Abstract
Outsourcing computation to remote parties (“workers”) is an increasingly common practice, owing in part to the growth of cloud computing. However, outsourcing raises concerns that outsourced tasks may be completed incorrectly, whether by accident or because workers cheat to minimize their cost and optimize their gain. The goal of this paper is to explore, using game theory, the conditions under which the incentives for all parties can be configured to efficiently disincentivize worker misbehavior, either inadvertent or deliberate. By formalizing multiple scenarios with game theory, we establish conditions to discourage worker cheating that take into account the dynamics of multiple workers, workers with limited capacity, and changing levels of trust. A key novelty of our work is modeling the use of a reputation system to decide how computation tasks are allocated to workers based on their reliability, and we provide insights on strategies for using a reputation system to increase the expected quality of results. Overall, our results contribute to make outsourcing computation more reliable, consistent, and predictable.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Notes
- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 5.
- 6.
- 7.
2.3% and 3.9% in the second and third quarters of 2013, respectively, according to a Kaspersky Lab study (http://www.kaspersky.ca/internet-security-center/threats/spam-statistics-report-q2-2013).
- 8.
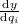 is the derivative of y with respect to \(q_i\).
is the derivative of y with respect to \(q_i\).
References
Aljuraidan, J., Bauer, L., Reiter, M.K., Beckerle, M.: Introducing reputation systems to the economics of outsourcing computations to rational workers. Technical report CMU-CyLab-16-001, Carnegie Mellon University, January 2016
Anati, I., Gueron, S., Johnson, S., Scarlat, V.: Innovative technology for CPU based attestation and sealing. In: Workshop on Hardware and Architectural Support for Security and Privacy (2013)
Awerbuch, B., Kutten, S., Peleg, D.: Competitive distributed job scheduling (extended abstract). In: 24th ACM Symposium on Theory of Computing, pp. 571–580 (1992)
Belenkiy, M., Chase, M., Erway, C.C., Jannotti, J., Küpçü, A., Lysyanskaya, A.: Incentivizing outsourced computation. In: Proceedings of the 3rd International Workshop on Economics of Networked Systems, NetEcon 2008 (2008)
Briggs, H.: Optimal cartel trigger strategies and the number of firms. Rev. Ind. Organ. 11(4), 551–561 (1996)
Commerce, B.E., Jsang, A., Ismail, R.: The beta reputation system. In: 15th Bled Electronic Commerce Conference (2002)
Friedman, J.W.: A non-cooperative equilibrium for supergames. Rev. Econ. Stud. 38(1), 1–12 (1971)
Goldwasser, S., Kalai, Y.T., Rothblum, G.N.: Delegating computation: interactive proofs for muggles. In: 40th ACM Symposium on Theory of Computing, May 2008
Hoekstra, M., Lal, R., Pappachan, P., Rozas, C., Phegade, V., del Cuvillo, J.: Using innovative instructions to create trustworthy software solutions. In: Workshop on Hardware and Architectural Support for Security and Privacy (2013)
Ishai, Y., Kushilevitz, E., Ostrovsky, R.: Efficient arguments without short PCPs. In: 22nd IEEE Conference on Computational Complexity, June 2007
Jøsang, A., Ismail, R., Boyd, C.: A survey of trust and reputation systems for online service provision. Decis. Support Syst. 43(2), 618–644 (2007)
Kerr, R., Cohen, R.: Smart cheaters do prosper: defeating trust and reputation systems. In: AAMAS 2009, pp. 993–1000 (2009)
Krugman, P.R.: Trigger strategies and price dynamics in equity and foreign exchange markets. Technical report 2459, National Bureau of Economic Research (1987)
Mckeen, F., Alexandrovich, I., Berenzon, A., Rozas, C., Shafi, H., Shanbhogue, V., Savagaonkar, U.: Innovative instructions and software model for isolated execution. In: Workshop on Hardware and Architectural Support for Security and Privacy (2013)
Nojoumian, M., Lethbridge, T.C.: A new approach for the trust calculation in social networks. In: Filipe, J., Obaidat, M.S. (eds.) ICETE 2006. CCIS, vol. 9, pp. 64–77. Springer, Heidelberg (2008). doi:10.1007/978-3-540-70760-8_6
Nojoumian, M., Stinson, D.R.: Socio-rational secret sharing as a new direction in rational cryptography. In: Grossklags, J., Walrand, J. (eds.) GameSec 2012. LNCS, vol. 7638, pp. 18–37. Springer, Heidelberg (2012). doi:10.1007/978-3-642-34266-0_2
Penmatsa, S.: Game theory based job allocation/load balancing in distributed systems with applications to grid computing. Ph.D. thesis, The University of Texas at San Antonio (2007)
Pham, V., Khouzani, M.H.R., Cid, C.: Optimal contracts for outsourced computation. In: Poovendran, R., Saad, W. (eds.) GameSec 2014. LNCS, vol. 8840, pp. 79–98. Springer, Cham (2014). doi:10.1007/978-3-319-12601-2_5
Porter, R.H.: Optimal cartel trigger price strategies. J. Econ. Theor. 29(2), 313–338 (1983)
Schuster, F., Costa, M., Fournet, C., Gkantsidis, C., Peinado, M., Mainar-Ruiz, G., Russinovich, M.: VC3: trustworthy data analytics in the cloud using SGX. In: 36th IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy, May 2015
Teacy, W., Patel, J., Jennings, N., Luck, M.: Travos: trust and reputation in the context of inaccurate information sources. Auton. Agent. Multi-Agent Syst. 12(2), 183–198 (2006)
Tran, T., Cohen, R.: Improving user satisfaction in agent-based electronic marketplaces by reputation modelling and adjustable product quality. In: AAMAS 2004, pp. 828–835 (2004)
Trusted Computing Group: Trusted platform module main specification, version 1.2, revision 103 (2007)
Walfish, M., Blumberg, A.J.: Verifying computations without reexecuting them. Commun. ACM 58(2), 74–84 (2015)
Whitby, A., Jøsang, A., Indulska, J.: Filtering out unfair ratings in Bayesian reputation systems. In: Proceedings of 7th International Workshop on Trust in Agent Societies, vol. 6, pp. 106–117 (2004)
Yagoubi, B., Medebber, M.: A load balancing model for grid environment. In: 22nd International Symposium on Computer and Information Sciences, pp. 1–7 (2007)
Acknowledgments
This work was supported in part by NSF grant 1330599 and by the Army Research Laboratory under Cooperative Agreement Number W911NF-13-2-0045 (ARL Cyber Security CRA). The views and conclusions contained in this document are those of the authors and should not be interpreted as representing the official policies, either expressed or implied, of the Army Research Laboratory or the U.S. Government. The U.S. Government is authorized to reproduce and distribute reprints for Government purposes notwithstanding any copyright notation here on.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2017 International Financial Cryptography Association
About this paper
Cite this paper
Aljuraidan, J., Bauer, L., Reiter, M.K., Beckerle, M. (2017). Introducing Reputation Systems to the Economics of Outsourcing Computations to Rational Workers. In: Grossklags, J., Preneel, B. (eds) Financial Cryptography and Data Security. FC 2016. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 9603. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-662-54970-4_4
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-662-54970-4_4
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-662-54969-8
Online ISBN: 978-3-662-54970-4
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)


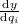 is the derivative of y with respect to
is the derivative of y with respect to