator-metal (MIM) waveguide side-coupled with two identical stub resonators. This phenomenon can be well explained by the analytic model and the relative phase analysis based on the scattering matrix theory. In sensing applications, the sensitivity of the proposed structure is about 1.1 × 103 nm/RIU and its figure of merit is as high as 2 × 105 at λ = 980 nm, which is due to the sharp asymmetric Fano line-shape with an ultra-low transmittance at this wavelength. This plasmonic structure with such high figure of merits and footprints of only about 0.2 μm2 may find important applications in the on-chip nano-sensors.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Miroshnichenko E, Flach S, Kivshar YS (2010) Fano resonances in nanoscale structures. Rev Mod Phys 82(3):2257–2298
Luk’yanchuk B, Zheludev NI, Maier SA, Halas NJ, Nordlander P, Giessen H, Chong CT (2010) The Fano resonance in plasmonic nanostructures and metamaterials. Nat Mater 9(9):707–715
Verellen N, Sonnefraud Y, Sobhani H, Hao F, Moshchalkov VV, Van Dorpe P, Nordlander P, Maier SA (2009) Fano resonances in individual coherent plasmonic nanocavities. Nano Lett 9:1663–1667
Chen JJ, Li Z, Zhang X, Xiao JH, Gong QH (2013) Submicron bidirectional all-optical plasmonic switches. Sci Rep 3:1451. doi:10.1038/srep01451, Published online 2013 March 14
Fedotov VA, Rose M, Prosvirnin SL, Papasimakis N, Zheludev NI (2007) Sharp trapped-mode resonances in planar metamaterials with a broken structural symmetry. Phys Rev Lett 99:147401
Christ A, Martin OJF, Ekinei Y, Gippius NA, Tikhodeev SG (2008) Symmetry breaking in a plasmonic metamaterial at optical wavelength. Nano Lett 8:2171–2175
Christ A, Ekinei Y, Solak HH, Gippius NA, Tikhodeev SG, Martin OFJ (2007) Controlling the Fano interference in a plasmonic lattice. Phys Rev B 76:201405
Liu N, Kaiser S, Giessen H (2008) Magnetoinductive and electroinductive coupling in plasmonic metamaterial molecules. Adv Mater 20:4521–4525
Liu N, Langguth L, Weiss T, Kastel J, Fleischhauer M, Pfau T, Giessen H (2009) Plasmonic analogue of electromagnetically induced transparency at the Drude damping limit. Nat Mater 8:758–762
Zhang S, Genov DA, Wang Y, Liu M, Zhang X (2008) Plasmon-induced transparency in metamaterials. Phys Rev Lett 101:047401
Hentschel M, Saliba M, Vogelgesang R, Giessen H, Alivisatos AP, Liu N (2010) Transition from isolated to collective modes in plasmonic oligomers. Nano Lett 10:2721–2726
Liu N, Weiss T, Mesch M, Langguth L, Eigenthaler U, Hirscher M, Sönnichsen C, Giessen H (2010) Planar metamaterial analogue of electromagnetically induced transparency for plasmonic sensing. Nano Lett 10:1103–1107
Aydin K, Pryce IM, Atwater HA (2010) Symmetry breaking and strong coupling in planar optical metamaterials. Opt Express 18:13407–13417
Artar A, Yanik AA, Altug H (2011) Multispectral plasmon-induced transparency in coupled meta-atoms. Nano Lett 11:1685–1689
Hentschel M, Dregely D, Vogelgesang R, Giessen H, Liu N (2011) Plasmonic oligomers: the role of individual particles in collective behavior. Acs Nano 5:2042–2050
Rahmani M, Lukiyanchuk B, Ng B, Tavakkoli KGA, Liew YF, Hong MH (2011) Generation of pronounced Fano resonances and tuning of subwavelength spatial light distribution in plasmonic pentamers. Opt Express 19:4949–4956
Zhang J, Bai WL, Cai LK, Xu Y, Song GF, Gan QQ (2011) Observation of ultra-narrow band plasmon induced transparency based on large-area hybrid plasmon-waveguide systems. Appl Phys Lett 99:181120
Kekatpure RD, Barnard ES, Cai W, Brongersma M (2010) Phase-coupled plasmon-induced transparency. Phys Rev Lett 104:243902
He YR, Zhou H, Jin Y, He SL (2011) Plasmon induced transparency in a dielectric waveguide, Appl Phys Lett 99:043113
Zhang Y, Darmawan S, Tobing LYM, Mei T, Zhang DH (2011) Coupled resonator-induced transparency in ring-bus-ring Mach–Zehnder interferometer. J Opt Soc Am B 28(1):28–36
Chen JJ, Li Z, Yue S, Gong QH (2011) Compact and high–resolution plasmonic wavelength demultiplexers based on Fano interference. Opt Express 19:9976–9985
Han Z, Bozhevolnyi SI (2011) Plasmon-induced transparency with detuned ultracompact Fabry–Perot resonators in integrated plasmonic devices. Opt Express 19:3251–3257
Chen JJ, Li Z, Lei M, Fu XL, Xiao JH, Gong QH (2012) Plasmonic y-splitters of high wavelength resolution based on strongly-coupled-resonator effects. Plasmonics 7:441–445
Piao X, Yu S, Park N (2012) Control of Fano asymmetry in plasmon induced transparency and its application to plasmonic waveguide modulator. Opt Express 20(17):18994–18999
Lu H, Liu XM, Mao D, Gong YK, Wang GX (2011) Induced transparency in nanoscale plasmonic resonator systems. Opt Lett 36:3233–3235
Chen JJ, Wang C, Zhang R, Xiao JH (2012) Multiple plasmon-induced transparencies in coupled-resonator systems. Opt Lett 37:5133–5135
Wang G, Lu H, Liu X (2012) Dispersionless slow light in MIM waveguide based on a plasmonic analogue of electromagnetically induced transparency. Opt Express 20:20902–20907
Chen JJ, Li Z, Yue S, Xiao JH, Gong QH (2012) Plasmon-induced transparency in asymmetric T-shape single slit. Nano Lett 12:2494–2498
Lu H, Liu X, Mao D, Wang G (2012) Plasmonic nanosensor based on Fano resonance in waveguide-coupled resonators. Opt Lett 37:3780–3782
Johnson PB, Christy RW (1972) Optical constants of the noble metals. Phys Rev B 6:4370–4379
Ameling R, Langguth L, Hentschel M, Mesch M, Braun PV, Giessen H (2010) Cavity-enhanced localized plasmon resonance sensing. Appl Phys Lett 97:253116
Becker J, Truegler A, Jakab A, Hohenester U, Soennichsen C (2010) The optimal aspect ratio of gold nanorods for plasmonic bio-sensing. Plasmonics 5:161
Haus HA (1984) Waves and fields in optoelectronics. Prentice Hall, New York
Economou EN (1969) Surface plasmons in thin films. Phys Rev 182(2):539–554
Veronis G, Fan S (2005) Bends and splitters in metal–dielectric–metal subwavelength plasmonic waveguides. Appl Phys Lett 87:131102
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant nos. 11204018, 61177085, and 51172030) and the National Basic Research Program of China (Grants 2010CB923200, 2009CB930504, and 2013CB328704).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, J., Li, Z., Zou, Y. et al. Coupled-Resonator-Induced Fano Resonances for Plasmonic Sensing with Ultra-High Figure of Merits. Plasmonics 8, 1627–1631 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-013-9580-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-013-9580-4