Abstract
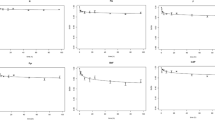
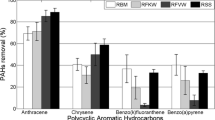
Biodegradation of PAH-contaminated soil was studied by a slurry reactor test and a soil column test. The initial total concentration 1000 ppm PAH soil was decreased to 50…100 ppm in the slurry reactor in 6 weeks. In the soil columns the concentration was decreased to 120…770 ppm in 4 weeks. Addition of coniferous tree bark enhanced degradation significantly in the soil column tests, but not in slurry reactor tests. Use of inoculants had only a slight positive effect in slurry tests; the effect was even negative in the degradation of 5–6 ring compounds in some soil column tests.
The experiences were applied to practical scale by using a composting method where bark is used as a bulking agent. High moisture content is maintained in the heap and the leaching water is circulated until the target concentration is reached. The different functions of the bark addition is discussed.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Civilini, M. (1994), Fate of creosote compounds during compostin, Microbiology Europe, vol 2, no 6, 16–24.
Fengel, D., Wegener, G. (1984) Wood Chemistry, Ultrastructure reactions, Walter de Gruyter, Berlin and New York.
Freeman, H.M., Sferra, PR. (eds),(1991), Innovative Hazardous Waste treatment technology series vol 3, Technomic Publishing Co., Pennsylvania USA.
Keck, J., Sims, R.C., Coover, M., Park, K., Symons, B. (1989), Evidence for cooxidation of polynuclear aromatic hydrocarbons in soil, Wat. Res., vol 23, no 12, 1467–1476.
Linz, D.G., Neuhauser, F., Middleton, A.C. (1991), Perspectives on bioremediation in the gas industry, in Sayler, G.S. et.al. (1991), 25–36.
Ministry of the Environment of Finland (1994), Contaminated soil site survey and remediation project, Helsinki.
Müeller, J.G., Lantz, S.E., Blattmann, B.O., Chapman, P.J. (1991), Bench-scale evaluation of alternative biological treatment processes for the remediation of pentachlorophenol- an creosote-contaminated materials: slurry-phase bioremediation, Environ. Sci. Technol. vol 25, no 6, 1055–1061.
Müeller, J.G., Lantz, S.E., Ross, D., Colvin, R.J., Middaugh, D.P., Pritchard, P.H. (1993), Strategy using bioreactors and specially selected microorganisms for bioremediation of groundwater contaminated with creosote and pentachlorophenol, Environ. Sci. Technol. vol 27, no 4,691…698.
Pollard, S.J.R., Hrudey, S.E., Fedorak, P.M. (1994), Bioremediation of petroleum- and creosote-contaminated soils: a review of constraints, Waste Management & Research vol 12, 173…194.
Sayler, G.S., Fox, R., Blackburn, J.W. (eds.) (1991), Environmental Biotechnology for Waste Treatment, Environmental Sci. Research vol 41, Plenum Press, New York.
Seman, P-O., Svedberg, R. (1990), Sanering av kreosotkontaminerad mark, Swedish Wood Preservation Institute, Reports no 162, Stockholm (in Swedish).
Silvennoinen, H., Uotila, J., Lilja, R., Laakso, P. (1994), Petäjäveden kreosoottipitoisen maa-aineksen ja sedimentin biohajoavuus, Final report 30.6.1994, Imatran Voima Oy, ympäristönsuojeluyksikkö, Helsinki, (in Finnish). (Biodegradability of the PAH-contaminated soil and sediment from Petäjävesi).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 1996 Springer Science+Business Media Dordrecht
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Lilja, R., Uotila, J., Silvennoinen, H. (1996). Bioremediation of PAH-Contaminated Soil. In: de Bertoldi, M., Sequi, P., Lemmes, B., Papi, T. (eds) The Science of Composting. Springer, Dordrecht. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-009-1569-5_86
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-009-1569-5_86
Publisher Name: Springer, Dordrecht
Print ISBN: 978-94-010-7201-4
Online ISBN: 978-94-009-1569-5
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive