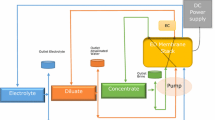
Abstract
The production of commercial quantities of chlorine gas and alkali-metal-hydroxides is performed by electrolysis of brine solutions in a chloralkali cell.
The most advanced technology for this process requires membrane electrolysis cells. For good performance of these cells there is a demand for high purity brines with extremely low levels of divalent cations ( magnesium, calcium, strontium ) and low levels of sulphate anions.
The following discussion describes how ion exchangers with chelating functional groups meet the required specifications.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Klipper, R.M., Hoffmann, H., Mitschker, A., Wagner, R., The influence of morphology and degree of substitution on the selectivity of chelating resins, Ion exchange for Industry, Ellis Horwood Limited, p.243 ( 1988 ).
German Offenlegungsschrift, DE 3345898.
Fields, E.K., J.Amer. Chem. Soc., 74, p.1528 ( 1952 ).
( 4 )Kabachnik, M.J., Medved, T.V., Dokl. Akad. Nauk SSSR, 83, p.689 ( 1952 ).
Moedritzer, K., Irani, R.R., J. Organ. Chem., 31, p.1603 ( 1966 ).
Ullmanns Enzyklopadie der technischen Chemie, Band 13, p.295–308.
Krauß, D., Sabrowski, E., Schwachula, G., Funktionalisierte Polyrnere auf Acrylatbasis I, Plaste und Kautschuk, 29, p.449–451 ( 1982 ).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 1992 United Kingdom Atomic Energy Authority
About this paper
Cite this paper
Klipper, R.M., Hoffmann, H., Augustin, T. (1992). The Removal of Divalent Anions and Cations from Feed Brine for Chloralkali-Electrolysis Cells by Utilization of Ion Exchange Technology. In: Slater, M.J. (eds) Ion Exchange Advances. Springer, Dordrecht. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-011-2864-3_54
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-011-2864-3_54
Publisher Name: Springer, Dordrecht
Print ISBN: 978-1-85166-882-3
Online ISBN: 978-94-011-2864-3
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive