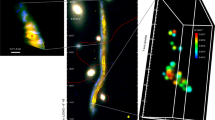
Abstract
Despite 30 years of molecular spectroscopy of dark clouds little is understood about the internal structure of these objects and consequently about the initial conditions that give rise to star and planet formation. This is largely due to the fact that molecular clouds are primarily composed of molecular hydrogen, which is virtually inaccessible to direct observation. The traditional methods used to derive the basic physical properties of these clouds therefore make use of observations of trace H2 surrogates, namely those rare molecules with sufficient dipole moments to be easily detected by radio spectroscopic techniques (e.g., Lada 1996, Myers 1999), and interstellar dust, whose thermal emission can be detected by radio continuum techniques (e.g., André et al. 2000). However, as discussed in the previous article in this book by M. Walmsley and collaborators, the interpretation of results derived from these methods is not always straightforward (see also Alves, Lada, & Lada 1999 and Zucconi, Walmsley, & Galli 2001). Several poorly constrained effects inherent in these techniques (e.g., deviations from local thermodynamic equilibrium, opacity variations, chemical evolution, small-scale structure, depletion of molecules, unknown emissivity properties of the dust, unknown dust temperature) make the construction of an unambiguous picture of the physical structure of these objects a very difficult task. There is a clear need for a less complicate and more robust tracer of H2 to access not only the physical structure of these objects but also to accurately calibrate molecular abundances and dust emissivity inside these clouds. The deployment of sensitive, large format infrared array cameras on large telescopes however, has fulfilled this need by enabling the direct measurement of the dust extinction toward thousands of individual background stars observed through the densest regions of a molecular cloud. Such measurements are free from the complications that plague molecular-line or dust emission data and enable detailed maps of cloud density structure to be constructed.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alves, J., Lada, C.J., Lada, E.A., Kenyon, S., & Phelps, R. 1998, ApJ, 506, 292
Alves, J., Lada, C.J., & Lada, E.A. 1999, ApJ, 515, 265
Alves, J., Lada, C.J., & Lada, E.A. 2001, Nature, 409, 159
André, P., Ward-Thompson, D., & Barsony, M. 2000, Protostars and Planets IV, (Tucson: University of Arizona Press), eds. Mannings, V., Boss, A.P., Russell, S.S.
Bergin, E., Ciardi, D., Lada, C., Alves, J., Lada, E. 2001, 557, 209
Bok, B. & Reilly, E. 1947, ApJ, 105, 255
Bourke, T., Hyland, A., Robinson, G., James, S. Wright, C. 1995, MNRAS, 276, 1067
de Geus, E., de Zeeuw, P. & Lub, J. 1989, A&A, 216, 44
Fiege, J., & Pudritz, R. 2000, MNRAS, 311, 85
Harvey, D., Wilner, D., Lada, C., Myers, P., Alves, J., Chen, H. 2001, ApJ, in press
Kramer, C., Alves, J., Lada, C., Lada, E., Sievers, A., Ungerechts, H., Walmsley, M. 1997, A&A, 329, 33
Kramer, C., Alves, J., Lada, C.J., Lada, E.A., Sievers, A., Ungerechts, H., Walmsley, C.M. 1999, A&A, 342, 257
Lada, C.J., Lada, E.A., Clemens, D.P., & Bally, J. 1994, ApJ, 429, 694
Lada, C.J. 1996, Proceedings of IAU Symposium CO: Twenty—Five Years of Millimeter-Wave Spectroscopy, eds. W.B. Latter et al., (Kluwer-Dordrecht), 387
Lada, C.J., Alves, J., Lada, E.A. 1999, ApJ, 512, 250
Launhardt, R. & Henning, T. 1997, A&A 326, 329
Lombardi, M. & Alves, J. 2001, A&A, in press
Ostriker, J. 1964, ApJ, 140, 1056
Reipurth, B. 1983, A&A, 117, 183
Reipurth, B., Nyman, L. & Chini, R. 1996, A&A, 314, 258
Thoraval, S., Boissé, P., Duvert, G. 1999, A&A, 351, 1051
Zucconi, A., Walmsley, M., Galli, D. 2001, A&A, in press
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2002 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Alves, J., Lada, C., Lada, E., Lombardi, M., Bergin, E.A. (2002). Molecular Cloud Structure: The VLT View. In: Alves, J.F., McCaughrean, M.J. (eds) The Origins of Stars and Planets: The VLT View. ESO Astrophysics Symposia. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-662-40277-1_4
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-662-40277-1_4
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-662-39255-3
Online ISBN: 978-3-662-40277-1
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive