Purpose
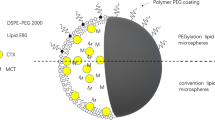
Pegylated and nonpegylated cetyl alcohol/polysorbate nanoparticles (E78 NPs) are being tested as drug carriers for specific tumor and brain targeting. Because these nanoparticle formulations are designed for systemic administration, it is important to test the compatibility of these lipid-based NPs with blood and blood cells.
Methods
The hemocompatibility of E78 NPs was evaluated with a particular focus on hemolytic activity, platelet function, and blood coagulation. Human red blood cell lysis was determined by measuring hemoglobin release. Activation and aggregation of human platelets were determined using flow cytometry and aggregometry, respectively. Finally, the whole blood clotting time was measured using human blood.
Results
E78 NPs did not cause in vitro red blood cell lysis at concentrations up to 1 mg/mL. In addition, under conditions tested, E78 and polyethylene glycol (PEG)-coated E78 NPs (PEG-E78 NPs) did not activate platelets. In fact, both NP formulations very rapidly inhibited agonist-induced platelet activation and aggregation in a dose-dependent manner. Additionally, E78 NPs significantly prolonged in vitro whole blood clotting time at a concentration of 500 μg/mL or greater.
Conclusions
It was concluded that PEG-coated and nonpegylated E78 NPs have potential blood compatibility at clinically relevant doses. Based on the calculated nanoparticle-to-platelet ratio, the concentration at which E78 NPs could potentially affect platelet function in vivo was approximately 1 mg/mL.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. Kreuter (1996) ArticleTitleNanoparticles and microparticles for drug and vaccine delivery J. Anat. 189 IssueIDPt 3 503–505 Occurrence Handle8982823
P. R. Lockman R. J. Mumper M. A. Khan D. D. Allen (2002) ArticleTitleNanoparticle technology for drug delivery across the blood–brain barrier Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 28 1–13 Occurrence Handle10.1081/DDC-120001481 Occurrence Handle11858519
A. K. Gupta M. Gupta (2005) ArticleTitleSynthesis and surface engineering of iron oxide nanoparticles for biomedical applications Biomaterials 26 3995–4021 Occurrence Handle10.1016/j.biomaterials.2004.10.012 Occurrence Handle15626447
A. K. Gupta A. S. Curtis (2004) ArticleTitleSurface modified superparamagnetic nanoparticles for drug delivery: interaction studies with human fibroblasts in culture J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 15 493–496 Occurrence Handle10.1023/B:JMSM.0000021126.32934.20 Occurrence Handle15332623
A. Brownlie I. F. Uchegbu A. G. Schatzlein (2004) ArticleTitlePEI-based vesicle-polymer hybrid gene delivery system with improved biocompatibility Int. J. Pharm. 274 41–52 Occurrence Handle10.1016/j.ijpharm.2003.12.029 Occurrence Handle15072781
I. Constantinescu E. Levin M. Gyongyossy-Issa (2003) ArticleTitleLiposomes and blood cells: a flow cytometric study Artif. Cells Blood Substit. Immobil. Biotechnol. 31 395–424 Occurrence Handle10.1081/BIO-120025410 Occurrence Handle14672416
R. L. Juliano M. J. Hsu D. Peterson S. L. Regen A. Singh (1983) ArticleTitleInteractions of conventional or photopolymerized liposomes with platelets in vitro Exp. Cell Res. 146 422–427 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0014-4827(83)90144-1 Occurrence Handle6873198
R. Male W. E. Vannier J. D. Baldeschwieler (1992) ArticleTitlePhagocytosis of liposomes by human platelets Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 89 9191–9195 Occurrence Handle1409624
L. W. Reinish M. B. Bally H. C. Loughrey P. R. Cullis (1988) ArticleTitleInteractions of liposomes and platelets Thromb. Haemost. 60 518–523 Occurrence Handle3238654
G. Zbinden H. Wunderli-Allenspach L. Grimm (1989) ArticleTitleAssessment of thrombogenic potential of liposomes Toxicology 54 273–280 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0300-483X(89)90063-2 Occurrence Handle2705196
L. M. Pinto R. Pereira E. Paula Particlede G. Nucci Particlede M. H. Santana J. L. Donato (2004) ArticleTitleInfluence of liposomal local anesthetics on platelet aggregation in vitro J. Liposome Res. 14 51–59 Occurrence Handle10.1081/LPR-120039697 Occurrence Handle15461932
M. Miyamoto S. Sasakawa T. Ozawa H. Kawaguchi Y. Ohtsuka (1989) ArticleTitlePlatelet aggregation induced by latex particles. I. Effects of size, surface potential and hydrophobicity of particles Biomaterials 10 251–257 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0142-9612(89)90101-4 Occurrence Handle2500991
M. Miyamoto S. Sasakawa T. Ozawa H. Kawaguchi Y. Ohtsuka (1990) ArticleTitleMechanisms of blood coagulation induced by latex particles and the roles of blood cells Biomaterials 11 385–388 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0142-9612(90)90091-4 Occurrence Handle2207226
J. M. Koziara P. R. Lockman D. D. Allen R. J. Mumper (2003) ArticleTitleIn situ blood–brain barrier transport of nanoparticles Pharm. Res. 20 1772–1778 Occurrence Handle10.1023/B:PHAM.0000003374.58641.62 Occurrence Handle14661921
J. M. Koziara P. R. Lockman D. D. Allen R. J. Mumper (2004) ArticleTitlePaclitaxel nanoparticles for the potential treatment of brain tumors J. Control. Release 99 259–269 Occurrence Handle10.1016/j.jconrel.2004.07.006 Occurrence Handle15380635
P. R. Lockman J. M. Koziara R. J. Mumper D. D. Allen (2004) ArticleTitleNanoparticle surface charges alter blood–brain barrier integrity and permeability J. Drug Target. 12 635–641 Occurrence Handle10.1080/10611860400015936 Occurrence Handle15621689
M. O. Oyewumi R. A. Yokel M. Jay T. Coakley R. J. Mumper (2004) ArticleTitleComparison of cell uptake, biodistribution and tumor retention of folate-coated and PEG-coated gadolinium nanoparticles in tumor-bearing mice J. Control. Release 95 613–626 Occurrence Handle10.1016/j.jconrel.2004.01.002 Occurrence Handle15023471
M. O. Oyewumi R. J. Mumper (2002) ArticleTitleGadolinium-loaded nanoparticles engineered from microemulsion templates Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 28 317–328 Occurrence Handle10.1081/DDC-120002847 Occurrence Handle12026224
S. Shalel S. Streichman A. Marmur (2002) ArticleTitleThe mechanism of hemolysis by surfactants: effect of solution composition J. Colloid Interface Sci. 252 66–76 Occurrence Handle10.1006/jcis.2002.8474
C. Chouly L. Bordenave R. Bareille V. Guerin A. Baquey D. Pouliquen C. Baquey P. Jallet (1994) ArticleTitleIn vitro study of the hemocompatibility of superparamagnetic contrast agent for magnetic resonance imaging Clin. Mater. 15 293–301 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0267-6605(94)90061-2 Occurrence Handle10147174
C. M. Jackson Y. Nemerson (1980) ArticleTitleBlood coagulation Annu. Rev. Biochem. 49 765–811 Occurrence Handle10.1146/annurev.bi.49.070180.004001 Occurrence Handle6996572
T. Matsuda H. Takano Y. Taenaka K. Hayashi T. Nakamura (1981) ArticleTitleRole of surface charge on blood coagulation Polym. Preprints Jpn. 30 1668–1671
A. L. Colpey (1977) Platelets and physiological defense mechanism G. Gaetano S. Garattini (Eds) Platelets. A Multidisciplinary Approach Raven Press New York 161–197
Y. Ozaki (1998) ArticleTitleMeasurements of platelet aggregation and attempts for standardization Sysmex J. Int. 8 15–22
F. Ahmed P. Alexandridis H. Shankaran S. Neelamegham (2001) ArticleTitleThe ability of poloxamers to inhibit platelet aggregation depends on their physicochemical properties Thromb. Haemost. 86 1532–1539 Occurrence Handle11776324
R. Gref M. Luck P. Quellec M. Marchand E. Dellacherie S. Harnisch T. Blunk R. H. Muller (2000) ArticleTitle‘Stealth’ corona-core nanoparticles surface modified by polyethylene glycol (PEG): influences of the corona (PEG chain length and surface density) and of the core composition on phagocytic uptake and plasma protein adsorption Colloids Surf., B Biointerfaces 18 301–313
H. Otsuka Y. Nagasaki K. Kataoka (2003) ArticleTitlePEGylated nanoparticles for biological and pharmaceutical applications Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 55 403–419 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0169-409X(02)00226-0 Occurrence Handle12628324
D. Bazile C. Prud'homme M. T. Bassoullet M. Marlard G. Spenlehauer M. Veillard (1995) ArticleTitleStealth Me.PEG-PLA nanoparticles avoid uptake by the mononuclear phagocytes system J. Pharm. Sci. 84 493–498 Occurrence Handle7629743
H. Fujii S. Fujii H. Togashi M. Yoshioka K. Nakai H. Satoh I. Sakuma O. Kenmotsu A. Kitabatake (2000) ArticleTitleAttenuation of hypothermia-induced platelet activation and platelet adhesion to artificial surfaces in vitro by modification of hemoglobin to carry S-nitric oxide and polyethylene glycol Thromb. Res. 100 519–528 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0049-3848(00)00364-9 Occurrence Handle11152932
M. Amiji K. Park (1993) ArticleTitleSurface modification of polymeric biomaterials with poly(ethylene oxide), albumin, and heparin for reduced thrombogenicity J. Biomater. Sci., Polym. Ed. 4 217–234
C. Pan J. Wang H. Sun P. Yang Y. Leng J. Chen G. Wan N. Huang (2004) ArticleTitleResearch of plasma adsorption and action of platelet adhesion of Dacron modified by plasma surface modification Sheng Wu Yi Xue Gong Cheng Xue Za Zhi 21 536–540 Occurrence Handle15357426
J. E. Burchenal C. R. Deible T. E. Deglau A. J. Russell E. J. Beckman W. R. Wagner (2002) ArticleTitlePolyethylene glycol diisocyanate decreases platelet deposition after balloon injury of rabbit femoral arteries J. Thromb. Thrombolysis 13 27–33 Occurrence Handle10.1023/A:1015364024487 Occurrence Handle11994557
R. Male D. G. Moon J. S. Garvey W. E. Vannier J. D. Baldeschwieler (1993) ArticleTitleOrgan distributions of liposome-loaded rat platelets Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 195 276–281 Occurrence Handle10.1006/bbrc.1993.2041 Occurrence Handle8363608
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Koziara, J.M., Oh, J.J., Akers, W.S. et al. Blood Compatibility of Cetyl Alcohol/Polysorbate-Based Nanoparticles. Pharm Res 22, 1821–1828 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11095-005-7547-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11095-005-7547-7