Abstract
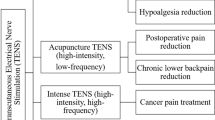
In this paper we will implement a transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS) designed for medical applications in order to reduce acute and chronic pains. This procedure uses electrical currents pulses applied on the skin area via electrodes. Two kinds of stimulation are adopted: the peripheral nerve stimulation (PNS) and the spinal cord stimulation (SCS). In either, a small pulse generator sends electrical pulses to the nerves (in PNS stimulation) or to the spinal cord (SCS stimulation). Previous studies on TENS technique showed that the obtained results are not very satisfactory and depend on the patient’s state, condition, age, and stimulation parameters. In order to optimize the conditions and parameters stimulation during treatments, we present in this paper a new strategy called pulse width modulation stimulation (PWM-TENS) based on a parametric computing of frequency, current intensity, pulse duration of stimuli. To implement our approach, we used an embedded platform under Arduino-Uno with five several programs depending on the pain category and according to international medical standards and specifications. The first tests on 15 volunteer patients showed satisfaction ratio (EVA) after 5–12 days and a pain reduction between 80 and 20 after 1 month of stimulation. This result is important because it prolongs the analgesic effect and reduces therapeutic rehabilitation period. The medical aspect of the subject is to have a medical tool that allows objective evaluations for short and medium periods of pain treatments with dynamic evaluation metrics.

















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Catley, M. J., Gibson, W., Wand, B. M., Meads, C., & O’Connell, N. (2015). Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation for chronic pain-An overview of Cochrane reviews. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD011890.
Cruccu, G., Aziz, T. Z., Garcia-Larrea, L., Hansson, P., Jensen, T. S., & Lefaucheur, J. P. (2007). EFNS guidelines on neurostimulation therapy for neuropathic pain. European Journal of Neurology, 14(9), 952–970.
Flowerdew, M., & Gadsby, J. (1997). A review of the treatment of chronic low back pain with acupuncture like transcutaneous electric nerve stimulation and transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation. Complementary Therapies in Medicine, 5, p193–p201.
Ladame, P. (1985). Historical note on its origin electrotherapy. Medical electricity in Geneva in the 18th century. Medical Revue Suisse Romande, 10, 553–572.
Khadilkar, A., Milne, S., Brosseau, L., Robinson, V., Saginur, M., & Shea, B. (2005). Electrical nerve stimulation for chronic low-back pain. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews, 5(3), CD003008.
Wahibab, B., & Boutaleb, R. (2011). Bendaouia. Réalisation d’un stimulateur anti douleur Advanced Technology Development Center C.D.T.A, Algeria.
Bournier, E., Altier, C., Hildebrand, M., & Zamponi, G. W. (2014). Calcium-permeable ion channels in pain signaling. Physiological Reviews, 94(1), 81–140.
Malcolm, A. R., Hellreich, P. D., Johnson, D. W., & Chen, J. J. (2015). Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation for chronic post-herpetic neuralgia. International Journal of Dermatology, 54(4), 476–480. https://doi.org/10.1111/ijd.12385.
Bjordal, J. M., Johnson, M. I., & Ljunggreen, A. E. (2003). Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS) can reduce postoperative analgesic consumption. A meta-analysis with assessment of optimal treatment parameters for postoperative pain. European Journal of Pain, 7(2), 181–188.
Gadsby, J., & Flowerdew, M. (1997). A review of the treatment of chronic low back pain with acupuncture like transcutaneous electric nerve stimulation and transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation. Complementary Therapies in Medicine, 5, 193–201.
Johnson, M., & Martinson, M. (2007). Efficacity of electrical nerve stimulation for chronic musculoskeletal pain: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Pain, 130(1–2), 157–165.
Matsuo, H., Uchida, K., Nakajima, H., Guerrero, A. R., Watanabe, S., Takeura, N., et al. (2014). Early transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation reduces hyperalgesia and decreases activation of spinal cells in mice with neuropathic pain. Pain Journal, 155(9), 1888–1901.
Shen, Y., Yin, Z., Fan, Y., Chen, C.-F., Dai, W., Yi, W., et al. (2015). Comparison of the effects of contralaterally controlled functional electrical stimulation and neuromuscular electrical stimulation on upper extremity functions in patients with stroke. CNS & Neurological Disorders-Drug Targets Journal, 14(10), 1260–1266.
Fox, E. J., & Melzack, R. (1976). Comparison of transcutaneous electrical stimulation and acupuncture in the treatment of chronic pain. Advances in Pain Research and Therapy, 1, 797–801.
De Santana, J. M., & Sluka, K. A. (2008). Antinociceptive effect of transcutaneous electric nerve stimulation (TENS) is mediated by ventrolateral periaqueductal grey (vlPAG). In Proceedings of the XII world congress in pain, Glasgow, Scotland.
Loeser, J. D., & Treede, R. D. (2008). The kyoto protocol of IASP basic pain terminology. Pain Journal, 137(3), 473–477. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pain.2008.04.025.
Buchmuller, A., Navez, M., Milletre-Bernardin, M., Pouplin, S., Presles, E., Lantéri-Minet, M., et al. (2012). Value of TENS for relief of chronic low back pain with or without radicular pain. European Journal of Pain, 16(5), 656–665.
Doucet, B. M., Lam, A., & Griffin, L. (2012). Neuromuscular electrical stimulation for skeletal muscle function. Journal of Biology and Medicine, 85(2), 201–215.
Sluka, K. A., et al. (2006). Increased release of serotonin in the spinal cord during low, but not high, frequency transcutaneous electric nerve stimulation in rats with joint inflammation. Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation, 87(8), 1137–1140.
Proctor, M. L., Smith, C. A., Farquhar, C. M., & Stones, R. W. (2002). Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation and acupuncture for primary dysmenorrhoea. Cochrane Database System Review, (1), CD002123. https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD002123.
Johnson, M., & Martinson, M. (2007). Efficacy of electrical nerve stimulation for chronic musculoskeletal pain: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Pain Journal, 130, 157–165.
Popa, L., Constantinescu, A., Muresanu, D. F., Irimie, A., Balanescu, N. R., & Popescu, C. D. (2013). Clinical improvement and cortical adaptations after functional electrical stimulation in Parkinson’s disease patients. CNS & Neurological Disorders-Drug Targets, 12(2), 265–273.
Acknowledgements
This work is conduct with the cooperation of the National Institute of Biomedical Studies of Tunis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bouafif, L., Ellouze, N. Electronic implementation of a PWM electrical nerve stimulation system for medical treatment of acute and chronic pains. Analog Integr Circ Sig Process 95, 499–511 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10470-018-1174-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10470-018-1174-9