Abstract
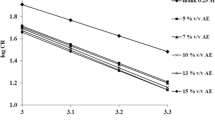
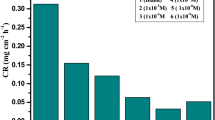
The passivation and pitting corrosion of tin in sodium gluconate (SG) solutions was studied by using potentiodynamic and cyclic voltammetric techniques. Some samples were examined by X-ray and SEM. The effect of the concentration of gluconate ion, pH, potential scanning rate, successive cyclic voltammetry, switching potential and progressive additions of halide ions on the passivation and pitting corrosion of a tin anode was discussed. The data obtained show that low concentrations of SG have an inhibition effect on the pitting corrosion of tin in neutral media. The pitting corrosion of tin increases with increasing SG concentrations due to the formation of soluble tin-gluconate complex. The critical pitting potential depends on the gluconate ion concentration, pH and scan rate. Two cathodic peaks are observed in the cathodic polarization curve, corresponding to the reduction of the dissolved pitting corrosion products. The critical pitting potential shifts progressively to more negative values with increasing halide ion concentration. In all experiments, the aggressive action of halides decreased in the order Cl−>Br−>I−.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. R. Willey,Br. Corros. J. 7 (1972) 29.
V. K. Gouda, E. N. Rizkalla, S. Abd El Wahab and E. M. Ibrahim,Corros. Sci. 1 (1981) 21.
J. C. Sherlock and S. C. Britton,Br. Corros. J. 8 (1973) 210.
H. Leidheiser Jr., A. F. Rauch, E. M. Ibrahim and R. D. Granata,J. Electrochem. Soc. 129 (1982) 1657.
M. Pugh, L. M. Warner and D. R. Gabe,Corros. Sci. 7 (1967) 807.
M. S. Abdel Aal and F. H. Assaf,J. Electrochem. Soc. India 30-1 (1981) 38.
A. M. Azzam, S. S. Abd El Rehim and M. H. Fawzy,J. Appl. Chem. Biotech. 23 (1973) 563.
F. M. Abd El Wahab, J. M. Abd El Kader, H. A. El Sayed and A. M. Shams El Din,Corros. Sci. 18 (1978) 997.
T. Dickinson and S. Lotfi,Electrochim. Acta 23 (1978) 513.
H. Do Duc and P. Tissot,Corros. Sci. 19 (1979) 179.
S. S. Abd El Rehim, A. El Sayed and A. A. El Samahi,Surf. Coat. Technol. 27 (1986) 205.
S. S. Abd El Rehim, A. A. El Samahi and A. El Sayed,Br. Corros. J. 20 (1985) 196.
E. Mor and G. Bonino, Proceedings of the 3rd European symposium on Corrosion Inhibitors, University of Ferrara, Ferrara, (1970), p. 659.
E. Mor and C. Wrubl,Br. Corros. J. 11 (1976) 199.
M. W. Ranney, Corrosion Inhibitors Manufacture and Technology, Noyes, Park Ridge, NJ (1976) p. 30.
L. Zhu and Z. Shi-zhong,J. East China Inst. Chem. Technol., Shanghai (1985) 338.
C. Wrubl, E. D. Mor and U. Montini, Proceedings of the 6th European symposium on Corrosion Inhibitors, University of Ferrara, Ferrara, (1985), p. 557.
J. S. Roti and P. A. Thomas, Proc. Corrosion '84 NACE conference, New Orleans, LA Houston, TX (1984), p. 318.
O. Lahodny-Sare,RAD Yugoslav Acad. Sci. Arts 394(18) (1982) 1.
O. Lahodny-Sare, Proceedings of the 5th European symposium on Corrosion Inhibitors, University of Ferrara, Ferrara (1980), p. 609.
A. M. Shams El Din and F. M. Abd El Wahab,Electrochim. Acta 9 (1964) 883.
N. N. Zagoskin, S. V. Shishkina and A. G. Morachevskii,Zh. Prikl. Khim. 63(8) (1990) 1818.
N. Hampson and N. E. Spencer,Br. Corros. J. 3 (1968) 1.
T. N. Maksin, B. Z. Zmbova and D. S. Veselinovic,J. Serb. Chem. Soc. 56(6) (1991) 334–341.
S. Goldstone, ‘Textbook of Physical Chemistry’, 2nd ed., Van Nostrand, London (1956), p. 945.
J. M. West, ‘Electrodeposition and Corrosion Processes’ Van Nostrand Reinhold, London (1970) p. 123.
F. A. Cotton, G. Wilkinson, ‘Advanced Inorganic Chemistry’, John Wiley & Sons, 3rd ed., London (1972) p. 475.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Refaey, S.A.M. Passivation and pitting corrosion of tin in gluconate solutions and the effect of halide ions. J Appl Electrochem 26, 503–507 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01021973
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01021973