Abstract
Introduction
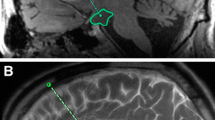
Hypothalamic hamartomas (HHs) are rare non-neoplastic lesions which cause drug-resistant epilepsy with associated behavioural, psychiatric and endocrine issues. With the development of new minimally invasive techniques for the treatment of HH, there is a need to reappraise the effectiveness and safety of each approach. We review the outcomes of HH patients treated surgically, utilizing intraoperative magnetic resonance imaging (IOMRI), by a team of Alder Hey NHS Foundation Trust tumour and epilepsy neurosurgeons since 2011.
Methods
Patient records of all HH cases operated on since 2011 were reviewed to confirm history of presentation and clinical outcomes.
Results
Ten patients have undergone surgery for HH under the dual care of Alder Hey tumour and epilepsy neurosurgeons during this period. Eight cases had a midline transcallosal, interforniceal approach with the remaining 2 having a transcallosal, transforaminal approach. All patients had an IOMRI scan, with 40% needing further tumour resection post-IOMRI. Forty percent had a total resection, 3 patients had near-total resection and 3 patients had subtotal resection (~ 30% tumour residual on post-operative MRI). No new neurological complications developed post-operatively. Hypothalamic axis derangements were seen in 3 cases, including 1 diabetes insipidus with hypocortisolaemia, 1 hypodipsia and 1 transient hyperphagia. Eighty percent are seizure free; the remaining two patients have had significant improvements in seizure frequency.
Conclusions
IOMR was used to tailor the ideal tumour resection volume safely based on anatomy of the lesion, which combined with the open transcallosal, interforniceal route performed by surgeons experienced in the approach resulted in excellent, safe and effective seizure control.












Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
19 July 2018
The authors apologize to have sent a final manuscript draft omitting “Athanasius Chawira” from the list of authors. The correct list of authors is given in this article.
The original article has been corrected.
References
Maixner W (2006) Hypothalamic hamartomas—clinical, neuropathological and surgical aspects. Childs Nerv Syst 22(8):867–873
Fenoglio KA, Wu J, Kim DY, Simeone TA, Coons SW, Rekate H, Rho JM, Kerrigan JF (2007) Hypothalamic hamartoma: basic mechanisms of intrinsic epileptogenesis. Semin Pediatr Neurol 14(2):51–59
Mittal S, Mittal M, Montes JL, Farmer JP, Andermann F (2013) Hypothalamic hamartomas. Part 1. Clinical, neuroimaging, and neurophysiological characteristics. Neurosurg Focus 34(6):E6
Brandberg G, Raininko R, Eeg-Olofsson O (2004) Hypothalamic hamartoma with gelastic seizures in Swedish children and adolescents. Eur J Paediatr Neurol 8(1):35–44
Rekate HL (2011) Management of hypothalamic hamartomas: progress due to alignment of the stars. Neurosurg Focus 30(2):1–3
Roth J, Bercu MM, Constantini S (2013) Combined open microsurgical and endoscopic resection of hypothalamic hamartomas. J Neurosurg Pediatr 11(5):491–494
Wait SD, Abla AA, Killory BD, Nakaji P, Rekate HL (2011) Surgical approaches to hypothalamic hamartomas. Neurosurg Focus 30(2):E2
Bulteau C, Dorfmüller G, Fohlen M, Jalin C, Oliver MV, Delalande O (2008) Epilepsy surgery during infancy and early childhood in France. Neurochirurgie 54(3):342–346
Calisto A, Dorfmüller G, Fohlen M, Bulteau C, Conti A, Delalande O (2014) Endoscopic disconnection of hypothalamic hamartomas: safety and feasibility of robot-assisted, thulium laser-based procedures. J Neurosurg Pediatr 14(6):563–572
Régis J, Bartolomei F, de Toffol B, Genton P, Kobayashi T, Mori Y, Takakura K, Hori T, Inoue H, Schröttner O, Pendl G, Wolf A, Arita K, Chauvel P (2000) Gamma knife surgery for epilepsy related to hypothalamic hamartomas. Neurosurgery 47(6):1343–1352
Régis J, Scavarda D, Tamura M, Villeneuve N, Bartolomei F, Brue T, Morange I, Dafonseca D, Chauvel P (2007) Gamma knife surgery for epilepsy related to hypothalamic hamartomas. Semin Pediatr Neurol 14(2):73–79
Rosenfeld JV, Feiz-Erfan I (2007) Hypothalamic hamartoma treatment: surgical resection with the transcallosal approach. Semin Pediatr Neurol 14(2):88–98
Procaccini E, Dorfmuller G, Fohlen M, Bulteau C, Delalande O (2006) Surgical Management of Hypothalamic Hamartomas with Epilepsy: the Stereoendoscopic Approach. Oper Neurosurg 59(suppl_4):ONS-336–ONS-346, https://doiorg.liverpool.idm.oclc.org/10.1227/01.NEU.0000233900.06146.72
Ng YT, Rekate HL, Prenger EC, Chung SS, Feiz-Erfan I, Wang NC, Varland MR, Kerrigan JF (2006) Transcallosal resection of hypothalamic hamartoma for intractable epilepsy. Epilepsia 47(7):1192–1202
Andrew M, Parr JR, Stacey R, Rosenfeld JV, Hart Y, Pretorius P, Nijhawan S, Zaiwalla Z, McShane MA (2008) Transcallosal resection of hypothalamic hamartoma for gelastic epilepsy. Childs Nerv Syst 24(2):275–279
Goodden J, Pizer B, Pettorini B, Williams D, Blair J, Didi M, Thorp N, Mallucci C (2014) The role of surgery in optic pathway/hypothalamic gliomas in children: clinical article. J Neurosurg Pediatr 13(1):1–12
Millward CP, da Rosa SP, Avula S, Ellenbogen JR, Spiteri M, Lewis E, Didi M, Mallucci C (2015) The role of early intra-operative MRI in partial resection of optic pathway/hypothalamic gliomas in children. Childs Nerv Syst 31(11):2055–2062
Kubben PL, van Santbrink H, ter Laak-Poort M, Weber JW, Vles JSH, Granzen B, van Overbeeke JJ, Cornips EMJ (2012) Implementation of a mobile 0.15-T intraoperative MR system in pediatric neuro-oncological surgery: feasibility and correlation with early postoperative high-field strength MRI. Childs Nerv Syst 28(8):1171–1180
Avula S, Mallucci CL, Pizer B, Garlick D, Crooks D, Abernethy LJ (2012) Intraoperative 3-Tesla MRI in the management of paediatric cranial tumours—initial experience. Pediatr Radiol 42(2):158–167
Levy R, Cox RG, Hader WJ, Myles T, Sutherland GR, Hamilton MG (2009) Application of intraoperative high-field magnetic resonance imaging in pediatric neurosurgery: clinical article. J Neurosurg Pediatr 4(5):467–474
Kremer P, Tronnier V, Steiner HH, Metzner R, Ebinger F, Rating D, Hartmann M, Seitz A, Unterberg A, Wirtz CR (2006) Intraoperative MRI for interventional neurosurgical procedures and tumor resection control in children. Childs Nerv Syst 22(7):674–678
Olavarria G, Tomita T (2005) Use of a compact intraoperative low-field magnetic imager in pediatric neurosurgery. Childs Nerv Syst 21(2):114
Giordano M, Arraez C, Samii A, Samii M, di Rocco C (2016) Neurosurgical tools to extend tumor resection in pediatric hemispheric low-grade gliomas: iMRI. Childs Nerv Syst 32(10):1915–1922
Roder C, Breitkopf M, MS, Bisdas S, Freitas RS, Dimostheni A, Ebinger M, Wolff M, Tatagiba M, Schuhmann MU (2016) Beneficial impact of high-field intraoperative magnetic resonance imaging on the efficacy of pediatric low-grade glioma surgery. Neurosurg Focus 40(3):E13
Kurwale NS, Chandra SP, Chouksey P, Arora A, Garg A, Sarkar C, Bal C, Tripathi M (2015) Impact of intraoperative MRI on outcomes in epilepsy surgery: preliminary experience of two years. Br J Neurosurg 29(3):380–385
Sacino MF, Ho CY, Murnick J, Keating RF, Gaillard WD, Oluigbo CO (2016) The role of intraoperative MRI in resective epilepsy surgery for peri-eloquent cortex cortical dysplasias and heterotopias in pediatric patients. Neurosurg Focus 40(3):E16
Sommer B, Schlaffer SM, Coras R, Blumcke I, Hamer HM, Stefan H, Buchfelder M (2014) Intraoperative use of high-field MRI in hypothalamic hamartomas associated with epilepsy: clinico-pathological presentation of five adult patients. Acta Neurochir 156(10):1865–1878
Mittal S, Mittal M, Montes JL, Farmer JP, Andermann F (2013) Hypothalamic hamartomas. Part 2. Surgical considerations and outcome. Neurosurg Focus 34(6):E7
Téllez-Zenteno JF, Serrano-Almeida C, Moien-Afshari F (2008) Gelastic seizures associated with hypothalamic hamartomas. An update in the clinical presentation, diagnosis and treatment. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat 4(6):1021–1031
Rosenfeld JV, Harvey AS, Wrennall J, Zacharin M, Berkovic SF (2001) Transcallosal resection of hypothalamic hamartomas, with control of seizures, in children with gelastic epilepsy. Neurosurgery 48(1):108–118
Harvey AS, Freeman JL, Berkovic SF, Rosenfeld JV (2003) Transcallosal resection of hypothalamic hamartomas in patients with intractable epilepsy. Epileptic Disord 5(4):257–265
Rosenfeld JV, Freeman JL, Harvey AS (2004) Operative technique: the anterior transcallosal transseptal interforniceal approach to the third ventricle and resection of hypothalamic hamartomas. J Clin Neurosci 11(7):738–744
Régis J, Scavarda D, Tamura M, Nagayi M, Villeneuve N, Bartolomei F, Brue T, Dafonseca D, Chauvel P (2006) Epilepsy related to hypothalamic hamartomas: surgical management with special reference to gamma knife surgery. Childs Nerv Syst 22(8):881–895
Wilfong AA, Curry DJ (2013) Hypothalamic hamartomas: optimal approach to clinical evaluation and diagnosis. Epilepsia 54(SUPPL. 9):109–114
Türe U, Yaşargil MG, Al-Mefty O (1997) The transcallosal-transforaminal approach to the third ventricle with regard to the venous variations in this region. J Neurosurg 87(5):706–715
Régis J, Helen Cross J, Kerrigan JF (2017) Achieving a cure for hypothalamic hamartomas: a Sisyphean quest? Epilepsia 58:7–11
Kameyama S, Shirozu H, Masuda H, Ito Y, Sonoda M, Akazawa K (2016) MRI-guided stereotactic radiofrequency thermocoagulation for 100 hypothalamic hamartomas. J Neurosurg 124(5):1503–1512
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors ceftify that they have no affiliations with or involvement in any organization or entitiy with any financial interest (such as honoria;educational grants;participation in speakers' bureaus;membership, employment, consultancies, stock ownership, or other equity interest; and expert testimony or patientlicensing arrangments), or non financial interest (such as personal or professional relationships, affiliations, knowledge or beliefs) in the subject matter or materials discussed in this manuscript.
Additional information
The original version of this article was revised: the original version of this article unfortunately contained an error. The authors apologize to have sent a final manuscript draft omitting “Athanasius Chawira” from the list of authors. The correct list of authors is given in this article.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
van Tonder, L., Burn, S., Iyer, A. et al. Open resection of hypothalamic hamartomas for intractable epilepsy revisited, using intraoperative MRI. Childs Nerv Syst 34, 1663–1673 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-018-3786-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-018-3786-x