Abstract
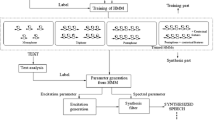
In this paper, we present several methods to reduce the computational and memory cost to embed HMM-based TTS system. We firstly decrease the number of HMMs by applying decision tree based context clustering technique. Secondly propose address-based model compression technique to compress the model size without degradation in synthesis speech quality. Thirdly reduce the feature vector size to decrease computational and memory resources. Finally, fixed-point implementation is taken to fit the TTS system requirements to embedded devices’ resource. Experimental results show that the system size can be compressed to 3.61MB from 293MB, memory and computational cost are low enough for real-time embedded application. Subjective evaluation shows that the synthesis speech quality is fairly good.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Levy, C., Linares, G., Nocera, P., Bonastre, J.-F.: Reducing computational and memory cost for cellular phone embedded speech recognition system. In: Proc. ICASSP (2004)
Tokuda, K., Masuko, T., Miyazaki, N., Kobayashi, T.: Hidden Markov Models Based on Multi-Space Probability Distribution for Pitch Pattern Modeling. In: Proc. ICASSP (1999)
Zen, H., Tokuda, K., Masuko, T., Kobayashi, T., Kitamura, T.: Hidden Semi-Markov Model Based Speech Synthesi. In: Proc. ICSLP, pp. 1180–1185 (2004)
Tokuda, K., Kobayashi, T.: S. Imai, “Speech parameter generation from HMM using dynamic features. In: Proc. ICASSP, pp. 660–663 (1995)
Shinoda, K., Watanabe, T.: Acoustic Modeling Based on the MDL Principle for speech recognition. In: Proc. EuroSpeech, pp. 99–102 (1997)
Wakita, H.: Linear prediction voice synthesizers: line spectrum pair (LSP) is the newest of several techniques. Speech Technol., 17–22 (1981)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2011 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Fu, R., Zhao, Z., Tu, Q. (2011). Reducing Computational and Memory Cost for HMM-Based Embedded TTS System. In: Zeng, D. (eds) Applied Informatics and Communication. ICAIC 2011. Communications in Computer and Information Science, vol 224. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-23214-5_78
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-23214-5_78
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-642-23213-8
Online ISBN: 978-3-642-23214-5
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)