Abstract
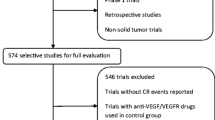
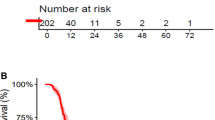
Glioblastoma is one of the most common primary brain tumors in adults. The current treatment strategies failed to achieve satisfactory outcomes. Anti-vascular endothelial growth factor (anti-VEGF) agents have been proposed to enhance the survival and quality of life in these patients. To investigate this, different databases were searched in addition to hand searching. Relevant studies were screened and only ten randomized controlled trials (RCTs) met the eligibility criteria; six of them were considered for meta-analysis. Eligible RCTs were assessed regarding risk of bias using the Cochrane tool. Relevant data were extracted and meta-analysis was conducted using the random effects model analysis on RevMan software. One thousand seventy-eight patients in the anti-VEGF group and 946 patients in the control group were available for analysis. No statistically significant improvement in the overall survival (OS) was detected for anti-VEGF (OR 0.87, 95% CI 0.7–1.09, p = 0.23) or bevacizumab subgroup (OR 0.84, 95% CI 0.65–1.08, p = 0.17) compared to standard therapy alone. However, the progression-free survival (PFS) showed a significant improvement with both anti-VEGF (OR 0.76, 95% CI 0.65–0.89, p = 0.0007) and bevacizumab subgroup (OR 0.75, 95% CI 0.65–0.87, p = 0.0001). In conclusion, anti-VEGF agents can improve the PFS but not OS in glioblastoma patients. The current evidence is not satisfactory to declare a new therapeutic line. Further RCTs with sharply determined outcomes and assessment methods are required.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- OS:
-
overall survival
- PFS:
-
progression-free survival
- VEGF:
-
vascular endothelial growth factor
References
Ostrom QT, Gittleman H, Fulop J, Liu M, Blanda R, Kromer C et al (2015) CBTRUS statistical report: primary brain and central nervous system tumors diagnosed in the United States in 2008–2012. Neuro-Oncology 17 Suppl 4:iv1–iv62
Louis DN, Perry A, Reifenberger G, von Deimling A, Figarella-Branger D, Cavenee WK, Ohgaki H, Wiestler OD, Kleihues P, Ellison DW (2016) The 2016 World Health Organization Classification of Tumors of the Central Nervous System: a summary. Acta Neuropathol 131:803–820
Stupp R, Mason WP, van den Bent MJ, Weller M, Fisher B, Taphoorn MJB, Belanger K, Brandes AA, Marosi C, Bogdahn U, Curschmann J, Janzer RC, Ludwin SK, Gorlia T, Allgeier A, Lacombe D, Cairncross JG, Eisenhauer E, Mirimanoff RO (2005) Radiotherapy plus concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide for glioblastoma. N Engl J Med 352:987–996
Das S, Marsden PA (2013) Angiogenesis in glioblastoma. N Engl J Med 369:1561–1563
Hicklin DJ, Ellis LM (2005) Role of the vascular endothelial growth factor pathway in tumor growth and angiogenesis. J Clin Oncol 23:1011–1027
Ellis LM, Hicklin DJ (2008) VEGF-targeted therapy: mechanisms of anti-tumour activity. Nat Rev Cancer 8:579–591
Jain RK, Duda DG, Clark JW, Loeffler JS (2006) Lessons from phase III clinical trials on anti-VEGF therapy for cancer. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 6:24–40
Nabors LB, Fink KL, Mikkelsen T, Grujicic D, Tarnawski R, Nam DH, Mazurkiewicz M, Salacz M, Ashby L, Zagonel V, Depenni R, Perry JR, Hicking C, Picard M, Hegi ME, Lhermitte B, Reardon DA (2015) Two cilengitide regimens in combination with standard treatment for patients with newly diagnosed glioblastoma and unmethylated MGMT gene promoter: results of the open-label, controlled, randomized phase II CORE study. Neuro-Oncology 17:708–717
Taal W, Oosterkamp HM, Walenkamp AME, Dubbink HJ, Beerepoot LV, Hanse MCJ, Buter J, Honkoop AH, Boerman D, de Vos FYF, Dinjens WNM, Enting RH, Taphoorn MJB, van den Berkmortel FWPJ, Jansen RLH, Brandsma D, Bromberg JEC, van Heuvel I, Vernhout RM, van der Holt B, van den Bent MJ (2014) Single-agent bevacizumab or lomustine versus a combination of bevacizumab plus lomustine in patients with recurrent glioblastoma (BELOB trial): a randomised controlled phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol 15:943–953
Gilbert MR, Dignam JJ, Armstrong TS, Wefel JS, Blumenthal DT, Vogelbaum MA, Colman H, Chakravarti A, Pugh S, Won M, Jeraj R, Brown PD, Jaeckle KA, Schiff D, Stieber VW, Brachman DG, Werner-Wasik M, Tremont-Lukats IW, Sulman EP, Aldape KD, Curran WJ Jr, Mehta MP (2014) A randomized trial of bevacizumab for newly diagnosed glioblastoma. N Engl J Med 370:699–708
Chinot OL, Wick W, Mason W, Henriksson R, Saran F, Nishikawa R, Carpentier AF, Hoang-Xuan K, Kavan P, Cernea D, Brandes AA, Hilton M, Abrey L, Cloughesy T (2014) Bevacizumab plus radiotherapy–temozolomide for newly diagnosed glioblastoma. N Engl J Med 370:709–722
Balana C, De Las Penas R, Sepúlveda JM, Gil-Gil MJ, Luque R, Gallego O et al (2016) Bevacizumab and temozolomide versus temozolomide alone as neoadjuvant treatment in unresected glioblastoma: the GENOM 009 randomized phase II trial. J Neuro-Oncol 127:569–579
Batchelor TT, Mulholland P, Neyns B, Nabors LB, Campone M, Wick A, Mason W, Mikkelsen T, Phuphanich S, Ashby LS, DeGroot J, Gattamaneni R, Cher L, Rosenthal M, Payer F, Jürgensmeier JM, Jain RK, Sorensen AG, Xu J, Liu Q, van den Bent M (2013) Phase III randomized trial comparing the efficacy of cediranib as monotherapy, and in combination with lomustine, versus lomustine alone in patients with recurrent glioblastoma. J Clin Oncol 31:3212–3218
Cloughesy T, Finocchiaro G, Belda-Iniesta C, Recht L, Brandes AA, Pineda E, Mikkelsen T, Chinot OL, Balana C, Macdonald DR, Westphal M, Hopkins K, Weller M, Bais C, Sandmann T, Bruey JM, Koeppen H, Liu B, Verret W, Phan SC, Shames DS (2017) Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicenter phase II study of onartuzumab plus bevacizumab versus placebo plus bevacizumab in patients with recurrent glioblastoma: efficacy, safety, and hepatocyte growth factor and O 6-methylguanine–DNA met. J Clin Oncol 35:343–351
Duerinck J, Du Four S, Vandervorst F, D’Haene N, Le Mercier M, Michotte A et al (2016) Randomized phase II study of axitinib versus physicians best alternative choice of therapy in patients with recurrent glioblastoma. J Neuro-Oncol 128:147–155
Friedman HS, Prados MD, Wen PY, Mikkelsen T, Schiff D, Abrey LE, Yung WKA, Paleologos N, Nicholas MK, Jensen R, Vredenburgh J, Huang J, Zheng M, Cloughesy T (2009) Bevacizumab alone and in combination with irinotecan in recurrent glioblastoma. J Clin Oncol 27:4733–4740
Field KM, Simes J, Nowak AK, Cher L, Wheeler H, Hovey EJ, Brown CSB, Barnes EH, Sawkins K, Livingstone A, Freilich R, Phal PM, Fitt G, CABARET/COGNO investigators, Rosenthal MA (2015) Randomized phase 2 study of carboplatin and bevacizumab in recurrent glioblastoma. Neuro-Oncology 17:1504–1513
Giovagnoli AR (1993) Crossed aphasia. Report of a rare case in a glioblastoma patient. Neurol Sci 14:329–332
