Abstract
In this chapter, we shall introduce a shuffled linear regression model for joint data decoding and device identification in IoT networks. It is first formulated as a maximum likelihood estimation (MLE) problem. To solve this MLE problem, two algorithms are presented: one is based on sorting, and the other algorithm returns an approximate solution to the MLE problem. Next, theoretical analysis on the shuffled linear regression based on the algebraic-geometric theory is presented. Based on the analysis, an algebraically initialized expectation-maximization algorithm is introduced to solve the problem.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Notes
- 1.
We do not distinguish between p and
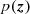 .
.
References
Abid, A., Zou, J.: A stochastic expectation-maximization approach to shuffled linear regression. In: Proceedings of the 56th Annual Allerton Conference on Communication, Control, and Computing, pp. 470–477. IEEE, Piscataway (2018)
Abid, A., Poon, A., Zou, J.: Linear regression with shuffled labels (2017). Preprint. arXiv:1705.01342
Boutsidis, C., Drineas, P., Magdon-Ismail, M.: Near-optimal coresets for least-squares regression. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory. 59(10), 6880–6892 (2013)
Hsu, D.J., Shi, K., Sun, X.: Linear regression without correspondence. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS), pp. 1531–1540 (2017)
Lazard, D.: Thirty years of polynomial system solving, and now? J. Symb. Comput. 44(3), 222–231 (2009)
Lian, W., Zhang, L., Yang, M.H.: An efficient globally optimal algorithm for asymmetric point matching. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 39(7), 1281–1293 (2016)
Marques, M., Stosić, M., Costeira, J.: Subspace matching: unique solution to point matching with geometric constraints. In: Proceedings of the International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 1288–1294. IEEE, Piscataway (2009)
Narayanan, A., Shmatikov, V.: Robust de-anonymization of large sparse datasets. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy, pp. 111–125 (2008)
Pananjady, A., Wainwright, M.J., Courtade, T.A.: Linear regression with shuffled data: statistical and computational limits of permutation recovery. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 64(5), 3286–3300 (2018)
Peng, L., Song, X., Tsakiris, M.C., Choi, H., Kneip, L., Shi, Y.: Algebraically-initialized expectation maximization for header-free communication. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Acoustics Speech Signal Processing (ICASSP), pp. 5182–5186 (2019)
Pradhan, S.S., Kusuma, J., Ramchandran, K.: Distributed compression in a dense microsensor network. IEEE Signal Process. Manag. 19(2), 51–60 (2002)
Scaglione, A., Servetto, S.: On the interdependence of routing and data compression in multi-hop sensor networks. Wirel. Netw. 11(1–2), 149–160 (2005)
Slawski, M., Ben-David, E., et al.: Linear regression with sparsely permuted data. Electron. J. Stat. 13(1), 1–36 (2019)
Tsakiris, M.C., Peng, L.: Homomorphic sensing. In: Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML), pp. 6335–6344 (2019)
Tsakiris, M.C., Peng, L., Conca, A., Kneip, L., Shi, Y., Choi, H.: An algebraic-geometric approach to shuffled linear regression (2018). Preprint. arXiv: 1810.05440
Unnikrishnan, J., Haghighatshoar, S., Vetterli, M.: Unlabeled sensing with random linear measurements. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory. 64(5), 3237–3253 (2018)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2020 Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Shi, Y., Dong, J., Zhang, J. (2020). Shuffled Linear Regression. In: Low-overhead Communications in IoT Networks. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-15-3870-4_5
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-15-3870-4_5
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-15-3869-8
Online ISBN: 978-981-15-3870-4
eBook Packages: EngineeringEngineering (R0)


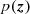 .
.