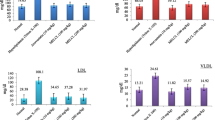
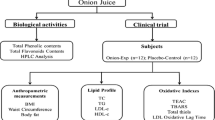
Abstract
In the literature of traditional medicine garlic (Allium sativum, Linn) is reported to be very effective against heart disease.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature
Dymock W., Warden C.J.H. & Hooper D. (1893) Pharmacographia Indica, Vol.III, p.488. Publisher Kegan Paul, Trench, Trubner & Co. Ltd. London Reprinted by Hamdard Foundation, Karachi in 1972.
Krtichevsky, D. (1975) Effect of garlic oil on experimental atherosclerosis, Artery, 1, 319–323.
Bordia, A., Arora, S.K. Kothari, L.K., Jain, R.C. Rathore, B.S., Rathore, A.S., Dobe, M.K. & Bhu. N. (1975). The protective action of essential oils of onion and garlic in cholesterol fed rabbits. Atherosclerosis, 22, 103–109.
Jain, R.C. (1976) Onion and garlic in experimental cholesterol induced atherosclerosis. Indian J.Med.Res., 64, 1509–1515.
Jain, R.C. (1977) Effect of garlic on serum lipids, coagulability and fibrinolytic activity of blood (letter). Am.J.Clin.Nutr., 30, 1380–1381.
Jain R.C. & Konar, D.B. (1978) Effect of garlic oil in experimental cholesterol atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis, 29, 125–129.
Jain, R.C. (1978) Effect of alcoholic extract of garlic in atherosclerosis. Am. J. Clin. Nutr., 11, 1982–1983.
Brodia, A.K. & Verma, S.K. (1978) Garlic on the reversibility of experimental atherosclerosis. Indian Heart J., 30, 47–50.
Bordia, A.K., & Verma, S.K. (1980) Effect of garlic feeding on regression of experimental atherosclerosis in rabbits, Artery, 7, 428–437.
Kritchevsky, D., Tepper, S.A. Morrisey, R. & Klurfeld, D. (1980) Influence of garlic oil on cholesterol metabolism in rats. Nutr.Rept. Int., 22, 641–645.
Chang, M.W. & Johnson, M.A. (1980) Effect of garlic on carbohydrate metabolism and lipid synthesis in rats. J. Nutr., 110, 931–936.
Bordia, A. (1981) Effect of garlic on blood lipids in patients with coronary heart disease. Am. J. Clin. Nutr., 34, 2100–2103.
Arora, R.R. & Arora, S. (1981) Comparative effects of Clofibrate, garlic and onion on alimentary hyperlipemia, Atherosclerosis, 39, 447–452.
Chi, M.S. Koh, E.T. & Stewart, T.J. (1982) Effects of garlic on lipid metabolism in rats fed cholesterol or lard. J. Nutr., 112, 241–248.
Kamanna, V.S. & Chandrasekhara, N. (1982) Effect of garlic (Allium sativum Linn) on serum lipoproteins and lipoprotein cholesterol levels in albino rats rendered hypercholesteremic by feeding cholesterol. Lipids, 17, 483–486.
Cavalito, C.J. & Bailey, J.H. (1944) Allicin the Antibacterial Principle of Allium sativum. 1. Isolation, Physical Properties and Antibacterial Action. J. Amer.Chem.Soc., 66, 1950–51.
Cavalito, C.J., Buck, J.S. & Suter, S.M. (1944) Allicin, the Antibacterial Principle of Allium sativum II. Determination of the Chemical Structure. J.Am.Chem.Soc., 66, 1952–54.
Stoll, A., & Seebeck, E. (1950) The Synthesis of Natural Alliin. Experientia, 6, 330; and
Stoll, A., & Seebeck, E. (1950) Helv. Chim. acta., 32, 197 & 866 (1949).
Itokawa, Y., Inoue, K., Sasagawa, S. & Fujiwara, M. (1973) Effect of S-methylcysteine sulfoxide, S-allyl-cysteine sulfoxide and related sulphur-containing amino acids on lipid metabolism of experimental hypercholesterolemic rats. J.Nutr., 103, 88–92.
Augusti, K.T. & Mathew, P.T. (1974) Lipidlowering effect of allicin (diallyl disulfide-oxide) on long term feeding to normal rats. Experientia, 30, 468–470.
Shih J.C.H. (1982) Avian models for research in atheroscherosis and cholesterol metabolism. Fed.Amer.Soc.Exptl.Biology., (April 15,1982) p.2475.
Shih J.C.H. (1983) Atherosclerosis in Japanese quails and the effect of lipvic acid. Federation Proc. 42, 2494–2497.
Qureshi, A.A., Burger, W.C., Elson, C.E. & Benevenga, J.N. (1982) Effects of cereals and culture filtrate of Trichoderma viride on lipid metabolism of swine. Lipids, 17, 924–934.
Qureshi, A.A., Abuirmeileh, N., Burger, W.C., Din Z.Z. & Elson, C.E. (1982) Effect of AMO 1618 on cholesterol and fatty acid metabolism in chickens and rats. Atherosclerosis, 46, 203–216.
Gornall, A.G., Bardawill, C.J. & David, M.M. (1949) Determination of serum proteins by means of the biuret reaction. J.Biol.Chem., 177, 751–766.
Kostner G.M. (1976) Enzymatic determination of cholesterol in high density lipoprotein fractions prepared by polyanion precipitation Clin.Chem., 22, 695–698.
Lobos-Virella, M.F., Stone, P., Ellis, S. & Colwell, J.A. (1977) Cholesterol determination in high density lipoproteins separated by three different methods. Clin.Chem., 23, 882–884.
Snedecor, G.W.& Cochran, W.G. (1971) Statistical Methods, 6th ed., pp. 258–298. The Iowa State University Press, Ames, IA. U.S.A.
Leveille, G.A., Romsos, D.R., Yeh, Y.Y. & O’Hea, E.K. (1975) Lipid biosynthesis in the chick. A consideration of site of synthesis, influence of diet and possible regulartory mechanisms. Poult.Sci., 54, 1075–1093.
O’Hea, E.K. & Leveille, G.A. (1968) Lipogenesis in isolated adipose tissue of the domestic chick (Gallus domesticus). Comp.Biochem. Physiol., 26, 111–120.
Vanderhoek, J.Y., Makheja, A.N. & Bailey, J.M. (1980) Inhibition of fatty acid oxygenases by onion and garlic oils. Evidence for the mechanism by which these oils inhibit platelet aggregation Biochem.Pharmacol., 29, 3169–3173.
Kaunitz, H. (1977) Repair Function of Cholesterol Versus the Lipid Theory of Arteriosclerosis. Chemistry and Industry, 761–763.
Imai, H., Werthessen, N.T., Subromanyam, V., Le Quesne, P.W. & Soloway, A.H. (1980) Angiotoxicity of Oxygenated Sterols and Possible Precursors. Science (U.S.A.) 207, 651–653.
Ampofo, O. (1977) Plants that heal. World Health (W.H.O., Geneva, Switzerland) pp 26–30 (November issue).
Farnsworth, N.R. & Bingel A.S. (1977). Problems and Prospects of Discovering New Drugs from High Plants by Pharmacological Screening New Natural Products and Plant Drugs with Pharmacological, Biological or Therapeutical Activity. Editors Wagner, H. & Wolf, P., pp, 1–22. Springer-Verlag, Berlin, Heidelberg, New York.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 1986 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Ahmad, Y. (1986). Hypcholesterolemic Effect of Allium sativum Linn. and its Potential Protective Action Against Coronary Heart Disease. In: Rahman, Au. (eds) Natural Product Chemistry. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-71425-2_2
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-71425-2_2
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-642-71427-6
Online ISBN: 978-3-642-71425-2
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive