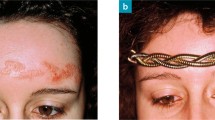
Abstract
Nummular eczema is a noninfectious inflammatory dermatosis with multifactorial trigger etiology in combination with epidermal barrier dysregulation. It is characterized by severe pruritus and well-demarcated coin-shaped lesions and, in many cases, refractory course of disease. Elimination of trigger factors in combination with topical and systemic anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial therapy according to stage of disease is essential. Topical treatment of first choice during the acute stage (vesicles, erosion, exudation) is corticosteroids in combination with desiccating, antiseptic solutions and wet bandages. In subacute and chronic eczema, topical corticosteroids as pastes and calcineurin inhibitors are recommended. In disseminated or relapsing eczema, combination with phototherapy can be useful. Systemic antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory therapy (antibiotics, corticosteroids) is indicated in severe cases or recurrent refractory eczema. In single cases immunosuppressive therapy with other agents (ciclosporin, methotrexate) may be necessary to achieve remission.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jiamton S, Tangjaturonrusamee C, Kulthanan K. Clinical features and aggravating factors in nummular eczema in Thais. Asian Pac J Allergy Immunol. 2012;31:36–42.
Further Reading
Basler RS, Lynch PJ. Can you recognize and treat mycosis fungoides? Geriatrics. 1978;33(11):55–62.
Belknap BS, Dobson RL. Efficacy of halcinonide cream, 0,1 percent, in the treatment of moderate and severe dermatoses. Cutis. 1981;27(4):433–5.
Bettoli V, Tosti A, Varotti C. Nummular eczema during isotretinoin treatment. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1987;16(3 Pt 1):617.
Blum G, Yawalkar SJ. Evaluation of halometasone cream in the treatment of paediatric patients with acute eczematous dermatoses. J Int Med Res. 1983;11 Suppl 1:8–12.
Bos JD, van Garderen ID, Krieg SR, Poulter LW. Different in situ distribution patterns of dendritic cells having Langerhans (T6+) and interdigitating (RFD1+) cell immunophenotype in psoriasis, atopic dermatitis, and other inflammatory dermatoses. J Invest Dermatol. 1986;87(3):358–61.
Burgdorf WHC, Plewig G, Wolff HH, Landthaler M, editors. Braun-Falco’s dermatology. 3rd ed. Berlin: Springer; 2009.
Herz G, Yawalkar SJ, Weirich EG. Evaluation of halometasone ointment in the treatment of paediatric patients with chronic eczematous dermatoses. J Int Res. 1983;11 Suppl 1:21–5.
Hornstein OP. Remarks and recommendations on the definition and classification of eczematous diseases. Z Hautkr. 1986;61(18):1281–96.
Jansen T, Küppers U, Plewig G. Sulzberger-Garbe exudative discoid and lichenoid chronic dermatosis (“Oid-Oid disease”)—reality or fiction? Hautarzt. 1992;43(7):426–31.
Lange L, Rietschel E, Hunzelmann N, Hartmann K. Elevated levels of tryptase in children with nummular eczema. Allergy. 2008;63:941–50.
Moore MM, Elpern DJ, Carter DJ. Severe, generalized nummular eczema secondary to Interferon Alfa-2b plus Ribavirin combination therapy in a patient with chronic hepatitis C virus infection. Arch Dermatol. 2004;140:215–7.
Noren P, Melin L. The effect of combined topical steroid and habitreversal treatment in patients with atopic dermatitis. Br J Dermatol. 1989;121:359–66.
Parish WE, Welbourn E, Champion RH. Hypersensitivity to bacteria in eczema. IV. Cytotoxic effect of antibacterial antibody on skin cells acquiring bacterial antigens. Br J Dermatol. 1976;95:493–506.
Pavithran K. Non-pruritic eczemas as presenting manifestation of leprosy. Indian J Lepr. 1990;62(2):202–7.
Ring J, Przybilla B, Ruzicka T, et al., editors. Handbook of atopic eczema. 2nd ed. Berlin: Springer; 2005.
Ring J, Alomar A, Bieber T, Deleuran M, Fink-Wagner A, Gelmetti C, et al. Guidelines for treatment of atopic eczema (atopic dermatitis) part I. J Eur Acad Dermatol. Venereol. 2012a;26(8):1045-60.
Ring J, Alomar A, Bieber T, Deleuran M, Fink-Wagner A, Gelmetti C et al. Guidelines for treatment of atopic eczema (atopic dermatitis) Part II. J Eur Acad Dermatol. Venereol. 2012b;26(9):1176–93.
Roberts H, Orchard D. Methotrexate is a safe and effective treatment for paediatric discoid (nummular) eczema: a case series of 25 children. Australas J Dermatol. 2010;51(2):128–30.
Satoh T, Takayama K, Sawada Y, Yokozeki H, Nishioka K. Chronic nodular prurigo associated with nummular eczema: possible involvement of odontogenic infection. Acta Derm Venereol. 2003;83:376–7.
Veien NK, Hattel T, Justesen O, Nørholm A. Diagnostic procedures for eczema patients. Contact Dermatitis. 1987;17(1):35–40.
Volden G. Successful treatment of therapy-resistant atopic dermatitis with clobetasol propionate and a hydrocolloid occlusive dressing. Acta Derm Venereol Suppl (Stockh). 1992;176:126–8.
Yawalkar SJ, Macarol V, Maontanari C. An overview of international clinical trials with halometasone cream. J Int Med Res. 1983;11 Suppl 1:1–7.
Yawalkar SJ, Macarol V, Maontanari C. An overview of international clinical trials with halometasone ointment in chronic eczematous dermatoses. J Int Med Res. 1983;11 Suppl 1:13–20.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2015 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Todorova, A., Bruckbauer, H., Ring, J. (2015). Nummular Eczema. In: Katsambas, A.D., Lotti, T.M., Dessinioti, C., D’Erme, A.M. (eds) European Handbook of Dermatological Treatments. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-662-45139-7_67
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-662-45139-7_67
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-662-45138-0
Online ISBN: 978-3-662-45139-7
eBook Packages: MedicineMedicine (R0)