Abstract
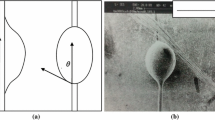
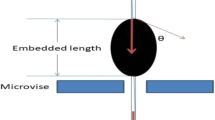
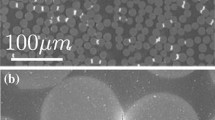
Three micromechanical teat methods to measure the interface shear strength in polymer matrix composites are reviewed. The classical pull-out test and the newer push-in test both offer specific advantages, but the actually used analysis schemes are shown to be often too elementary. We present a more complete micromechanical analysis of a third experiment, namely the fragmentation test. It is shown theoretically that, for increasing applied strains, the fibre aspect ratio can reach values which are lower than those predicted by Kelly’s shear-lag model. A method is proposed to estimate the different components of the interface shear strength, i.e. the bond shear strength, the friction strength and the matrix yield strength.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- D:
-
fibre diameter (m)
- Ef :
-
fibre Young’s modulus (MPa)
- Em :
-
matrix Young’s modulus (MPa)
- Fdeb :
-
force needed to provoke debonding a t the interface (N)
- Fpo :
-
maximum load applied to the fibre to pull the fibre out of the matrix (N)
- Fpi :
-
maximum load necessary to de bond the fibre completely in the push-in test (N)
- Ffr :
-
maximum load necessary to break the fibre (N)
- Gm :
-
matrix shear modulus (MPa)
- L:
-
fibre length (m)
- Lc :
-
critical fibre length (m)
- m:
-
dimensionless length of the fibre inelastic zone
- n:
-
elastic constant
- r:
-
fibre radius (m)
- s:
-
fibre aspect ratio (LID)
- sc :
-
critical fibre aspect ratio
- T:
-
thickness of the specimen (m)
- Vf :
-
fibre volume fraction
- x:
-
coordinate along the fibre axis
- α:
-
elastic constant, function of the fibre and matrix elastic properties
- ∈1 :
-
strain applied at the specimen (in the fibre direction)
- ∈mr :
-
fracture strain of the matrix
- ∈fr :
-
fracture strain of the fibre
- σfr :
-
tensile strength of the fibre (MPa)
- σf :
-
tensile stress in the fibre (MPa)
- σf, max :
-
maximum tensile stress in the fibre due to elastic stress transfer (MPa)
- τav, po :
-
average interfacial shear strength measured by the pull-out test (MPa)
- τav, pi :
-
average interfacial shear strength measured by the push-in test (MPa)
- τav, fr :
-
average interfacial shear strength measured by the fragmentation test
- τdeb :
-
bond shear strength of the interface (MPa)
- τe :
-
shear stress at the interface (MPa)
- τe, max :
-
maximum shear stress at the interface (MPa)
- τi :
-
constant shear stress at the fibre ends (MPa)
- τi, fr :
-
frictional shear strength of the interface (MPa)
- τmax’ po :
-
maximum average shear strength measured by the pull-out test (MPa)
- τmy :
-
matrix yield strength (MPa)
References
COX, H.L., Br. J. Appl. Phys., 3, (1952), 72
ROSEN, W., AIAA Journal, 2, N° 11, (1964), 1985
KELLY, A., DAVIES, G.J., Metallurgical reviews, 10, N° 37, (1965), 1
TYSON, W.R., DAVIES, G.J., Br. J. Appl. Phys., 16, (1965), 199
PIGGOTT, M.R., Acta Metallurgica, 14, nov., (1966), 1429
THEOCARIS, P.S., in “The role of the polymeric matrix in the processing and structural properties of composite materials”, Edited by Seferis,J.C., Nicolais, L., Plenum press, (1983), 481
GRESZCZUK, L., Interfaces in composites, American Society for testing and materials, S.T.P. 452, (1969), 42
PITKETHLY, M.P., DOBLE, J.B., in “Interfacial phenomena in composite materials” (IPCM ‘89), Editor F.R. Jones, Butterworths Scientific, (1989), 35
BARTOS, P., J. of Mat. Sci., 15, (1980), 3122
VLASSAK, J., Micromechanical study of the fibre-matrix adhesion in polymer matrix composites“, Eng. Thesis, MTM, K.U.Leuven, (1989) (in dutch)
MARSHALL, D.B., OLIVER, W.C., J. Am. Ceramic. Soc., 70 (8), (1987), 542
GRANDE, D.H., MANDELL, J.F., HONG, K.C.C., J. of Mat. Sci., 23, (1988), 311
WEIHS, T., NIX, W., Scripte Metallurgica, 22, (1988), 271
NETRAVALY, A.N., Composite Science and technology, 34, (1989), 289
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 1990 Elsevier Science Publishing Co., Inc.
About this paper
Cite this paper
Verpoest, I., Desaeger, M., Keunings, R. (1990). Critical Review of Direct Micromechanical Test Methods for Interfacial Strength Measurements in Composites. In: Ishida, H. (eds) Controlled Interphases in Composite Materials. Springer, Dordrecht. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-011-7816-7_60
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-011-7816-7_60
Publisher Name: Springer, Dordrecht
Print ISBN: 978-94-011-7818-1
Online ISBN: 978-94-011-7816-7
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive