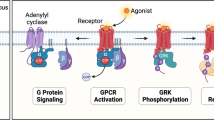
Abstract
Catecholamines and other transmitters released from adrenal chromaffin cells play central roles in the “fight-or-flight” response and exert profound effects on cardiovascular, endocrine, immune, and nervous system function. As such, precise regulation of chromaffin cell exocytosis is key to maintaining normal physiological function and appropriate responsiveness to acute stress. Chromaffin cells express a number of different G protein coupled receptors (GPCRs) that sense the local environment and orchestrate this precise control of transmitter release. The primary trigger for catecholamine release is Ca2+ entry through voltage-gated Ca2+ channels, so it makes sense that these channels are subject to complex regulation by GPCRs. In particular G protein βγ heterodimers (Gβγ) bind to and inhibit Ca2+ channels. Here I review the mechanisms by which GPCRs inhibit Ca2+ channels in chromaffin cells and how this might be altered by cellular context. This is related to the potent autocrine inhibition of Ca2+ entry and transmitter release seen in chromaffin cells. Recent data that implicate an additional inhibitory target of Gβγ on the exocytotic machinery and how this might fine tune neuroendocrine secretion are also discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albillos A, Carbone E, Gandia L, Garcia AG, Pollo A (1996a) Opioid inhibition of Ca2+ channel subtypes in bovine chromaffin cells: selectivity of action and voltage-dependence. Eur J Neurosci 8:1561–1570
Albillos A, Gandia L, Michelena P, Gilabert JA, del Valle M, Carbone E, Garcia AG (1996b) The mechanism of calcium channel facilitation in bovine chromaffin cells. J Physiol 494(Pt 3):687–695
Altier C, Khosravani H, Evans RM, Hameed S, Peloquin JB, Vartian BA, Chen L, Beedle AM, Ferguson SS, Mezghrani A, Dubel SJ, Bourinet E, McRory JE, Zamponi GW (2006) ORL1 receptor-mediated internalization of N-type calcium channels. Nat Neurosci 9:31–40
Alvarez YD, Ibanez LI, Uchitel OD, Marengo FD (2008) P/Q Ca2+ channels are functionally coupled to exocytosis of the immediately releasable pool in mouse chromaffin cells. Cell Calcium 43:155–164
Artalejo CR, Ariano MA, Perlman RL, Fox AP (1990) Activation of facilitation calcium channels in chromaffin cells by D1 dopamine receptors through a cAMP/protein kinase A-dependent mechanism. Nature 348:239–242
Artalejo CR, Adams ME, Fox AP (1994) Three types of Ca2+ channel trigger secretion with different efficacies in chromaffin cells. Nature 367:72–76
Bai J, Wang CT, Richards DA, Jackson MB, Chapman ER (2004) Fusion pore dynamics are regulated by synaptotagmin*t-SNARE interactions. Neuron 41:929–942
Bauer CS, Woolley RJ, Teschemacher AG, Seward EP (2007) Potentiation of exocytosis by phospholipase C-coupled G-protein-coupled receptors requires the priming protein Munc13-1. J Neurosci 27:212–219
Bean BP (1989) Neurotransmitter inhibition of neuronal calcium currents by changes in channel voltage dependence. Nature 340:153–156
Blackmer T, Larsen EC, Bartleson C, Kowalchyk JA, Yoon EJ, Preininger AM, Alford S, Hamm HE, Martin TF (2005) G protein betagamma directly regulates SNARE protein fusion machinery for secretory granule exocytosis. Nat Neurosci 8:421–425
Boarder MR, Marriott D, Adams M (1987) Stimulus secretion coupling in cultured chromaffin cells. Dependency on external sodium and on dihydropyridine-sensitive calcium channels. Biochem Pharmacol 36:163–167
Brede M, Nagy G, Philipp M, Sorensen JB, Lohse MJ, Hein L (2003) Differential control of adrenal and sympathetic catecholamine release by alpha 2-adrenoceptor subtypes. Mol Endocrinol 17:1640–1646
Brody DL, Patil PG, Mulle JG, Snutch TP, Yue DT (1997) Bursts of action potential waveforms relieve G-protein inhibition of recombinant P/Q-type Ca2+ channels in HEK 293 cells. J Physiol 499(Pt 3):637–644
Carabelli V, Lovallo M, Magnelli V, Zucker H, Carbone E (1996) Voltage-dependent modulation of single N-type Ca2+ channel kinetics by receptor agonists in IMR32 cells. Biophys J 70:2144–2154
Carabelli V, Giancippoli A, Baldelli P, Carbone E, Artalejo AR (2003) Distinct potentiation of L-type currents and secretion by cAMP in rat chromaffin cells. Biophys J 85:1326–1337
Carabelli V, Marcantoni A, Comunanza V, de Luca A, Diaz J, Borges R, Carbone E (2007) Chronic hypoxia up-regulates alpha1H T-type channels and low-threshold catecholamine secretion in rat chromaffin cells. J Physiol 584:149–165
Catterall WA (2000) Structure and regulation of voltage-gated Ca2+ channels. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 16:521–555
Catterall WA, Few AP (2008) Calcium channel regulation and presynaptic plasticity. Neuron 59:882–901
Chan SA, Polo-Parada L, Smith C (2005) Action potential stimulation reveals an increased role for P/Q-calcium channel-dependent exocytosis in mouse adrenal tissue slices. Arch Biochem Biophys 435:65–73
Chapman ER (2008) How does synaptotagmin trigger neurotransmitter release? Annu Rev Biochem 77:615–641
Chen XK, Wang LC, Zhou Y, Cai Q, Prakriya M, Duan KL, Sheng ZH, Lingle C, Zhou Z (2005) Activation of GPCRs modulates quantal size in chromaffin cells through G(betagamma) and PKC. Nat Neurosci 8:1160–1168
Colecraft HM, Patil PG, Yue DT (2000) Differential occurrence of reluctant openings in G-protein-inhibited N- and P/Q-type calcium channels. J Gen Physiol 115:175–192
Cooper CB, Arnot MI, Feng ZP, Jarvis SE, Hamid J, Zamponi GW (2000) Cross-talk between G-protein and protein kinase C modulation of N-type calcium channels is dependent on the G-protein beta subunit isoform. J Biol Chem 275:40777–40781
Currie KPM, Fox AP (1996) ATP serves as a negative feedback inhibitor of voltage-gated Ca2+ channel currents in cultured bovine adrenal chromaffin cells. Neuron 16:1027–1036
Currie KPM, Fox AP (1997) Comparison of N- and P/Q-type voltage-gated calcium channel current inhibition. J Neurosci 17:4570–4579
Currie KP, Fox AP (2000) Voltage-dependent, pertussis toxin insensitive inhibition of calcium currents by histamine in bovine adrenal chromaffin cells. J Neurophysiol 83:1435–1442
Currie KPM, Fox AP (2002) Differential facilitation of N- and P/Q-type calcium channels during trains of action potential-like waveforms. J Physiol 539:419–431
Davies A, Hendrich J, Van Minh AT, Wratten J, Douglas L, Dolphin AC (2007) Functional biology of the alpha(2)delta subunits of voltage-gated calcium channels. Trends Pharmacol Sci 28:220–228
De Waard M, Liu H, Walker D, Scott VE, Gurnett CA, Campbell KP (1997) Direct binding of G-protein betagamma complex to voltage-dependent calcium channels. Nature 385:446–450
de Wit H, Walter AM, Milosevic I, Gulyas-Kovacs A, Riedel D, Sorensen JB, Verhage M (2009) Synaptotagmin-1 docks secretory vesicles to syntaxin-1/SNAP-25 acceptor complexes. Cell 138:935–946
Diverse-Pierluissi M, Dunlap K, Westhead EW (1991) Multiple actions of extracellular ATP on calcium currents in cultured bovine chromaffin cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88:1261–1265
Dolphin AC (2003) G protein modulation of voltage-gated calcium channels. Pharmacol Rev 55:607–627
Elhamdani A, Palfrey HC, Artalejo CR (2001) Quantal size is dependent on stimulation frequency and calcium entry in calf chromaffin cells. Neuron 31:819–830
Elhamdani A, Azizi F, Artalejo CR (2006) Double patch clamp reveals that transient fusion (kiss-and-run) is a major mechanism of secretion in calf adrenal chromaffin cells: high calcium shifts the mechanism from kiss-and-run to complete fusion. J Neurosci 26:3030–3036
Elmslie KS, Zhou W, Jones SW (1990) LHRH and GTP-gamma-S modify calcium current activation in bullfrog sympathetic neurons. Neuron 5:75–80
Engisch KL, Nowycky MC (1996) Calcium dependence of large dense-cored vesicle exocytosis evoked by calcium influx in bovine adrenal chromaffin cells. J Neurosci 16:1359–1369
Ennion SJ, Powell AD, Seward EP (2004) Identification of the P2Y(12) receptor in nucleotide inhibition of exocytosis from bovine chromaffin cells. Mol Pharmacol 66:601–611
Eroglu C, Allen NJ, Susman MW, O’Rourke NA, Park CY, Ozkan E, Chakraborty C, Mulinyawe SB, Annis DS, Huberman AD, Green EM, Lawler J, Dolmetsch R, Garcia KC, Smith SJ, Luo ZD, Rosenthal A, Mosher DF, Barres BA (2009) Gabapentin receptor alpha2delta-1 is a neuronal thrombospondin receptor responsible for excitatory CNS synaptogenesis. Cell 139:380–392
Floras JS (2003) Sympathetic activation in human heart failure: diverse mechanisms, therapeutic opportunities. Acta Physiol Scand 177:391–398
Fox AP, Cahill AL, Currie KP, Grabner C, Harkins AB, Herring B, Hurley JH, Xie Z (2008) N- and P/Q-type Ca2+ channels in adrenal chromaffin cells. Acta Physiol 192:247–261
Fulop T, Smith C (2006) Physiological stimulation regulates the exocytic mode through calcium activation of protein kinase C in mouse chromaffin cells. Biochem J 399:111–119
Fulop T, Radabaugh S, Smith C (2005) Activity-dependent differential transmitter release in mouse adrenal chromaffin cells. J Neurosci 25:7324–7332
Gandia L, Garcia AG, Morad M (1993) ATP modulation of calcium channels in chromaffin cells. J Physiol 470:55–72
Garcia AG, Garcia-De-Diego AM, Gandia L, Borges R, Garcia-Sancho J (2006) Calcium signaling and exocytosis in adrenal chromaffin cells. Physiol Rev 86:1093–1131
Gerachshenko T, Schwartz E, Bleckert A, Photowala H, Seymour A, Alford S (2009) Presynaptic G-protein-coupled receptors dynamically modify vesicle fusion, synaptic cleft glutamate concentrations, and motor behavior. J Neurosci 29:10221–10233
Gillis KD (2000) Admittance-based measurement of membrane capacitance using the EPC-9 patch-clamp amplifier. Pflugers Arch 439:655–664
Grabner CP, Price SD, Lysakowski A, Fox AP (2005) Mouse chromaffin cells have two populations of dense core vesicles. J Neurophysiol 94:2093–2104
Gray AC, Raingo J, Lipscombe D (2007) Neuronal calcium channels: splicing for optimal performance. Cell Calcium 42:409–417
Grueter CE, Abiria SA, Dzhura I, Wu Y, Ham AJ, Mohler PJ, Anderson ME, Colbran RJ (2006) L-type Ca2+ channel facilitation mediated by phosphorylation of the beta subunit by CaMKII. Mol cell 23:641–650
Hamelink C, Tjurmina O, Damadzic R, Young WS, Weihe E, Lee HW, Eiden LE (2002) Pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating polypeptide is a sympathoadrenal neurotransmitter involved in catecholamine regulation and glucohomeostasis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:461–466
Harata NC, Aravanis AM, Tsien RW (2006) Kiss-and-run and full-collapse fusion as modes of exo-endocytosis in neurosecretion. J Neurochem 97:1546–1570
Harkins AB, Fox AP (2000) Activation of purinergic receptors by ATP inhibits secretion in bovine adrenal chromaffin cells. Brain Res 885:231–239
He L, Wu LG (2007) The debate on the kiss-and-run fusion at synapses. Trends Neurosci 30:447–455
Herlitze S, Hockerman GH, Scheuer T, Catterall WA (1997) Molecular determinants of inactivation and G protein modulation in the intracellular loop connecting domains I and II of the calcium channel alpha1A subunit. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94:1512–1516
Hernandez-Guijo JM, Carabelli V, Gandia L, Garcia AG, Carbone E (1999) Voltage-independent autocrine modulation of L-type channels mediated by ATP, opioids and catecholamines in rat chromaffin cells. Eur J Neurosci 11:3574–3584
Jarvis SE, Barr W, Feng ZP, Hamid J, Zamponi GW (2002) Molecular determinants of syntaxin 1 modulation of N-type calcium channels. J Biol Chem 277:44399–44407
