Abstract
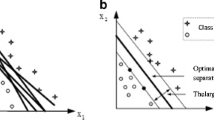
This article presents the use of Support Vector Machines (SVM) to diagnose the ischemic heart disease using heart images obtained from Single Proton Emission Computed Tomography (SPECT). The data set came from 267 different patients and was divided into several sub-sets containing training and validation data. The study consisted in comparing results of classifying cardiac SPECT images using SVMs with those obtained using another method of machine learning - CLIP3 - which is a combination of the decision tree algorithm and the rule induction algorithm. Validations carried out using a SPECT image database have shown that SVMs are good in generalising knowledge gained about multi-dimensional data with relatively little training data.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allender, S., et al.: European Cardiovascular Disease Statistics 2008 edition, European Heart Network (2008)
Burges, C.J.C.: A tutorial on support vector machines for pattern recognition. Data Mining and Knowledge Discovery 2(2), 955–974 (1998)
Burges, C.J.C., Crisp, D.: Uniqueness of the SVM solution. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, vol. 12, pp. 223–229. MIT Press, Cambridge (1999)
Ciecholewski, M.: Gallbladder Segmentation in 2-D Ultrasound Images Using Deformable Contour Methods. In: Torra, V., Narukawa, Y., Daumas, M. (eds.) MDAI 2010. LNCS (LNAI), vol. 6408, pp. 163–174. Springer, Heidelberg (2010)
Ciecholewski, M.: Gallbladder Boundary Segmentation from Ultrasound Images Using Active Contour Model. In: Fyfe, C., Tino, P., Charles, D., Garcia-Osorio, C., Yin, H. (eds.) IDEAL 2010. LNCS, vol. 6283, pp. 63–69. Springer, Heidelberg (2010)
Cios, K.J., Pedrycz, W., Swiniarski, R.: Data Mining Methods for Knowledge Discovery. Kluwer, Dordrecht (1998)
Clark, P., Niblett, T.: The CN2 algorithm. Machine Learning 3, 261–283 (1989)
Data Bases SPECT i SPECTF from UCI Machine Learning Repository, on-line http://www.ics.uci.edu/~mlearn/MLRepository.html
Fung, G., Stoeckel, J.: SVM feature selection for classification of SPECT images of Alzheimer’s disease using spatial information. Knowledge and Information Systems 11(2), 243–258 (2007)
Gunn, S.: Support vector machines for classification and regression. Technical Report, Dept. of Electronics and Computer Science, University of Southampton, Southampton, U.K (1998)
International Cardiovascular Disease Statistics 2009, Statistical Fact Sheet – Populations, American Heart Association (2009)
Kurgan, L.A., Cios, K.J., et al.: Knowledge discovery approach to automated cardiac SPECT diagnosis. Artificial Intelligence in Medicine 23(2), 149–169 (2001)
Osuna, E., Freund, R., Girosi, F.: An improved training algorithm for support vector machines. In: Principe, J., Gile, L., Morgan, N., Wilson, E. (eds.) Neural Networks for Signal Processing VII, pp. 276–285. IEEE, New York (1998)
Platt, J.: Fast training of support vector machines using sequential minimal optimization. In: Schölkopf, B., Burges, C.J., Smola, A.J. (eds.) Advances in Kernel Methods – Support Vector Learning, pp. 185–220. MIT Press, Cambridge (1999)
Quinlan, J.R.: C4.5: Programs for Machine Learning. Morgan Kaufmann, San Francisco (1993)
Salas–Gonzalez, D., Górriz, J.M., et al.: Selecting Regions of Interest in SPECT Images Using Wilcoxon Test for the Diagnosis of Alzheimers Disease. In: Graña Romay, M., Corchado, E., Garcia Sebastian, M.T. (eds.) HAIS 2010. LNCS, vol. 6076, pp. 446–451. Springer, Heidelberg (2010)
Vapnik, V.: The Nature of Statistical Learning Theory. Springer, New York (1995)
Vapnik, V.: Statistical Learning Theory. John Wiley & Sons, Inc., New York (1998)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2011 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Ciecholewski, M. (2011). Support Vector Machine Approach to Cardiac SPECT Diagnosis. In: Aggarwal, J.K., Barneva, R.P., Brimkov, V.E., Koroutchev, K.N., Korutcheva, E.R. (eds) Combinatorial Image Analysis. IWCIA 2011. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 6636. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-21073-0_38
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-21073-0_38
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-642-21072-3
Online ISBN: 978-3-642-21073-0
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)