Schoenhuber R, Vescovin E, Calcaterra Merli GA (1983) Temporal lobe glioblastoma presenting as Raeder paratrigeminal syndrome. Neurol Sci 4:117–119
Mahta A, Buhl R, Huang H, Jansen O, Kesari S, Ulmer S (2013) Sellar and supra-sellar glioblastoma masquerading as a pituitary macroadenoma. Neurol Sci 34:605–607
Salmaggi A, Duri S, Silvani A, Gaviani P, Milanesi I, Casali C, Di Meco F. Loco-regional treatments in first-diagnosis glioblastoma: literature review on association between Stupp protocol and Gliadel. Neurol Sci 2011; 32: 241–245
Liang H, Ding X, Zhou C, Zhang Y, Xu M, Zhang C, Xu L (2012) Knockdown of eukaryotic translation initiation factors 3B (EIF3B) inhibits proliferation and promotes apoptosis in glioblastoma cells. Neurol Sci 33:1057–1062
Silvani A, Eoli M, Salmaggi A, Erbetta A, Fariselli L, Boiardi A (2002) Intra-arterial ACNU and carboplatin versus intravenous chemotherapy with cisplatin and BCNU in newly diagnosed patients with glioblastoma. Neurol Sci 23:219–224
Boiardi A, Eoli M, Pozzi A, Salmaggi A, Broggi G, Silvani A (1999) Locally delivered chemotherapy and repeated surgery can improve survival in glioblastoma patients. Neurol Sci 20:43–48
Khasraw M, Ameratunga MS, Grant R, Wheeler H, Pavlakis N (2014) Antiangiogenic therapy for high-grade glioma. Cochrane Database Syst Rev (9). https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD008218.pub3
Yang S-B, Gao K-D, Jiang T, Cheng S-J, Li W-B (2017) Bevacizumab combined with chemotherapy for glioblastoma: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Oncotarget 8:57337–57344
Wen PY, Macdonald DR, Reardon DA, Cloughesy TF, Sorensen AG, Galanis E, DeGroot J, Wick W, Gilbert MR, Lassman AB, Tsien C, Mikkelsen T, Wong ET, Chamberlain MC, Stupp R, Lamborn KR, Vogelbaum MA, van den Bent MJ, Chang SM (2010) Updated response assessment criteria for high-grade gliomas: response assessment in neuro-oncology working group. J Clin Oncol 28:1963–1972
Abushouk AI, Ismail A, Salem AMA, Afifi AM, Abdel-Daim MM (2017) Cardioprotective mechanisms of phytochemicals against doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity. Biomed Pharmacother 90:935–946
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Appendices
Appendix 1
(((randomized controlled trial[pt] OR controlled clinical trial[pt]) OR(randomized OR randomized OR randomly OR placebo[tiab]) OR (trial[ti]) OR (“Clinical Trials as Topic”[MeSH Major Topic])) AND ((Glioblastoma[MeSH Terms]) OR Glioma*[Title/Abstract])) AND (((((Anti vascular endothelial growth factor [Title/Abstract]) OR (anti-VEGF[Title/Abstract]) OR (Bevacizumab*[Title/Abstract]) OR (ranibizumab*[Title/Abstract]) OR (cediranib*[Title/Abstract]))))
Appendix 2
#1 MeSH descriptor: [Glioblastoma] explode all trees
#2 “Glioma*”: ti,ab,kw
#3 #1 or #2
#4 Anti-VEGF: ti,ab,kw
#5 Bevacizumab: ti,ab,kw
#6 Ranibizumab: ti,ab,kw
#7 cediranib: ti,ab,kw
#8 Aflibercept: ti,ab,kw
#9#4 or #5 or #6 or #7 or #8
#10 #3 and #9
Appendix 3
#1 TS= Glioma*
#2 TS= Glioblastoma
#3 #1 OR #2
#4 TS= Anti vascular endothelial growth factor
#5 TS= anti-VEGF
#6 TS= Bevacizumab
#7 TS= ranibizumab
#8 TS= cediranib
#9 #4 OR #5 OR #6 OR #7 OR #8
#10 #3 AND #9
#11 TS=random*
#12 #10 AND #11
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xiao, Q., Yang, S., Ding, G. et al. Anti-vascular endothelial growth factor in glioblastoma: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Neurol Sci 39, 2021–2031 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-018-3568-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-018-3568-y