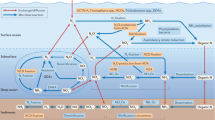
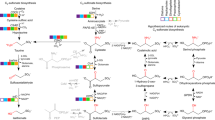
Abstract
Sulfur cycling in the biosphere is tightly interwoven with the cycling of carbon and nitrogen, through various biological and geochemical processes. Marine microorganisms, due to their high abundance, diverse metabolic activities, and tremendous adaptation potential, play an essential role in the functioning of global biogeochemical cycles and linking sulfur transformation to the cycling of carbon and nitrogen. Currently many coastal regions are severely stressed by hypoxic or anoxic conditions, leading to the accumulation of toxic sulfide. A number of recent studies have demonstrated that dissimilatory sulfur oxidation by heterotrophic bacteria can protect marine ecosystems from sulfide toxicity. Sulfur-oxidizing bacteria have evolved diverse phylogenetic and metabolic characteristics to fill an array of ecological niches in various marine habitats. Here, we review the recent findings on the microbial communities that are involved in the oxidation of inorganic sulfur compounds and address how the two elements of sulfur and carbon are interlinked and influence the ecology and biogeochemistry in the ocean. Delineating the metabolic enzymes and pathways of sulfur-oxidizing bacteria not only provides an insight into the microbial sulfur metabolism, but also helps us understand the effects of changing environmental conditions on marine sulfur cycling and reinforces the close connection between sulfur and carbon cycling in the ocean.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bamford V A, Bruno S, Rasmussen T, Appia-Ayme C, Cheesman M R, Berks B C, Hemmings A M. 2002. Structural basis for the oxidation of thiosulfate by a sulfur cycle enzyme. Embo J, 21: 5599–5610
Bao P, Li G X, Sun G X, Xu Y Y, Meharg A A, Zhu Y G. 2018. The role of sulfate-reducing prokaryotes in the coupling of element biogeochemical cycling. Sci Total Environ, 613–614: 398–408
Bardischewsky F, Quentmeier A, Rother D, Hellwig P, Kostka S, Friedrich C G. 2005. Sulfur dehydrogenase of Paracoccus pantotrophus: The heme-2 domain of the molybdoprotein cytochrome c complex is dispensable for catalytic activity. Biochemistry, 44: 7024–7034
Barton L L, Fardeau M L, Fauque G D. 2014. Hydrogen sulfide: A toxic gas produced by dissimilatory sulfate and sulfur reduction and consumed by microbial oxidation. Met Ions Life Sci, 14: 237–277
Barton L L, Fauque G D. 2009. Biochemistry, physiology and biotechnology of sulfate-reducing bacteria. Adv Appl Microbiol, 68: 41–98
Boden R, Borodina E, Wood A P, Kelly D P, Murrell J C, Scha fer H. 2011. Purification and characterization of dimethylsulfide monooxygenase from hyphomicrobium sulfonivorans. J Bacteriol, 193: 1250–1258
Bowles M W, Mogollón J M, Kasten S, Zabel M, Hinrichs K U. 2014. Global rates of marine sulfate reduction and implications for sub-seafloor metabolic activities. Science, 344: 889–891
Brinkhoff T, Giebel H A, Simon M. 2008. Diversity, ecology, and genomics of the Roseobacter clade: A short overview. Arch Microbiol, 189: 531–539
Brito J A, Sousa F L, Stelter M, Bandeiras T M, Vonrhein C, Teixeira M, Pereira M M, Archer M. 2009. Structural and functional insights into sulfide: Quinone oxidoreductase. Biochemistry, 48: 5613–5622
Brüser T, Lens P N L, Truper H G. 2000. The biological sulfur cycle. In: Lens P N L, Pol L, eds. Environmental Technologies to Treat Sulfur Pollution. London: IWA Publishing
Bullock H A, Luo H, Whitman W B. 2017. Evolution of dimethylsulfoniopropionate metabolism in marine phytoplankton and bacteria. Front Microbiol, 8: e0127288
Curson A R J, Todd J D, Sullivan M J, Johnston A W B. 2011. Catabolism of dimethylsulphoniopropionate: Microorganisms, enzymes and genes. Nat Rev Microbiol, 9: 849–859
Diaz R J, Rosenberg R. 2008. Spreading dead zones and consequences for marine ecosystems. Science, 321: 926–929
Dolata M M, Van Beeumen J J, Ambler R P, Meyer T E, Cusanovich M A. 1993. Nucleotide sequence of the heme subunit of flavocytochrome c from the purple phototrophic bacterium, Chromatium vinosum. A 2.6-kilobase pair DNA fragment contains two multiheme cytochromes, a flavoprotein, and a homolog of human ankyrin. J Biol Chem, 268: 14426–14431
Durham B P, Sharma S, Luo H, Smith C B, Amin S A, Bender S J, Dearth S P, Van Mooy B A S, Campagna S R, Kujawinski E B, Armbrust E V, Moran M A. 2015. Cryptic carbon and sulfur cycling between surface ocean plankton. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 112: 453–457
Epel B, Schäfer K O, Quentmeier A, Friedrich C, Lubitz W. 2005. Multifrequency EPR analysis of the dimanganese cluster of the putative sulfate thiohydrolase SoxB of Paracoccus pantotrophus. J Biol Inorg Chem, 10: 636–642
Friedrich C G, Bardischewsky F, Rother D, Quentmeier A, Fischer J. 2005. Prokaryotic sulfur oxidation. Curr Opin Microbiol, 8: 253–259
Friedrich C G, Rother D, Bardischewsky F, Quentmeier A, Fischer J. 2001. Oxidation of reduced inorganic sulfur compounds by bacteria: Emergence of a common mechanism? Appl Environ Microbiol, 67: 2873–2882
Frigaard N U, Dahl C. 2009. Sulfur metabolism in phototrophic sulfur bacteria. Adv Microb Physiol, 54: 103–200
González J M, Covert J S, Whitman W B, Henriksen J R, Mayer F, Scharf B, Schmitt R, Buchan A, Fuhrman J A, Kiene R P, Moran M A. 2003. Silicibacter pomeroyi sp. nov. and Roseovarius nubinhibens sp. nov., dimethylsulfoniopropionate-demethylating bacteria from marine environments. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol, 53: 1261–1269
González J M, Kiene R P, Moran M A. 1999. Transformation of sulfur compounds by an abundant lineage of marine bacteria in the α-Subclass of the class proteobacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol, 65: 3810–3819
González J M, Moran M A. 1997. Numerical dominance of a group of marine bacteria in the alpha-subclass of the class Proteobacteria in coastal seawater. Appl Environ Microbiol, 63: 4237–4242
Gregersen L H, Bryant D A, Frigaard N U. 2011. Mechanisms and evolution of oxidative sulfur metabolism in green sulfur bacteria. Front Microbiol, 2: 116
Griesbeck C, Schütz M, Schödl T, Bathe S, Nausch L, Mederer N, Vielreicher M, Hauska G. 2002. Mechanism of sulfide-quinone reductase investigated using site-directed mutagenesis and sulfur analysis. Biochemistry, 41: 11552–11565
Grote J, Jost G, Labrenz M, Herndl G J, Jürgens K. 2008. Epsilonproteo-bacteria represent the major portion of chemoautotrophic bacteria in sulfidic waters of pelagic redoxclines of the Baltic and Black Seas. Appl Environ Microbiol, 74: 7546–7551
Howard E C, Sun S, Biers E J, Moran M A. 2008. Abundant and diverse bacteria involved in DMSP degradation in marine surface waters. Environ Microbiol, 10: 2397–2410
Jiao N, Herndl G J, Hansell D A, Benner R, Kattner G, Wilhelm S W, Kirchman D L, Weinbauer M G, Luo T, Chen F, Azam F. 2010. Microbial production of recalcitrant dissolved organic matter: Long-term carbon storage in the global ocean. Nat Rev Microbiol, 8: 593–599
Jiao N, Robinson C, Azam F, Thomas H, Baltar F, Dang H, Hardman-Mountford N J, Johnson M, Kirchman D L, Koch B P, Legendre L, Li C, Liu J, Luo T, Luo Y W, Mitra A, Romanou A, Tang K, Wang X, Zhang C, Zhang R. 2014. Mechanisms of microbial carbon sequestration in the ocean—Future research directions. Biogeosciences, 11: 5285–5306
Jørgensen B B. 1982. Mineralization of organic matter in the sea bed—The role of sulphate reduction. Nature, 296: 643–645
Jørgensen B B. 2010. Big sulfur bacteria. Isme J, 4: 1083–1084
Jørgensen B B, Nelson D C. 2004. Sulfide oxidation in marine sediments: Geochemistry meets microbiology. Geol Soc Am Spec Pap, 379: 63–81
Kai F, Liesack W, Bo T. 1998. Elemental sulfur and thiosulfate disproportionation by Desulfocapsa sulfoexigens sp. nov. a new anaerobic bacterium isolated from marine surface sediment. Appl Environ Microbiol, 64: 119–125
Kappler U, Bennett B, Rethmeier J, Schwarz G, Deutzmann R, McEwan A G, Dahl C. 2000. Sulfite:Cytochromec oxidoreductase fromThiobacillus novellus. J Biol Chem, 275: 13202–13212
Kappler U, Maher M J. 2013. The bacterial SoxAX cytochromes. Cell Mol Life Sci, 70: 977–992
Kappler U, Schäfer H. 2014. Transformations of dimethyl sulfide. In: The Metal-Driven Biogeochemistry of Gaseous Compounds in the Environment. Springer Netherlands. 279–313
Kim H G, Doronina N V, Trotsenko Y A, Kim S W. 2007. Methylophaga aminisulfidivorans sp. nov., a restricted facultatively methylotrophic marine bacterium. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol, 57: 2096–2101
Lavik G, Stührmann T, Brüchert V, Van der Plas A, Mohrholz V, Lam P, Mussmann M, Fuchs B M, Amann R, Lass U, Kuypers M M M. 2009. Detoxification of sulphidic African shelf waters by blooming chemolithotrophs. Nature, 457: 581–584
Legendre L, Rivkin R B, Jiao N. 2018. Advanced experimental approaches to marine water-column biogeochemical processes. Ices J Mar Sci, 75: 30–42
Leloup J, Fossing H, Kohls K, Holmkvist L, Borowski C, Jørgensen B B. 2009. Sulfate-reducing bacteria in marine sediment (Aarhus Bay, Denmark): Abundance and diversity related to geochemical zonation. Environ Microbiol, 11: 1278–1291
Lenk S. 2011. Molecular ecology of key organisms in sulfur and carbon cycling in marine sediments. Dissertation for Doctoral Degree. Bremen: Max Planck Institute for Marine Microbiology
Lenk S, Arnds J, Zerjatke K, Musat N, Amann R, Mussmann M. 2011. Novel groups of Gammaproteobacteria catalyse sulfur oxidation and carbon fixation in a coastal, intertidal sediment. Environ Microbiol, 13: 758–774
Lenk S, Moraru C, Hahnke S, Arnds J, Richter M, Kube M, Reinhardt R, Brinkhoff T, Harder J, Amann R, Mußmann M. 2012. Roseobacter clade bacteria are abundant in coastal sediments and encode a novel combination of sulfur oxidation genes. Isme J, 6: 2178–2187
Li C, Cheng M, Algeo T J, Xie S C. 2015. A theoretical prediction of chemical zonation in early oceans (>520 Ma). Sci China Earth Sci, 58: 1901–1909
Li H, Li J, Lü C, Xia Y, Xin Y, Liu H, Xun L, Liu H. 2017. FisR activates σ54-dependent transcription of sulfide-oxidizing genes in Cupriavidus pinatubonensis JMP134. Mol Microbiol, 105: 373–384
Lidbury I, Kröber E, Zhang Z, Zhu Y, Murrell J C, Chen Y, Schäfer H. 2016. A mechanism for bacterial transformation of dimethyl sulfide to dimethyl sulfoxide: A missing link in the marine organic sulfur cycle. Environ Microbiol, 18: 2754–2766
Lin X, Wakeham S G, Putnam I F, Astor Y M, Scranton M I, Chistoserdov A Y, Taylor G T. 2006. Comparison of vertical distributions of prokaryotic assemblages in the anoxic Cariaco Basin and Black Sea by use of fluorescence in situ hybridization. Appl Environ Microbiol, 72: 2679–2690
Liu H, Xin Y, Xun L. 2014. Distribution, diversity, and activities of sulfur dioxygenases in heterotrophic bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol, 80: 1799–1806
Luther G W, Findlay A J, MacDonald D J, Owings S M, Hanson T E, Beinart R A, Girguis P R. 2011. Thermodynamics and kinetics of sulfide oxidation by oxygen: A look at inorganically controlled reactions and biologically mediated processes in the environment. Front Microbio, 2: 62
Lü C, Xia Y, Liu D, Zhao R, Gao R, Liu H, Xun L. 2017. Cupriavidus necator H16 uses flavocytochrome c-sulfide dehydrogenase to oxidize self-produced and added sulfide. Appl Environ Microbiol, 83: e01610–17
Mangold S, Valdés J, Holmes D S, Dopson M. 2011. Sulfur metabolism in the extreme acidophile Acidithiobacillus caldus. Front Microbiol, 2: 17
Marcia M, Ermler U, Peng G, Michel H. 2010. A new structure-based classification of sulfide: quinone oxidoreductases. Proteins, 78: 1073–1083
Moran M A, Belas R, Schell M A, González J M, Sun F, Sun S, Binder B J, Edmonds J, Ye W, Orcutt B, Howard E C, Meile C, Palefsky W, Goesmann A, Ren Q, Paulsen I, Ulrich L E, Thompson L S, Saunders E, Buchan A. 2007. Ecological genomics of marine Roseobacters. Appl Environ Microbiol, 73: 4559–4569
Moran M A, González J M, Kiene R P. 2003. Linking a bacterial taxon to sulfur cycling in the sea: Studies of the marine Roseobacter group. Geomicrobiol J, 20: 375–388
Mussmann M, Schulz H N, Strotmann B, Kjaer T, Nielsen L P, Rossello-Mora R A, Amann R I, Jorgensen B B. 2003. Phylogeny and distribution of nitrate-storing Beggiatoa spp. in coastal marine sediments. Environ Microbiol, 5: 523–533
Ogawa T, Furusawa T, Shiga M, Seo D, Sakurai H, Inoue K. 2010. Biochemical studies of a soxF-encoded monomeric flavoprotein purified from the green sulfur bacterium Chlorobaculum tepidum that Stimulates in Vitro thiosulfate oxidation. Biosci Biotech Biochem, 74: 771–780
Pokorna D, Zabranska J. 2015. Sulfur-oxidizing bacteria in environmental technology. Biotech Adv, 33: 1246–1259
Preisler A, de Beer D, Lichtschlag A, Lavik G, Boetius A, Jørgensen B B. 2007. Biological and chemical sulfide oxidation in a Beggiatoa inhabited marine sediment. Isme J, 1: 341–353
Quentmeier A, Friedrich C G. 2001. The cysteine residue of the SoxY protein as the active site of protein-bound sulfur oxidation of Paracoccus pantotrophus GB17. Febs Lett, 503: 168–172
Quentmeier A, Hellwig P, Bardischewsky F, Grelle G, Kraft R, Friedrich C G. 2003. Sulfur oxidation in Paracoccus pantotrophus: Interaction of the sulfur-binding protein SoxYZ with the dimanganese SoxB protein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 312: 1011–1018
Quentmeier A, Kraft R, Kostka S, Klockenkämper R, Friedrich C G. 2000. Characterization of a new type of sulfite dehydrogenase from Paracoccus pantotrophus GB17. Arch Microbiol, 173: 117–125
Reinartz M, Tschäpe J, Brüser T, Trüper H G, Dahl C. 1998. Sulfide oxidation in the phototrophic sulfur bacterium Chromatium vinosum. Archives Microbiol, 170: 59–68
Schäfer H. 2007. Isolation of Methylophaga spp. from marine dimethylsulfide-degrading enrichment cultures and identification of polypeptides induced during growth on dimethylsulfide. Appl Environ Microbiol, 73: 2580–2591
Schulz H N, Jørgensen B B. 2001. Big bacteria. Annu Rev Microbiol, 55: 105–137
Schütz M, Maldener I, Griesbeck C, Hauska G. 1999. Sulfide-quinone reductase from Rhodobacter capsulatus: Requirement for growth, periplasmic localization, and extension of gene sequence analysis. J Bacteriol, 181: 6516–6523
Schütz M, Shahak Y, Padan E, Hauska G. 1997. Sulfide-quinone reductase from Rhodobacter capsulatus. Purification, cloning, and expression. J Biol Chem, 272: 9890–9894
Selman M, Greenhalgh S, Diaz R, Sugg, Z. 2008. Eutrophication and hypoxia in coastal areas: A global assessment of the state of knowledge. J Am Geriatr Soc, 51: 1305–1317
Sievert S, Kiene R, Schulz-Vogt H. 2007. The sulfur cycle. Oceanography, 20: 117–123
Sorokin D Y, Tourova T P, Muyzer G. 2005. Citreicella thiooxidans gen. nov., sp. nov., a novel lithoheterotrophic sulfur-oxidizing bacterium from the Black Sea. Syst Appl Microbiol, 28: 679–687
Thamdrup B, Finster K, Hansen J W, Bak F. 1993. Bacterial disproportionation of elemental sulfur coupled to chemical reduction of iron or manganese. Appl Environ Microbiol, 59: 101–108
Verté F, Kostanjevecki V, De Smet L, Meyer T E, Cusanovich M A, Van Beeumen J J. 2002. Identification of a thiosulfate utilization gene cluster from the green phototrophic bacterium Chlorobium limicola. Biochemistry, 41: 2932–2945
Wagner-Döbler I, Biebl H. 2006. Environmental Biology of the marine Roseobacter lineage. Annu Rev Microbiol, 60: 255–280
Walsh D A, Zaikova E, Howes C G, Song Y C, Wright J J, Tringe S G, Tortell P D, Hallam S J. 2009. Metagenome of a versatile chemolithoautotroph from expanding oceanic dead zones. Science, 326: 578–582
Wasmund K, Mußmann M, Loy A. 2017. The life sulfuric: Microbial ecology of sulfur cycling in marine sediments. Environ Microbol Rep, 9: 323–344
Winkel M, de Beer D, Lavik G, Peplies J, Mußmann M. 2014. Close association of active nitrifiers with Beggiatoa mats covering deep-sea hydrothermal sediments. Environ Microbiol, 16: 1612–1626
Xia Y, Lü C, Hou N, Xin Y, Liu J, Liu H, Xun L. 2017. Sulfide production and oxidation by heterotrophic bacteria under aerobic conditions. Isme J, 11: 2754–2766
Xie S C, Chen J F, Wang F P, Xun L Y, Tang K, Zhai W D, Liu J H, Ma W T. 2017. Mechanisms of carbon storage and the coupled carbon, nitrogen and sulfur cycles in regional seas in response to global change. Sci China Earth Sci, 60: 1010–1014
Xin Y, Liu H, Cui F, Liu H, Xun L. 2016. Recombinant Escherichia coli with sulfide:quinone oxidoreductase and persulfide dioxygenase rapidly oxidises sulfide to sulfite and thiosulfate via a new pathway. Environ Microbiol, 18: 5123–5136
Zaikova E, Walsh D A, Stilwell C P, Mohn W W, Tortell P D, Hallam S J. 2009. Microbial community dynamics in a seasonally anoxic fjord: Saanich Inlet, British Columbia. Environ Microbiol, 12: 172–191
Zeyer J, Eicher P, Wakeham S G, Schwarzenbach R P. 1987. Oxidation of dimethyl sulfide to dimethyl sulfoxide by phototrophic purple bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol, 53: 2026–2032
Zhang L, Kuniyoshi I, Hirai M, Shoda M. 1991. Oxidation of dimethyl sulfide by Pseudomonas acidovorans DMR-11 isolated from peat biofilter. Biotechnol Lett, 13: 223–228
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (Grant No. 2016YFA0601103), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 41606134) and the Fundamental Research Funds of Shandong University as well.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hu, X., Liu, J., Liu, H. et al. Sulfur metabolism by marine heterotrophic bacteria involved in sulfur cycling in the ocean. Sci. China Earth Sci. 61, 1369–1378 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11430-017-9234-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11430-017-9234-x