Abstract
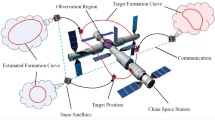
X-ray pulsar navigation is a critical and frontier technology for spacecraft’s autonomous navigation in future. Now an effective database of pulsars angle position with high precision has not been developed. The precision of pulsar angle position measurement could be greatly improved by observing a pulsar jointly at the same time with several satellites. While observing the same pulsar the satellites have to set their attitude and orbit coordinately. There should be a constraint of tasks, spatial graphs, agreements and time in the observing process. In paper a plan of observing a pulsar at the same time by several satellites is put forward, a method of multi-satellites coordinated control is presented, and a digital experiment is carried out for simulating the proposed scheme. As results, the plan is feasible, the controller of the satellites orbit position and attitude is stable, the plan and control method is especially suitable for X-ray pulsar interferometry so that the accuracy of pulsar angle position can be improved by observation with multi-satellites formation.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ren W, Beard RW. Distributed consensus in multi-vehicle coordinated control: theory and application. Publishing House of Electronics Industry;2014. p. 223–45.
Liu J. Simulation of sliding mode variable structure control. Beijing: The Press of Tsinghua University;2014. p. 495–539.
Vassar RH. Formation keeping for a pair of satellite in a circular orbit. J Guid Control Dyn. 1985;8(2):235–42.
Mcinnes CR et al. Autonomous ring formation for a planar constellation of satellites. J Guid Control Dyn. 1995;18(5):1215–7.
Terui F. Position and attitude control of a spacecraft by sliding mode control. Trans Jpn Soc Mech Eng C. 1998;64(621):1691–8.
Gaulocher S. Modeling the coupled translational and rotational relative dynamics for formation flying control. In: AIAA guidance, navigation, and control conference and exhibit. San Francisco, California, 2005. AIAA;2005-6091.
Ren W. Formation keeping and attitude alignment for multiple spacecraft through local interactions. J Guid Control Dyn. 2007;30(2):633–8.
Yunhua W, Xibin C. Coupling control of relative orbit and attitude for formation satellites. J Nanjing Univ Aeronaut Astronaut. 2010;42(1):13–20.
Liu Y, Jia Y. Formation control of discrete-time multi-agent systems by iterative learning approach. Int J Control Autom Syst. 2012;10(5):913–9.
Zhao L, Jia Y. Decentralized adaptive attitude synchronization control for spacecraft formation using nonsingular fast terminal sliding mode. Nonlinear Dyn. 2014;78:2779.
Huang Y, Jia Y, Matsuno F. Robust H∞ control for spacecraft formation flying with coupled translational and rotation dynamics. In: American Control Conference;2016. p. 4059–64.
Acknowledgements
Supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (Grant No. 2017YFB0503300, 2017YFB0503304).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2018 Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this paper
Cite this paper
Chen, Q., Bei, X., Zhang, H., Zhang, J. (2018). Coordinated Control of Multi-satellites Formation Flying for Pulsar Observation. In: Jia, Y., Du, J., Zhang, W. (eds) Proceedings of 2017 Chinese Intelligent Systems Conference. CISC 2017. Lecture Notes in Electrical Engineering, vol 459. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-10-6496-8_53
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-10-6496-8_53
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-10-6495-1
Online ISBN: 978-981-10-6496-8
eBook Packages: EngineeringEngineering (R0)