Abstract
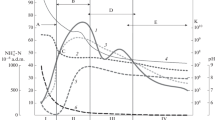
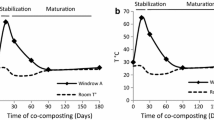
Community level physiological profiles (CLPPs) tested with Biolog microplates were studied for a maturity sequence of compost from source-separate collected organic waste and prunings. The composts were 42, 120 and 240 days old. Traditional maturity parameters like microbial biomass, pH and temperature significantly decreased with age. Principal component analysis and discriminant analysis showed distinctly different patterns of carbon source utilisation of the different composts. Five substrates were identified that significantly contributed to the difference in CLPPs.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson JPE, Domsch KH (1978) A physiological method for quantitative measurement of microbial biomass in soils. Soil Biol Biochem 10: 215 - 221
Bernal MP, Paredes C, Sanchez-Monedero MA, Cegarra J (1998) Maturity and stability parameters of composts prepared with a wide range of organic wastes. Biores Technol 63: 91 - 99
Carpenter-Boggs L, Kennedy AC, Reganold JP (1998) Use of phospholipid fatty acids and carbon source utilisation patterns to track microbial community succession in developing compost. Appl Environ Microbiol 64: 4062 - 4064
Choi K-H, Dobbs FC (1999) Comparison of two kinds of Biolog microplates ( GN and ECO) in their ability to distinguish among aquatic microbial communities. J Microbiol Meth 36: 203-213
Forster J (1995) Determination of soil pH. In: Alef K, Nannipieri P (eds) Methods in Applied Soil Microbiology and Biochemistry. Academic Press, Tokyo, p 55
Gajdos R (1992) The use of organic waste materials as organic fertilizers-recycling of plant nutrients. Acta Hortic 302: 325 - 331.
Garland JL (1996) Patterns of potential C source utilisation by rhizosphere communities. Soil Biol Biochem 28: 223 - 230
Garland JL, Mills AL (1991) Classification and characterisation of heterotrophic microbial communities on the basis of patterns of community-level sole-carbon-source utilisation. Appl Environ Microbiol 57: 2351 - 2359
Guckert JB, Can GJ, Johnson TD, Hamm BG, Davidson DH, Kumagai Y (1996) Community analysis by Biolog: curve integration for statistical analysis of activated sludge microbial habitats. J Microbiol Meth 27: 183 - 197
Heinemeyer O, Insam H, Kaiser EA, Walenzik G (1989) Soil microbial biomass measurements: an automated technique based on infra-red gas analysis. Plant Soil 116: 191 - 195
Hopkins DW, MacNnaughton SJ, O’Donnell AG (1991) A dispersion and differential centrifugation technique for representatively sampling microorganisms from soil. Soil Biol Biochem 23: 217 - 225
Lbekwe AM, Kennedy AC (1998) Phospholipid fatty acids profiles and carbon utilisation patterns for analysis of microbial community structure under field and greenhouse conditions. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 26: 151 - 163
Insam H (1997) A new set of substrates proposed for community characterisation in environmental samples. In: Insam H, Rangger A (eds) Microbial communities: functional versus structural approaches. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 259 - 260
Insam H, Amor K, Renner M, Crepaz C (1996) Changes in functional abilities of the microbial community during composting of manure. Microb Ecol 31: 77 - 87
Insam H, Feurle J, Rangger A (2001) Community level physiological profiles (Biolog substrate use tests) of environmental samples. In: Akkermans ADL, van Elsas JD, DeBruijn FJ (eds): Molecular Microbial Ecology Manual, 5`h Supplement, Kluwer, Amsterdam
Klamer M, Bath E (1998) Microbial community dynamics during composting of straw material studied using phospholipid fatty acid analysis. FEMS Microb Ecol 27: 9 - 20
Laine M.M, Haario H, Jorgensen (1997) Microbial functional activity during composting of chlorophenol-contaminated sawmill soil. J Microbiol Meth 30: 21 - 32
Lulu B (2000) Evaluation of soil organic matter pools of some Ethiopian agricultural soils and compost maturity: a microbial approach. Dissertation, University of Innsbruck, Innsbruck
Sharma S, Rangger A, Insam H (1998) Effects of decomposing maize litter on community level physiological profiles of soil bacteria. Microb Ecol 35: 301 - 310
SPSS (1998) Statistical package of the social sciences. SPSS Inc, Chicago
Tiquia SM, Tam NFY (2000) Co-composting of spent pig litter and sludge with forced aeration. Biores Technol 72: 1 - 7
Wong JWC, Mak KF, Chan NW, Lam A, Fang M, Zhou LX, Wu QT, Liao XD (2001) Cocompost of soybean residues and leaves in Hong Kong. Biores Technol 76: 99 - 106
Zak JC, Willig MR, Moorhead DL, Wildman HG (1994) Functional diversity of microbial communities: a quantitative approach. Soil Biol Biochem 26: 1101 - 1108
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2002 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Riddech, N., Klammer, S., Insam, H. (2002). Characterisation of Microbial Communities During Composting of Organic Wastes. In: Insam, H., Riddech, N., Klammer, S. (eds) Microbiology of Composting. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-662-08724-4_4
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-662-08724-4_4
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-642-08705-9
Online ISBN: 978-3-662-08724-4
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive