Abstract
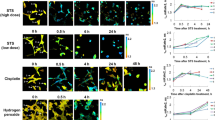
Apoptosis is an important process for maintaining tissue homeostasis and eliminating abnormal cells in multicellular organisms. Abnormality in apoptosis often leads to severe diseases such as cancers. Better understanding of its mechanisms and processes is therefore important. Accompanying molecular biology events of apoptosis is a series of cellular morphology changes: nucleus condensation, cell shrinkage and rounding, cell surface blebbing, dynamic blebbing, apoptotic membrane protrusions and nucleus fragmentations and finally, the formation and release of apoptotic bodies. It is difficult to detect cellular changes in the early phase of apoptosis due to the subtle changes at this phase. In the current study, we induced apoptosis in HeLa cells with H2O2 and used nuclear dye Hoechst 33258, mitochondria, lysosome and cytoplasmic protein specific aggregation-induced emission fluorogens (AIEgens), TPE-Ph-In, 2M-DABS and BSPOTPE to successfully perform live cell multiplexed imaging to investigate early apoptosis cellular events. We showed the gradual dissipation of mitochondria membrane potential until it is nondetectable by TPE-Ph-In. Increased mitophagy detected by TPE-Ph-In and 2M-DABS, condensed nucleus detected by Hoechst 33258, increased permeability and/or reduced integrity of nuclear membrane, and increased intracellular vesicles detected by 2M-DABS are some of the early events of apoptosis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alberts B, Johnson A, Lewis J, Morgan D, Raff M, Roberts K, Walter P. Molecular Biology of the Cell. 6th ed. New York: Garland Science, 2015. 2
Karam JA. Apoptosis in Carcinogenesis and Chemotherapy. Berlin: Springer, 2009
Slattery ML, Mullany LE, Sakoda LC, Wolff RK, Samowitz WS, Herrick JS. Apoptosis, 2018, 23: 237–250
Fuchs Y, Steller H. Cell, 2011, 147: 742–758
McArthur K, Whitehead LW, Heddleston JM, Li L, Padman BS, Oorschot V, Geoghegan ND, Chappaz S, Davidson S, San Chin H, Lane RM, Dramicanin M, Saunders TL, Sugiana C, Lessene R, Osellame LD, Chew TL, Dewson G, Lazarou M, Ramm G, Lessene G, Ryan MT, Rogers KL, van Delft MF, Kile BT. Science, 2018, 359: eaao6047
Shi Y. Methods Enzymol, 2008, 442: 141–156
Tinari A, Giammarioli AM, Manganelli V, Ciarlo L, Malorni W. Methods Enzymol, 2008, 442: 1–26
Tixeira R, Caruso S, Paone S, Baxter AA, Atkin-Smith GK, Hulett MD, Poon IKH. Apoptosis, 2017, 22: 475–477
Atkin-Smith GK, Paone S, Zanker DJ, Duan M, Phan TK, Chen W, Hulett MD, Poon IKH. Sci Rep, 2017, 7: 39846
Coleman ML, Sahai EA, Yeo M, Bosch M, Dewar A, Olson MF. Nat Cell Biol, 2001, 3: 339–345
Wickman G, Julian L, Olson MF. Cell Death Differ, 2012, 19: 735–742
Banfalvi G. Apoptosis, 2017, 22: 306–323
Chernyak BV, Izyumov DS, Lyamzaev KG, Pashkovskaya AA, Pletjushkina OY, Antonenko YN, Sakharov DV, Wirtz KWA, Skulachev VP. Biochim Biophys Acta, 2006, 1757: 525–534
Singh M, Sharma H, Singh N. Mitochondrion, 2007, 7: 367–373
Li Y, Wu Y, Chang J, Chen M, Liu R, Li F. Chem Commun, 2013, 49: 11335
Zhao N, Chen S, Hong Y, Tang BZ. Chem Commun, 2015, 51: 13599–13602
Yu CYY, Zhang W, Kwok RTK, Leung CWT, Lam JWY, Tang BZ. J Mater Chem B, 2016, 4: 2614–2619
Cheng Y, Dai J, Sun C, Liu R, Zhai T, Lou X, Xia F. Angew Chem Int Ed, 2018, 57: 3123–3127
Cheng Y, Sun C, Ou X, Liu B, Lou X, Xia F. Chem Sci, 2017, 8: 4571–4578
Cheng Y, Huang F, Min X, Gao P, Zhang T, Li X, Liu B, Hong Y, Lou X, Xia F. Anal Chem, 2016, 88: 8913–8919
Xu X, Huang J, Li J, Yan J, Qin J, Li Z. Chem Commun, 2011, 47: 12385–12387
Li Q, Li Z. Sci China Chem, 2015, 58: 1800–1809
Liang J, Feng G, Kwok RTK, Ding D, Tang B, Liu B. Sci China Chem, 2016, 59: 53–61
Nilsson C, Kågedal K, Johansson U, Öllinger K. Methods Cell Sci, 2003, 25: 185–194
Tong H, Hong Y, Dong Y, Häussler M, Li Z, Lam JWY, Dong Y, Sung HHY, Williams ID, Tang BZ. J Phys Chem B, 2007, 111: 11817–11823
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Hong Kong Branch of Chinese National Engineering Research Centres for Tissue Restoration and Reconstruction. We acknowledged the use of South Australian nodes of the Australian Microscopy & Microanalysis Research Facility and the Australian National Fabrication Facility at Flinders University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic supplementary material
11426_2018_9287_MOESM1_ESM.docx
Multiplexed imaging detection of live cell intracellular changes in early apoptosis with aggregation-induced emission fluorogens
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, Y., Liu, H., Zhao, N. et al. Multiplexed imaging detection of live cell intracellular changes in early apoptosis with aggregation-induced emission fluorogens. Sci. China Chem. 61, 892–897 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11426-018-9287-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11426-018-9287-x