Abstract
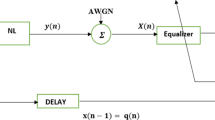
The adaptive algorithm has been widely used in the digital signal processing like channel estimation, channel equalization, echo cancellation, and so on. One of the most important adaptive algorithms is the NLMS algorithm. We present in this paper an multiple objective optimization approach to fast blind channel equalization. By investigating first the performance (mean-square error) of the standard fractionally spaced CMA (constant modulus algorithm) equalizer in the presence of noise, we show that CMA local minima exist near the minimum mean-square error (MMSE)equalizers. Consequently, CMA may converge to a local minimum corresponding to a poorly designed MMSE receiver with considerablely large mean-square error. The step size in the NLMS algorithm decides both the convergence speed and the residual error level, the highest speed of convergence and residual error level.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Krauss, T.P., Zoltowski, M.D., Leus, G.: Simple MMSE equalizers for CDMA downlink to restore chip sequence: Comparison to Zero-Forcing and Rake. In: ICASSP, vol. 5, pp. 2865–2868 (2000)
Hooli, K., Latva-aho, M., Juntti, M.: Multiple access interference suppression with linear chip equalizers in WCDMA downlinkreceivers. In: General Conference (Part A), GLOBECOM, pp. 467–471 (December 1999)
Mailaender, L.: Low-complexity implementation of CDMA downlink equalization. 3G Mobilec Communication Technologies 477, 396–400
Haykin, S.: Adaptive Filter Theory, 3rd edn. Prentice Hall (1996)
Golub, G.H., Van Loan, C.F.: Matrix Computation, 3rd edn. The Johns Hopkins University Press (1996)
Shynk, J.: Frequency-domain and multirate adaptive filtering. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine 9, 14–39 (1992)
Godard, D.N.: Self-recovering equalization and carrier tracking in two-dimensional data communication systems. IEEE Trans. on Communications
Fijalkow, I., Manlove, C.E., Johnson Jr., C.R.: Adaptive fractionally spaced blind CMA equalization: Excess MSE. IEEE Trans. on Signal Processing 46(1), 227–231 (1998)
Ding, Z., Kennedy, R.A., Anderson, B.D.O., Johnson Jr., C.R.: Ill-convergence of godard blind equalizers in data communication systems. IEEE Trans. On Communications 39
Johnson Jr., C.R., Dasgupta, S., Sethares, W.A.: Averaging analysis of local stability of a real constant modulus algorithm adaptive filter. IEEE
Brown, D.R., Schniter, P.B., Johnson Jr., C.R.: Computationally e cient blind equalization. In: 35th Annual Allerton Conference on Communication, Control, and Computing (September 1997)
Casas, R.A., Johnson Jr., C.R., Kennedy, R.A., Ding, Z., Malamut, R.: Blind adaptive decision feedback equalization: A class of channels resulting in illconvergence from a zero initialization. International Journal on Adaptive Control and Signal Processing Special Issue on Adaptive Channel Equalization
Johnson Jr., C.R., Anderson, B.D.O.: Godard blind equalizer error surface characteristics: White, zeromean, binary source case. International Journal of Adaptive Control and Signal Processing 9, 301–324
Nirmala Devi, R., Saikumar, T., Kishan Rao, K.: Adaptive MMSE Equalizer through LMS algorithm based CMA Channel Equalization. In: The Thrid International Conference on Network and Communications (NetCom-3.0), (accepted , Publish in LNICST, January 2-4, 2012)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2012 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Nirmala Devi, R., Saikumar, T., Kishan Rao, K. (2012). NLMS Algorithm Based CMA Channel Equalization through an Adaptive MMSE Equalizer. In: Satapathy, S.C., Avadhani, P.S., Abraham, A. (eds) Proceedings of the International Conference on Information Systems Design and Intelligent Applications 2012 (INDIA 2012) held in Visakhapatnam, India, January 2012. Advances in Intelligent and Soft Computing, vol 132. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-27443-5_78
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-27443-5_78
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-642-27442-8
Online ISBN: 978-3-642-27443-5
eBook Packages: EngineeringEngineering (R0)