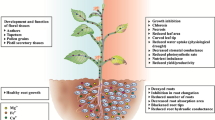
Abstract
Numerous investigations have demonstrated that even soil in which concentrations of individual elements do not exceed permissible limits can cause harmful effects in living organisms. In the present study, polluted-soil-induced oxidative stress was evaluated using Tradescantia clone 4430, which is widely used for genotoxicity evaluations, employing biochemical (superoxide dismutase (SOD), contents of ascorbic acid (AA), carotenoids (Car), hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), chlorophyll (Chl) a/b ratio), and molecular (RAPD and differential display (DD-PCR)) markers after long-term exposure. The activity (staining intensity) of SOD isoforms in Tradescantia leaves was higher in plants grown in all heavy-metal-polluted test soils compared to the control. No direct link between the soil pollution category and the contents of AA, Car, Chl a/b in Tradescantia leaves was revealed, but the concentration of H2O2 was shown to be a sensitive biochemical indicator that may appropriately reflect the soil contamination level. Both short-term (treatment of cuttings with H2O extracts of soil) and long-term (0.5 and 1.0 year) exposure increased MN frequencies, but the coincidence of the MN induction and the soil pollution level was observed only in some cases of long-term exposure. Soil (geno)toxin-induced polymorphism in the RAPD profile was determined with two primers in plants after long-term exposure to soils of an extremely hazard category. Transcript profiling of plants after long-term cultivation in test soils using DD-PCR showed that the majority of differentially expressed transcript-derived fragments (TDFs) were homologous to genes directly or indirectly participating in photosynthesis, the abiotic stress response, and signal transduction cascades.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akram NA, Shafiq F, Ashraf M (2017) Ascorbic acid – a potential oxidant scavenger and its role in plant development and abiotic stress tolerance. Front Plant Sci 8:613
Alloway BJ (2013) Sources of heavy metals and metalloids in soils. Springer, Dordrecht, pp 11–50
Al-Qurainy F, Alameri AA, Khan S (2010) RAPD profile for the assessment of genotoxicity on a medicinal plant Eruca sativa. J Med Plant Res 4:579–586
Altschul SF, Gish W, Miller W, Myers EW, Lipman DJ (1990) Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol 215:403–410
Anjum NA, Singh HP, Khan MIR, Masood A, Per TS, Negi A, Batish DR, Khan NA, Duarte AC, Pereira E, Ahmad I (2015) Too much is bad – an appraisal of phytotoxicity of elevated plant-beneficial heavy metal ions. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:3361–3382
Aras S, Soydam Aydin S, Aksoy Körpe D, Dönmez Ç (2012) Comparative genotoxicity analysis of heavy metal contamination in higher plants. In: Begum DG (ed) Ecotoxicology. InTech, p 146
Atienzar FA, Jha AN (2006) The random amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD) assay and related techniques applied to genotoxicity and carcinogenesis studies: a critical review. Mutat Res 613:76–102
Atienzar FA, Cheung VV, Jha AN, Depledge MH (2001) Fitness parameters and DNA effects are sensitive indicators of copper-induced toxicity in Daphnia magna. Toxicol Sci 59:241–250
Avalyan RE, Aghajanyan EA, Khosrovyan A et al (2017) Assessment of mutagenicity of water from Lake Sevan, Armenia with application of Tradescantia (clone 02). Mutat Res 800–802:8–13
Bahmani R, Kim D, Lee BD, Hwang S (2017) Over-expression of tobacco UBC1 encoding a ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme increases cadmium tolerance by activating the 20S/26S proteasome and by decreasing Cd accumulation and oxidative stress in tobacco Nicotiana tabacum. Plant Mol Biol 94:433–451
Beauchamp C, Fridovich I (1971) Superoxide dismutase: improved assays and an assay applicable to acrylamide gels. Anal Biochem 44:276–287
Benavides MP, Gallego SM, Tomaro ML (2005) Cadmium toxicity in plants. Braz J Plant Physiol 17:21–34
Benbouza H, Jacquemin JM, Baudoin JP, Mergeai G (2006) Optimization of a reliable, fast, cheap and sensitive silver staining method to detect SSR markers in polyacrylamide gels. Biotechnol Agron Soc Environ 10:77–81
Cakmak I, Horst WJ (1991) Effect of aluminium on lipid peroxidation, superoxide dismutase, catalase, and peroxidase activities in root tips of soybean (Glycine max). Physiol Plant 83:463–468
Carreras HA, Pignata ML, Saldiva PHN (2006) In situ monitoring of urban air in Córdoba, Argentina using the Tradescantia-micronucleus (Trad-MCN) bioassay. Atmos Environ 40:7824–7830
Cenkci S, Yıldız M, Ciğerci İH, Konuk M, Bozdağ A (2009) Toxic chemicals-induced genotoxicity detected by random amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD) in bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) seedlings. Chemosphere 76:900–906
Ceretti E, Zani C, Zerbini I, Viola G, Moretti M, Villarini M, Dominici L, Monarca S, Feretti D (2015) Monitoring of volatile and non-volatile urban air genotoxins using bacteria, human cells and plants. Chemosphere 120:221–229
Čėsnienė T, Kleizaitė V, Ursache R, Žvingila D, Radzevičius A, Patamsytė J, Rančelis V (2010) Soil-surface genotoxicity of military and urban territories in Lithuania, as revealed by Tradescantia bioassays. Mutat Res 697:10–18
Čėsnienė T, Kleizaitė V, Rančelis V, Žvingila D, Švabauskas K, Taraškevičius R (2014) Use of Tradescantia clone 4430 for direct long-term soil mutagenicity studies. Mutat Res 768:23–32
Čėsnienė T, Kleizaitė V, Bondzinskaitė S, Taraškevičius R, Žvingila D, Šiukšta R, Rančelis V (2017) Metal bioaccumulation and mutagenesis in a Tradescantia clone following long-term exposure to soils from urban industrial areas and closed landfills. Mutat Res 823:65–72
Chao YY, Hong CY, Kao CH (2010) The decline in ascorbic acid content is associated with cadmium toxicity of rice seedlings. Plant Physiol Biochem 48:374–381
Chibuike GU, Obiora SC (2014) Heavy metal polluted soils: effect on plants and bioremediation methods. Appl Environ Soil Sci 2014:1–12
Chung E, Cho CW, So HA, Kang JS, Chung YS, Lee JH (2013) Overexpression of VrUBC1, a mung bean E2 ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme, enhances osmotic stress tolerance in Arabidopsis. PLoS One 8:e66056
Cotelle S, Masfaraud JF, Férard JF (1999) Assessment of the genotoxicity of contaminated soil with the Allium/Vicia-micronucleus and the Tradescantia-micronucleus assays. Mutat Res Mol Mech Mutagen 426:167–171
Dale MP, Causton DR (1992) Use of the chlorophyll a/b ratio as a bioassay for the light environment of a plant. Funct Ecol 6:190–196
Davis BJ (1964) Disc electrophoresis – ii method and application to human serum proteins. Ann N Y Acad Sci 121:404–427
de Souza RB, de Souza CP, Bueno OC, Fontanetti CS (2017) Genotoxicity evaluation of two metallic-insecticides using Allium cepa and Tradescantia pallida: a new alternative against leaf-cutting ants. Chemosphere 168:1093–1099
Dogan I, Ozyigit II, Tombuloglu G, Sakcali MS, Tombuloglu H (2016) Assessment of cd-induced genotoxic damage in Urtica pilulifera L. using RAPD-PCR analysis. Biotechnol Biotechnol Equip 30:284–291
Doyle JJ, Doyle JL (1990) Isolation of plant DNA from fresh tissue. Focus 12:13–15
El-Tayeb MA, El-Enany AE, Ahmed NL (2006) Salicylic acid-induced adaptive response to copper stress in sunflower Helianthus annuus L. Plant Growth Regul 50:191–199
Emamverdian A, Ding Y, Mokhberdoran F, Xie Y (2015) Heavy metal stress and some mechanisms of plant defense response. In: Sci. World J. https://www.hindawi.com/journals/tswj/2015/756120/. Accessed 16 Mar 2018
Erturk FA, Ay H, Nardemir G, Agar G (2013) Molecular determination of genotoxic effects of cobalt and nickel on maize (Zea mays L.) by RAPD and protein analyses. Toxicol Ind Health 29:662–671
Fryzova R, Pohanka M, Martinkova P, Cihlarova H, Brtnicky M, Hladky J, Kynicky J (2018) Oxidative stress and heavy metals in plants. Rev Environ Contam Toxicol 245:129–156
Gao Y, Wang Y, Xin H, Li S, Liang Z (2017) Involvement of ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme (E2 gene family) in ripening process and response to cold and heat stress of Vitis vinifera. Sci Rep 7:13290
Ghiani A, Fumagalli P, Nguyen Van T et al (2014) The combined toxic and genotoxic effects of cd and as to plant bioindicator Trifolium repens L. PLoS One 9:e99239
Gill SS, Tuteja N (2010) Reactive oxygen species and antioxidant machinery in abiotic stress tolerance in crop plants. Plant Physiol Biochem 48:909–930
Gill SS, Anjum NA, Gill R, Yadav S, Hasanuzzaman M, Fujita M, Mishra P, Sabat SC, Tuteja N (2015) Superoxide dismutase—mentor of abiotic stress tolerance in crop plants. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:10375–10394
Guo YY, Yu HY, Kong DS et al (2016) Effects of drought stress on growth and chlorophyll fluorescence of Lycium ruthenicum Murr. seedlings. Photosynthetica 54:524–531
Gupta DK, Sandalio LM (2012) Metal toxicity in plants: perception, signaling and remediation. Springer Berlin Heidelberg, Berlin, Heidelberg
Gupta DK, Corpas FJ, Palma JM (2013) Heavy metal stress in plants. Springer-Verlag, Berlin Heidelberg
Hakanson L (1980) An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control a sedimentological approach. Water Res 14:975–1001
Hammer Ø, Harper DAT, Ryan PD (2001) PAST: paleontological statistics software package for education and data analysis. Palaeontol Electron 4:5–7
Hasan MK, Cheng Y, Kanwar MK, Chu XY, Ahammed GJ, Qi ZY (2017) Responses of plant proteins to heavy metal stress – a review. Front Plant Sci 8:1492
Hossain MA, Bhattacharjee S, Armin SM et al (2015) Hydrogen peroxide priming modulates abiotic oxidative stress tolerance: insights from ROS detoxification and scavenging. Front Plant Sci 6:420
Houmani H, Rodríguez-Ruiz M, Palma JM, Abdelly C, Corpas FJ (2016) Modulation of superoxide dismutase (SOD) isozymes by organ development and high long-term salinity in the halophyte Cakile maritima. Protoplasma 253:885–894
Işeri ÖD, Körpe DA, Yurtcu E et al (2011) Copper-induced oxidative damage, antioxidant response and genotoxicity in Lycopersicum esculentum Mill. and Cucumis sativus L. Plant Cell Rep 30:1713. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-011-1079-x
Isidori M, Lavorgna M, Ruso C et al (2016) Chemical and toxicological characterisation of anticancer drugs in hospital and municipal wastewaters from Slovenia and Spain. Environ Pollut 219:275–287
Islam F, Yasmeen T, Arif MS, Riaz M, Shahzad SM, Imran Q, Ali I (2016) Combined ability of chromium (Cr) tolerant plant growth promoting bacteria (PGPB) and salicylic acid (SA) in attenuation of chromium stress in maize plants. Plant Physiol Biochem 108:456–467
Juknys R, Vitkauskaitė G, Račaitė M, Venclovienė J (2012) The impacts of heavy metals on oxidative stress and growth of spring barley. Cent Eur J Biol 7:299–306
Kalavrouziotis IK, Koukoulakis PH, Papadopoulos AH (2009) Heavy metal interrelationships in soil in the presence of treated waste water. Global Nest J 11:497–509
Kasajima I (2017) Difference in oxidative stress tolerance between rice cultivars estimated with chlorophyll fluorescence analysis. BMC Res Notes 10:168
Khanna-Chopra R, Semwal VK (2011) Superoxide dismutase and ascorbate peroxidase are constitutively more thermotolerant than other antioxidant enzymes in Chenopodium album. Physiol Mol Biol Plants 17:339–346
Khosrovyan A, DelValls TA, Riba I (2014) Effects of simulated CO2 escape from sediments on the development of midge Chironomus riparius. Aquat Toxicol 156:230–239
Kitajima K, Hogan KP (2003) Increases of chlorophyll a/b ratios during acclimation of tropical woody seedlings to nitrogen limitation and high light. Plant Cell Environ 26:857–865
Knasmüller S, Gottmann E, Steinkellner H, Fomin A, Pickl C, Paschke A, Göd R, Kundi M (1998) Detection of genotoxic effects of heavy metal contaminated soils with plant bioassays. Mutat Res 420:37–48
Kong F, Zhou Y, Sun P, Cao M, Li H, Mao Y (2016) Identification of light-harvesting chlorophyll a/b-binding protein genes of Zostera marina L. and their expression under different environmental conditions. J Ocean Univ China 15:152–162
Kumar D, Chapagai D, Dean P, Davenport M (2015) Biotic and abiotic stress signaling mediated by salicylic acid. In: elucidation of abiotic stress signaling in plants. Springer, New York, pp 329–346
Kumpiene J, Brännvall E, Taraškevičius R, Aksamitauskas Č, Zinkutė R (2011) Spatial variability of topsoil contamination with trace elements in preschools in Vilnius, Lithuania. J Geochem Explor 108:15–20
Liu W, Li PJ, Qi XM, Zhou QX, Zheng L, Sun TH, Yang YS (2005) DNA changes in barley (Hordeum vulgare) seedlings induced by cadmium pollution using RAPD analysis. Chemosphere 61:158–167
Liu W, Yang YS, Zhou Q, Xie L, Li P, Sun T (2007) Impact assessment of cadmium contamination on rice (Oryza sativa L.) seedlings at molecular and population levels using multiple biomarkers. Chemosphere 67:1155–1163
Luna CM, González CA, Trippi VS (1994) Oxidative damage caused by an excess of copper in oat leaves. Plant Cell Physiol 35:11–15
Ma TH (1981) Tradescantia micronucleus bioassay and pollen tube chromatid aberration test for in situ monitoring and mutagen screening. Environ Health Perspect 37:85–90
Ma TH, Cabrera GL, Chen R, Gill BS, Sandhu SS, Vandenberg AL, Salamone MF (1994) Tradescantia micronucleus bioassay. Mutat Res 310:221–230
Ma TH, Xu C, Liao S et al (1996) In situ monitoring with the Tradescantia bioassays on the genotoxicity of gaseous emissions from a closed landfill site and an incinerator. Mutat Res 359:39–52
Majer BJ, Tscherko D, Paschke A, Wennrich R, Kundi M, Kandeler E, Knasmüller S (2002) Effects of heavy metal contamination of soils on micronucleus induction in Tradescantia and on microbial enzyme activities: a comparative investigation. Mutat Res 515:111–124
Maleki M, Ghorbanpour M, Kariman K (2017) Physiological and antioxidative responses of medicinal plants exposed to heavy metals stress. Plant Gene 11:247–254
Manios T, Stentiford EI, Millner PA (2003) The effect of heavy metals accumulation on the chlorophyll concentration of Typha latifolia plants, growing in a substrate containing sewage sludge compost and watered with metaliferus water. Ecol Eng 20:65–74
Marcato-Romain CE, Pinelli E, Pourrut B, Silvestre J, Guiresse M (2009) Assessment of the genotoxicity of Cu and Zn in raw and anaerobically digested slurry with the Vicia faba micronucleus test. Mutat Res 672:113–118
Mielli AC, Matta MEM, Nersesyan A, Saldiva PHN, Umbuzeiro GA (2009) Evaluation of the genotoxicity of treated urban sludge in the Tradescantia micronucleus assay. Mutat Res 672:51–54
Minocha R, Martinez G, Lyons B, Long S (2009) Development of a standardized methodology for quantifying total chlorophyll and carotenoids from foliage of hardwood and conifer tree species. Can J For Res 39:849–861
Mišík M, Ma TH, Nersesyan A et al (2011) Micronucleus assays with Tradescantia pollen tetrads: an update. Mutagenesis 26:215–221
Mitsui A, Ohta T (1961) Photooxidative consumption and photoreductive formation of ascorbic acid in green leaves. Plant Cell Physiol 2:31–44
Namdjoyan S, Kermanian H, Soorki AA et al (2017) Interactive effects of salicylic acid and nitric oxide in alleviating zinc toxicity of Safflower Carthamus tinctorius L. Ecotoxicology 26:752–761
Nei M, Li WH (1979) Mathematical model for studying genetic variation in terms of restriction endonucleases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 76:5269–5273
Netto AT, Campostrini E, de JG O, Bressan-Smith RE (2005) Photosynthetic pigments, nitrogen, chlorophyll a fluorescence and SPAD-502 readings in coffee leaves. Sci Hortic 104:199–209. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2004.08.013
Niu L, Liao W (2016) Hydrogen peroxide signaling in plant development and abiotic responses: crosstalk with nitric oxide and calcium. Front Plant Sci 7:230
Pandey C, Gupta M (2015) Selenium and auxin mitigates arsenic stress in rice (Oryza sativa L.) by combining the role of stress indicators, modulators and genotoxicity assay. J Hazard Mater 287:384–391
Patnaik AR, Achary VMM, Panda BB (2013) Chromium (VI)-induced hormesis and genotoxicity are mediated through oxidative stress in root cells of Allium cepa L. Plant Growth Regul 71:157–170
Pereira BB, de EO C Jr, Morelli S (2013) In situ biomonitoring of the genotoxic effects of vehicular pollution in Uberlandia, Brazil, using a Tradescantia micronucleus assay. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 87:17–22
Prasad KVS, Paradha Saradhi P, Sharmila P (1999) Concerted action of antioxidant enzymes and curtailed growth under zinc toxicity in Brassica juncea. Environ Exp Bot 42:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0098-8472(99)00013-1
Procházková D, Wilhelmová N, Pavlíková D, Száková J, Gichner T (2013) Zinc induces DNA damage in tobacco roots. Biol Plant 57:783–787
Rabhi M, Castagna A, Remorini D, Scattino C, Smaoui A, Ranieri A, Abdelly C (2012) Photosynthetic responses to salinity in two obligate halophytes: Sesuvium portulacastrum and Tecticornia indica. S Afr J Bot 79:39–47
Rodriguez E, Azevedo R, Fernandes P, Santos C (2011) Cr(VI) induces DNA damage, cell cycle arrest and polyploidization: a flow cytometric and comet assay study in Pisum sativum. Chem Res Toxicol 24:1040–1047
Rodriguez E, Azevedo R, Moreira H, Souto L, Santos C (2013) Pb2+ exposure induced microsatellite instability in Pisum sativum in a locus related with glutamine metabolism. Plant Physiol Biochem 62:19–22
Rout NP, Shaw BP (2001) Salt tolerance in aquatic macrophytes: ionic relation and interaction. Biol Plant 44:95–99
Sahu GK, Upadhyay S, Sahoo BB (2012) Mercury induced phytotoxicity and oxidative stress in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) plants. Physiol Mol Biol Plants 18:21–31
Schützendübel A, Polle A (2002) Plant responses to abiotic stresses: heavy metal-induced oxidative stress and protection by mycorrhization. J Exp Bot 53:1351–1365
Shahid M, Pourrut B, Dumat C et al (2014) Heavy-metal-induced reactive oxygen species: phytotoxicity and physicochemical changes in plants. In: Reviews of environmental contamination and toxicology volume 232. Springer, Cham, pp 1–44
Shakirova FM, Allagulova CR, Maslennikova DR, Klyuchnikova EO, Avalbaev AM, Bezrukova MV (2016) Salicylic acid-induced protection against cadmium toxicity in wheat plants. Environ Exp Bot 122:19–28
Shakya K, Chettri MK, Sawidis T (2008) Impact of heavy metals (copper, zinc, and lead) on the chlorophyll content of some mosses. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 54:412–421
Shaw BP, Rout NP (1998) Age-dependent responses of Phaseolus aureus to inorganic salts of mercury and cadmium. Acta Physiol Plant 20:85–90
Shen Y, Zhang Y, Chen J, Lin H, Zhao M, Peng H, Liu L, Yuan G, Zhang S, Zhang Z, Pan G (2013) Genome expression profile analysis reveals important transcripts in maize roots responding to the stress of heavy metal Pb. Physiol Plant 147:270–282
Singh S, Eapen S, D’Souza SF (2006) Cadmium accumulation and its influence on lipid peroxidation and antioxidative system in an aquatic plant, Bacopa monnieri L. Chemosphere 62:233–246
Singh M, Kumar J, Singh S et al (2015) Adaptation strategies of plants against heavy metal toxicity: a short review. Biochem Pharmacol 4:161
Sinha V, Pakshirajan K, Chaturvedi R (2014) Chromium (VI) accumulation and tolerance by Tradescantia pallida: biochemical and antioxidant study. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 173:2297–2306
Šiukšta R, Vaitkūnienė V, Rančelis V (2018) Is auxin involved in the induction of genetic instability in barley homeotic double mutants? Planta 247:483–498
Soydam Aydin S, Gökçe E, Büyük İ, Aras S (2012) Characterization of stress induced by copper and zinc on cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.) seedlings by means of molecular and population parameters. Mutat Res 746:49–55
Sposito JCV, Crispim B do A, Romãn AI et al (2017) Evaluation the urban atmospheric conditions in different cities using comet and micronuclei assay in Tradescantia pallida. Chemosphere 175:108–113
Steinkellner H, Mun-Sik K, Helma C, Ecker S, Ma TH, Horak O, Kundi M, Knasmüller S (1998) Genotoxic effects of heavy metals: comparative investigation with plant bioassays. Environ Mol Mutagen 31:183–191
Taspinar MS, Agar G, Alpsoy L, Yildirim N, Bozari S, Sevsay S (2011) The protective role of zinc and calcium in Vicia faba seedlings subjected to cadmium stress. Toxicol Ind Health 27:73–80
Uzilday B, Ozgur R, Sekmen AH, Turkan I (2015) Redox regulation and antioxidant defence during abiotic stress: what have we learned from Arabidopsis and its relatives? In: Reactive oxygen species and oxidative damage in plants under stress. Springer, Cham, pp 83–113
Van de Peer Y, De Wachter R (1994) TREECON for windows: a software package for the construction and drawing of evolutionary trees for the Microsoft Windows environment. Comput Appl Biosci 10:569–570
Velikova V, Loreto F (2005) On the relationship between isoprene emission and thermotolerance in Phragmites australis leaves exposed to high temperatures and during the recovery from a heat stress. Plant Cell Environ 28:318–327
Viehweger K (2014) How plants cope with heavy metals. Bot Stud 55:35
Wu FB, Chen F, Wei K, Zhang GP (2004) Effect of cadmium on free amino acid, glutathione and ascorbic acid concentrations in two barley genotypes (Hordeum vulgare L.) differing in cadmium tolerance. Chemosphere 57:447–454
Xie Y, Ye S, Wang Y et al (2015) Transcriptome-based gene profiling provides novel insights into the characteristics of radish root response to Cr stress with next-generation sequencing. Front Plant Sci 6:202
Xu ZQ, Ni SJ, Tuo XG, Zhang CJ (2008) Calculation of heavy metals’ toxicity coefficient in the evaluation of potential ecological risk index. Environ Sci Technol 31:112–115
Xu YH, Liu R, Yan L, Liu ZQ, Jiang SC, Shen YY, Wang XF, Zhang DP (2012) Light-harvesting chlorophyll a/b-binding proteins are required for stomatal response to abscisic acid in Arabidopsis. J Exp Bot 63:1095–1106
Yuan Z, Yao J, Wang F, Guo Z, Dong Z, Chen F, Hu Y, Sunahara G (2017) Potentially toxic trace element contamination, sources, and pollution assessment in farmlands, Bijie City, southwestern China. Environ Monit Assess 189:25
Zengin FK, Munzuroglu O (2005) Effects of some heavy metals on content of chlorophyll, proline and some antioxidant chemicals in bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) seedlings. Acta Biol Crac Ser Bot 47:157–164
Zhiguo E, Zhang Y, Li T et al (2015) Characterization of the ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme gene family in rice and evaluation of expression profiles under abiotic stresses and hormone treatments. PLoS One 10:e0122621
Zhou ZS, Guo K, Elbaz AA, Yang ZM (2009) Salicylic acid alleviates mercury toxicity by preventing oxidative stress in roots of Medicago sativa. Environ Exp Bot 65:27–34
Zhou GA, Chang RZ, Qiu LJ (2010) Overexpression of soybean ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme gene GmUBC2 confers enhanced drought and salt tolerance through modulating abiotic stress-responsive gene expression in Arabidopsis. Plant Mol Biol 72:357–367
Zinkutė R, Baltrūnas V, Taraškevičius R et al (2015) Quaternary interglacial sediments as possible natural sources of arsenic and molybdenum anomalies in stream sediments in Lithuania. J Environ Eng Landsc Manag 23:60–70
Funding
This work was supported by a grant from the Lithuanian Research Council MIP-042/2015.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
TČ and RŠ conceived and designed the experiments. RŠ, VK, SB, RT, LM, KM, and TČ conducted the experiments. RŠ, TČ, VK, and AS analyzed the data. RŠ, TČ, VK, DŽ, and AS wrote the paper.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Electronic supplementary material
Table S1
(DOCX 15 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Šiukšta, R., Bondzinskaitė, S., Kleizaitė, V. et al. Response of Tradescantia plants to oxidative stress induced by heavy metal pollution of soils from industrial areas. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26, 44–61 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-3224-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-3224-3