Kleppisch T, Ahnert-Hilger G, Gollasch M, Spicher K, Hescheler J, Schultz G, Rosenthal W (1992) Inhibition of voltage-dependent Ca2+ channels via alpha 2-adrenergic and opioid receptors in cultured bovine adrenal chromaffin cells. Pflugers Arch 421:131–137
Kuri BA, Chan SA, Smith CB (2009) PACAP regulates immediate catecholamine release from adrenal chromaffin cells in an activity-dependent manner through a protein kinase C-dependent pathway. J Neurochem 110:1214–1225
Lee HK, Elmslie KS (2000) Reluctant gating of single N-type calcium channels during neurotransmitter-induced inhibition in bullfrog sympathetic neurons. J Neurosci 20:3115–3128
Lim W, Kim SJ, Yan HD, Kim J (1997) Ca2+-channel-dependent and -independent inhibition of exocytosis by extracellular ATP in voltage-clamped rat adrenal chromaffin cells. Pflugers Arch 435:34–42
Lindau M, Neher E (1988) Patch-clamp techniques for time-resolved capacitance measurements in single cells. Pflugers Arch 411:137–146
Lukyanetz EA, Neher E (1999) Different types of calcium channels and secretion from bovine chromaffin cells. Eur J Neurosci 11:2865–2873
Lymperopoulos A, Rengo G, Funakoshi H, Eckhart AD, Koch WJ (2007) Adrenal GRK2 upregulation mediates sympathetic overdrive in heart failure. Nat Med 13:315–323
Marcantoni A, Carabelli V, Comunanza V, Hoddah H, Carbone E (2008) Calcium channels in chromaffin cells: focus on L and T types. Acta Physiol 192:233–246
Marcantoni A, Vandael DH, Mahapatra S, Carabelli V, Sinnegger-Brauns MJ, Striessnig J, Carbone E (2010) Loss of Cav1.3 channels reveals the critical role of L-type and BK channel coupling in pacemaking mouse adrenal chromaffin cells. J Neurosci 30:491–504
McDavid S, Currie KP (2006) G-proteins modulate cumulative inactivation of N-type (Cav2.2) calcium channels. J Neurosci 26:13373–13383
Moore JM, Papke JB, Cahill AL, Harkins AB (2006) Stable gene silencing of synaptotagmin I in rat PC12 cells inhibits Ca2+-evoked release of catecholamine. Am J Physiol 291:C270–C281
Nagy G, Reim K, Matti U, Brose N, Binz T, Rettig J, Neher E, Sorensen JB (2004) Regulation of releasable vesicle pool sizes by protein kinase A-dependent phosphorylation of SNAP-25. Neuron 41:417–429
Novara M, Baldelli P, Cavallari D, Carabelli V, Giancippoli A, Carbone E (2004) Exposure to cAMP and beta-adrenergic stimulation recruits Ca(V)3 T-type channels in rat chromaffin cells through Epac cAMP-receptor proteins. J Physiol 558:433–449
Patil PG, de Leon M, Reed RR, Dubel S, Snutch TP, Yue DT (1996) Elementary events underlying voltage-dependent G-protein inhibition of N-type calcium channels. Biophys J 71:2509–2521
Photowala H, Blackmer T, Schwartz E, Hamm HE, Alford S (2006) G protein betagamma-subunits activated by serotonin mediate presynaptic inhibition by regulating vesicle fusion properties. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:4281–4286
Polo-Parada L, Chan SA, Smith C (2006) An activity-dependent increased role for L-type calcium channels in exocytosis is regulated by adrenergic signaling in chromaffin cells. Neuroscience 143:445–459
Powell AD, Teschemacher AG, Seward EP (2000) P2Y purinoceptors inhibit exocytosis in adrenal chromaffin cells via modulation of voltage-operated calcium channels. J Neurosci 20:606–616
Rizo J, Rosenmund C (2008) Synaptic vesicle fusion. Nat Struct Mol Biol 15:665–674
Schonn JS, Maximov A, Lao Y, Sudhof TC, Sorensen JB (2008) Synaptotagmin-1 and -7 are functionally overlapping Ca2+ sensors for exocytosis in adrenal chromaffin cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105:3998–4003
Sorensen JB (2009) Conflicting views on the membrane fusion machinery and the fusion pore. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 25:513–537
Stephens GJ (2009) G-protein-coupled-receptor-mediated presynaptic inhibition in the cerebellum. Trends Pharmacol Sci 30:421–430
Stotz SC, Zamponi GW (2001) Structural determinants of fast inactivation of high voltage-activated Ca(2+) channels. Trends Neurosci 24:176–181
Sudhof TC, Rothman JE (2009) Membrane fusion: grappling with SNARE and SM proteins. Science 323:474–477
Takiyyuddin MA, De Nicola L, Gabbai FB, Dinh TQ, Kennedy B, Ziegler MG, Sabban EL, Parmer RJ, O’Connor DT (1993) Catecholamine secretory vesicles. Augmented chromogranins and amines in secondary hypertension. Hypertension 21:674–679
Tedford HW, Zamponi GW (2006) Direct G protein modulation of Cav2 calcium channels. Pharmacol Rev 58:837–862
Twitchell WA, Rane SG (1993) Opioid peptide modulation of Ca(2+)-dependent K+ and voltage-activated Ca2+ currents in bovine adrenal chromaffin cells. Neuron 10:701–709
Ulate G, Scott SR, Gonzalez J, Gilabert JA, Artalejo AR (2000) Extracellular ATP regulates exocytosis in inhibiting multiple Ca(2+) channel types in bovine chromaffin cells. Pflugers Arch 439:304–314
Villanueva M, Wightman RM (2007) Facilitation of quantal release induced by a D1-like receptor on bovine chromaffin cells. Biochemistry 46:3881–3887
Villarroya M, Olivares R, Ruiz A, Cano-Abad MF, de Pascual R, Lomax RB, Lopez MG, Mayorgas I, Gandia L, Garcia AG (1999) Voltage inactivation of Ca2+ entry and secretion associated with N- and P/Q-type but not L-type Ca2+ channels of bovine chromaffin cells. J Physiol 516(Pt 2):421–432
Wang CT, Grishanin R, Earles CA, Chang PY, Martin TF, Chapman ER, Jackson MB (2001) Synaptotagmin modulation of fusion pore kinetics in regulated exocytosis of dense-core vesicles. Science 294:1111–1115
Weiss JL, Burgoyne RD (2001) Voltage-independent inhibition of P/Q-type Ca2+ channels in adrenal chromaffin cells via a neuronal Ca2+ sensor-1-dependent pathway involves Src family tyrosine kinase. J Biol Chem 276:44804–44811
Weiss N, Tadmouri A, Mikati M, Ronjat M, De Waard M (2007) Importance of voltage-dependent inactivation in N-type calcium channel regulation by G-proteins. Pflugers Arch 454:115–129
Wightman RM, Jankowski JA, Kennedy RT, Kawagoe KT, Schroeder TJ, Leszczyszyn DJ, Near JA, Diliberto EJ Jr, Viveros OH (1991) Temporally resolved catecholamine spikes correspond to single vesicle release from individual chromaffin cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88:10754–10758
Wolfe JT, Wang H, Howard J, Garrison JC, Barrett PQ (2003) T-type calcium channel regulation by specific G-protein betagamma subunits. Nature 424:209–213
Womack MD, McCleskey EW (1995) Interaction of opioids and membrane potential to modulate Ca2+ channels in rat dorsal root ganglion neurons. J Neurophysiol 73:1793–1798
Yoon EJ, Gerachshenko T, Spiegelberg BD, Alford S, Hamm HE (2007) Gbetagamma interferes with Ca2+-dependent binding of synaptotagmin to the soluble N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive factor attachment protein receptor (SNARE) complex. Mol Pharmacol 72:1210–1219
Yoon EJ, Hamm HE, Currie KP (2008) G protein betagamma subunits modulate the number and nature of exocytotic fusion events in adrenal chromaffin cells independent of calcium entry. J Neurophysiol 100:2929–2939
Acknowledgments
Work in my lab is supported by the National Institutes of Health National Institute of Neurological Disorders And Stroke [Grant R01-NS052446].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
A commentary to this article can be found at doi:10.1007/s10571-010-9611-z.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Currie, K.P.M. Inhibition of Ca2+ Channels and Adrenal Catecholamine Release by G Protein Coupled Receptors. Cell Mol Neurobiol 30, 1201–1208 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-010-9596-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-010-9596-7