Abstract
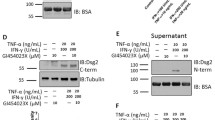
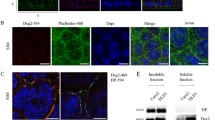
Intestinal epithelial intercellular junctions regulate barrier properties, and have been linked to epithelial differentiation and programmed cell death (apoptosis). However, mechanisms regulating these processes are poorly defined. Desmosomes are critical elements of intercellular junctions; they are punctate structures made up of transmembrane desmosomal cadherins termed desmoglein-2 (Dsg2) and desmocollin-2 (Dsc2) that affiliate with the underlying intermediate filaments via linker proteins to provide mechanical strength to epithelia. In the present study, we generated an antibody, AH12.2, which recognizes Dsg2. We show that Dsg2 but not another desmosomal cadherin, Dsc2, is cleaved by cysteine proteases during the onset of intestinal epithelial cell (IEC) apoptosis. Small interfering RNA-mediated down-regulation of Dsg2 protected epithelial cells from apoptosis. Moreover, we report that a C-terminal fragment of Dsg2 regulates apoptosis and Dsg2 protein levels. Our studies highlight a novel mechanism by which Dsg2 regulates IEC apoptosis driven by cysteine proteases during physiological differentiation and inflammation. (Supported by grants from the German Research Foundation — La 2359/1-1, the NIH — DK-55679, DK — 61379 (A.N) and the CCFA — fellowship award to A.M.H. and P.N.D).
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
Literatur
Fouquet S, Lugo-Martinez VH, Faussat AM, Renaud F, Cardot P, Chambaz J, Pincon-Raymond M, Thenet S (2004) Early loss of E-cadherin from cell-cell contacts is involved in the onset of anoikis in enterocytes. J Biol Chem 279: 43061–43069
Getsios S, Huen AC, Green KJ (2004) Working out the strength and flexibility of desmosomes. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 5: 271–2
Kottke MD, Delva E, Kowalczyk AP (2006) The desmosome: cell science lessons from human diseases. J Cell Sci 119: 797–806
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2008 Springer Medizin Verlag Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Laukötter, M.G. et al. (2008). Desmoglein-2: Ein neuer Regulator der Apoptose im intestinalen Epithel. In: Arbogast, R., Schackert, H.K., Bauer, H. (eds) Chirurgisches Forum 2008. Deutsche Gesellschaft für Chirurgie, vol 37. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-78833-1_52
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-78833-1_52
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-540-78821-8
Online ISBN: 978-3-540-78833-1
eBook Packages: Medicine (German Language)