Abstract
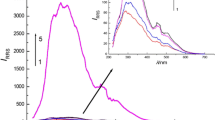
In a weakly acid medium, some aminoglycoside antibiotics, such as kanamycin (KANA), gentamicin (GEN), tobramycin (TOB), and neomycin (NEO), or acid bisazo dye pontamine sky blue (PSB) can only produce very weak resonance Rayleigh scattering (RRS) signals. However, when the two agents react with each other to form the ion association complexes, the RRS intensity can be enhanced greatly and a new RRS spectrum and a significant enhancement of the RRS intensity in the wavelength range 350–600 nm can be observed. The maximum scattering peak is at 580 nm. There is a linear relationship between the RRS intensity and the antibiotic concentration in the range 0.01–6.0 μg mL−1 at 580 nm. This RRS method has therefore been developed for the determination of trace levels of aminoglycoside antibiotics. The detection limits (3σ) of the four antibiotics, whose order of sensitivity is KANA>NEO>TOB>GEN, are 5.8–6.9 ng mL−1. This method has a good selectivity and has been successfully applied to the quick determination of antibiotics not only for injections and ear drops, but clinic serum samples as well. In addition, quantum chemistry-based analysis of the reaction mechanism, the factors influencing the RRS spectra, and the reasons for the enhancement of RRS are discussed.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhao M (1999) Chin J Antibiotics 24:319
Barnes WG (1984) Aminoglycoside assay methods, the aminoglycoside antibiotic: a guide to therapy,1st edn. CRC, Boca Raton, Florida, p 201
The Pharmacopoeia Committee of the People's Republic of China (2000) The pharmacopoeia of the People's Republic of China, 2nd version. Chemical Industry Press, Beijing, p 312
Gambardella P, Punziano R, Gionti M (1985) J Chromatogr 348:229
Stead DA, Richards RME (1997) J Chromatogr B Biomed 693:415
Zakhari NA (1990) Anal Lett 23:1843
Al-Ghabsha TS (1987) Microchem J 36:323
Kubo H, Huang YS, Kinoshita T (1989) Bunseki Kagaku 38:215
Cai WM, Cheng G, Tan HS (1990) Chin J Pharm 25:25
Pasternack RF, Bustamante C, Collings PJ, Giannetto A, Gibbs EJ (1993) J Am Chem Soc 115:5393
Huang CZ, Li KA, Tong SY (1996) Anal Chem 68:2259
Huang CZ, Li KA, Tong SY (1997) Anal Chem 69:514
Liu SP, Hu XL, Luo HQ, Fan L (2002) Sci China (Series B) 45:173
Liu SP, Luo HQ, Li NB, Liu ZF, Zheng WX (2001) Anal Chem 73:3907
Liu SP, Zho GM, Liu ZF (1998) Anal Lett 14:799
Liu SP, Liu Q, Liu ZF, Li M, Huang CZ (1999) Anal Chim Acta 379:53
Liu SP, Liu ZF, Huang CZ (1998) Anal Sci 14:799
Liu SP, Liu ZF, Luo HQ (2000) Anal Chim Acta 407:255
Pasternack RF, Collings PJ (1995) Science 269:935
Liu SP, Liu ZF (1995) Spectrochim Acta 51A:1178
Edition of Editorial Board of Chinese Macropaedia (1991) Chinese macropaedia biology. Chinese Macropaedia Press, Beijing, p 1374
Mukhamedzyanov RM, Lihoded VA (1991) Antibiot Khimioter 36:14
Xi YX, Lang HY, Xie ZH (1996) J Xi'an Jiaotong Univ 30:104
Yuan C, Jia L, Wang JX (1999) Chin J Pharm Anal 19:108
Fang B, Hu SS, Li PB (1989) Chin J Anal Chem 17:636
Naveh A (1984) J Appl Bacteriol 56:457
Gaikwad A, Gómez-Hens A, Pérez-Bendito D (1993) Anal Lett 26:97
The Medical Executive Department of Sanitation Ministry of The People's Repulic of China (1997) National clinic analysis procedure, 2nd edn. Southeast University Press, Nanjing, p 193
Wu LW (1989) Curative medicine monitoring. People's Sanitation Press, Beijing, p 380
Acknowledgements
This project is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hu, X.L., Liu, S.P. & Li, N. Resonance Rayleigh scattering spectra for studying the interaction of aminoglycoside antibiotics with pontamine sky blue and their analytical applications. Anal Bioanal Chem 376, 42–48 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-003-1878-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-003-1878-1