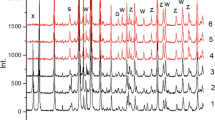
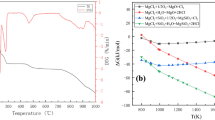
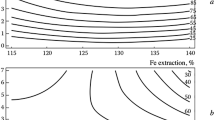
Abstract
Rhenium production from copper and molybdenum sulphides involves the use of a pyrometallurgical process. In traditional pyrometallurgy processes, gases emissions produce unacceptable air pollution and damage the extractive metallurgy equipment, leading to high production cost. Due to the environmental disadvantages presented by the oxidizing roasting, in this paper the carbothermal reduction process application on molybdenum–copper sulphides with Re, is studied as a possible alternative. The main purpose of the study is to concentrate the element (Re) applying non-traditional process, with low operating costs and good environmental response avoiding polluting gases such as SO2. The concentrates were previously treated by an alkaline leaching process to remove impurities such as As, Se and Sb. These impurities are penalized and in addition they produce a calcine that is inefficient from an economic and a production point of view. The traditional production of Re involves Re oxide volatilization during the molybdenite processing, which is then condensed at low temperature to generate a dilute solution of a Re compound. The results show that Re was collected as metallic Re and in a form of a carbide compound avoiding Re2O7 volatilization and reducing total gases emissions in ≈ 36%.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hosseinzadeh M, Ranjbar M, Alizadeh M. Effect of operational parameters and internal recycle on rhenium solvent extraction from leach liquors using a mixer-settler. Eng Sci Technol Int J. 2014;17:45–9.
Braga PFA. Characterization and processing of molybdenite in the region of Campo Formoso, Bahia. Ph.D. thesis, Escuela Politécnica de la Universidad de Sao Paulo; 2013.
Bazán V, Sarquis P, Brandaleze E, Orozco I. Characterization of the Argentine copper concentrates to evaluate the possibility of a pirometallurgy industry, Ingeniare. Rev Chil Ing. 2010;18(3):343–9.
Tintayaa WQ, Chandraa D, Jahangira A, Harrisb M, Casadevalla A, Dadachovab E, Gravekampa C. Nontoxic radioactive listeria is a highly effective therapy against metastatic pancreatic cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA PNAS. 2013;110(21):8668–73.
Naumov AV. Rhythms of rhenium. Russ J Nonferrous Met. 2007;48(6):418–23.
Xie GW, Li MM, Yang YW. The development and applications of the dust and rhenium recovery integrated device of calcination exhaust of molybdenum concentrate which contain rhenium. Adv Mater Res. 2013;753(755):40–3.
Bazán V, Brandaleze E, Santini L, Sarquis P. Argentinean copper concentrates: structural aspects and thermal behaviour. Int J Nonferrous Metall. 2013;2:128–35.
Zhao Y, Hou Y, Cui Y, Liang H, Li L. Recovery of copper from copper sulphide concentrate by sulfation roasting. Int J Nonferrous Metall. 2015;4:9–13.
Kar BB. Carbothermic reduction of hydro-refining spent catalyst to extract molybdenum. Int J Miner Process. 2005;75:249–53.
Bale CW, Bélisle E, Chartrand P, Degterov SA, Eriksson G, Gheribi AE, Hack K, Jung IH, Kang YB, Melançon AD, Pelton AD, Petersen S, Robelin C, Sangster J, Spencer P, Van Ende MA. FactSage thermochemical software and databases—2010–2016. CALPHAD: Comput Coupling Phase Diagrams Thermochem. 2016;54:35–53.
Wang Y, Fan L, Yan B, Fan T, Xu M, Gong H. Kinetic study on preparation of substoichiometric titanium oxide via carbothermal process. J Ther Anal Calorim. 2015;122:635–44.
Aydinyan SV, Kiraskosyan HV, Niazyan OM, Kharatyan SL. DTA/TGA study of copper molybdate carbothermal reduction. Chem J Armen. 2015;68(2):196–206.
Juneja JM, Singh S, Bose DK. Investigations on the extraction of molybdenum and rhenium values from low grade molybdenite concentrate. Hydrometallurgy. 1996;41:201–9.
Drábek M, Stein H. Molybdenite Re–Os dating of Mo–Th–Nb–REE rich marbles: pre-Variscan processes in Moldanubian Variegated Group (Czech Republic). Geol Carpath. 2015;66(3):173–9.
Wang LY, Dong J, Cai J. Study on mechanism of molybdenum concentrate roasting. Adv Mater Res. 2012;455–456:60–4.
Bale CW, Chartrand P, Degterov SA, Eriksson G, Hack K, Ben Mahfoud R, Melançon AD, Pelton AD, Petersen S. FactSage thermochemical software and databases. CALPHAD: Comput Coupling Phase Diagrams Thermochem. 2002;26(2):189–228.
Pelton AD. Thermodynamic database development—modeling and phase diagram calculations in oxide systems. Rare Met. 2006;25(5):473–80.
Bale CW, Bélisle E, Chartrand P, Degterov SA, Eriksson G, Hack K, Jung IH, Kang YB, Melançon AD, Pelton AD, Robelina C, Petersen S. FactSage thermochemical software and databases—recent developments. CALPHAD: Comput Coupling Phase Diagrams Thermochem. 2009;33:295–311.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Brandaleze, E., Bazán, V., Orozco, I. et al. Application of thermal analysis to the rhenium recovery process from copper and molybdenum sulphides minerals. J Therm Anal Calorim 133, 435–441 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-018-7104-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-018-7104-3