Abstract
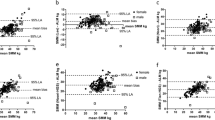
The aim of this study was to evaluate and compare segmental bioimpedance spectroscopy (SBIS) measurements of arm volume and muscle to 40K and MRI measurements. 31 hemodialysis (HD) patients (17 male and 14 female, weight, 55.7±4.5 kg, BMI 27.6±5.5 m3/kg) were studied pre HD. MRI and partial body 40K of the arm (PBKArm) were measured. Arm bioimpedance was measured with the Hydra bioimpedance spectroscopic device (Xitron 4200). The length of the arm from wrist to ipsilateral shoulder was measured with soft tape. Arm extracellular (Re) and intracellular resistance (Ri) were obtained from a program based on Cole-Cole model provided by Xitron. Extracellular (ECVa) and Intracellular volumes (ICVa) in the arm were calculated. Arm fluid volume using SBIS was defined as VArm =ECVa+ ICVa. The correlation of the VArm and arm skeletal muscle (MSMRI) was R2=0.65 (MSMRI =0.89*Varm+0.15), that between PBKArm to VArm (R2 =0.53, VArm =2.34*PBKArm + 2.1) and to MSMRI (R2=0.36, MSMRI=2.4* PBKArm + 7.6), respectively. This study shows that arm SBIS measurement provides an easy, portable, low-cost technique for estimation of muscle mass in the arm, which can be performed frequently.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wielopolski L, Ramirez LM, Gallagher D, Heymsfield SB, Wang ZM (2006) Measuring partial body potassium in the arm versus total body potassium. J Appl Physiol 101:945–949
Pierson RN ed. (2000) Quality of the body cell. Springer, New York
De Lorenzo A, Andreoli A, Matthie JR, Withers PO (1997) Predicting body cell mass with bioimpedance by using theoretical methods: a technological review. J Appl Physiol 82:1542-1558
Zhu F, Kuhlmann MK, Kaysen GA, Sarkar SR, Kaitwatcharachai C, Khilnani R, Leonard EF, Wang J, Heymsfield S, Levin NW (2006) Use of MRI and Dilution technique to calibrate segmental bioimpedance for hemodialysis patients. J Appl Physiol 100:717-724
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2007 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Carter, M. et al. (2007). Estimation of Arm Muscle Mass in Hemodialysis Patients by Segmental Bioimpedance (SBIS) MRI and K Techniques. In: Scharfetter, H., Merwa, R. (eds) 13th International Conference on Electrical Bioimpedance and the 8th Conference on Electrical Impedance Tomography. IFMBE Proceedings, vol 17. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-73841-1_203
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-73841-1_203
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-540-73840-4
Online ISBN: 978-3-540-73841-1
eBook Packages: EngineeringEngineering (R0)