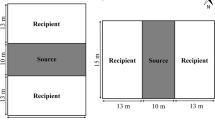
Abstract
In recent years, an attention to the gene flow problem of dispersal of artificially modified genes to the natural environment by airborne pollen is increasing rapidly. Especially for wind-pollinated crop, there is a possibility that pollen diffuses quite widely depending on meteorological conditions. In order to deal with such problems, it is necessary to develop the model that can estimate the pollen dispersal and the hybridization mating appropriately. In this paper, I present an aerobiological mechanistic model for assessing pollen dispersal and hybridization using hourly data. This model considers hourly change of the meteorological conditions and daily change of biological conditions. And it was constructed for estimating the spatial distribution of hybridization percentage in a recipient field. The effectiveness of the model was certified by the field experiments. The model was constructed in consideration of physical processes and biological processes. The algorithms presented here can be applied to estimate the total pollen deposition and hybridization mating for many kinds of plants.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gliddon CJ (1999) Gene flow and risk assessment. In: Lutman PJW (ed) Gene flow and agriculture. Relevance for transgenic crops. Proceedings of a conference, University of Keele. British Crop Protection Council, Farnham, Surrey, pp 49–56
Kawashima S, Matsuo K, Du M, Oka M, Daido H, Takahashi Y, Kobayashi T, Inoue S, Yonemura S (2002) Relationship between percentage of wind-pollinated maize hybrids and distance from donor pollen source. Jpn J Palyn 48:1–12
Kwon YW, Kim DS, Yim K-O (2001) Herbicide-resistant genetically modified crop: assessment and management of gene flow. Weed Biol Manage 1:96–107
Lavigne C, Klein EK, Couvet D (2002) Using seed purity data to estimate an average pollen mediated gene flow from crops to wild relatives. Theor Appl Genet 104:139–145
Losey JE, Raynor LS, Carter ME (1999) Transgenic pollen harms monarch larvae. Nature 399:214
Louette D, Charrier A, Berthand J (1997) In situ conservation of maize in Mexico: genetic diversity and maize seed management in a traditional community. Econ Bot 51:20–38
Quist D, Chapela IH (2001) Transgenic DNA introgressed into traditional maize landraces in Oaxaca, Mexico. Nature 414:541–543
Richards CM, Church S, McCauley DE (1999) The influence of population size and isolation on gene flow by pollen in silene alba. Evolution 53:63–73
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2011 Springer Science+Business Media B.V.
About this paper
Cite this paper
Kawashima, S., Hama, T. (2011). Pollen Dispersal and Hybridization Model for Risk Assessment of Genetically Modified Crops. In: Steyn, D., Trini Castelli, S. (eds) Air Pollution Modeling and its Application XXI. NATO Science for Peace and Security Series C: Environmental Security. Springer, Dordrecht. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-007-1359-8_118
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-007-1359-8_118
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Dordrecht
Print ISBN: 978-94-007-1358-1
Online ISBN: 978-94-007-1359-8
eBook Packages: Earth and Environmental ScienceEarth and Environmental Science (R0)