Abstract
To extend the range of blind signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) estimation and reduce complexity at the same time, a new algorithm is presented based on a signal subspace approach using the sample covariance matrix of the received signal and combined information criterion (CIC) in information theory. CIC overcomes the disadvantages of both Akaike information criterion’s (AIC) under penalization and minimum description length’s (MDL) over penalization and its likelihood form is deduced. The algorithm needs no prior knowledge of modulation types, baud rate or carrier frequency of the signals. Computer simulation shows that the algorithm can blindly estimate the SNR of digital modulation signals commonly used in additional white Gaussian noise (AWGN) channels and Rayleigh fading channels with small samples, and the mean estimation error is less than 1dB for SNR ranging from -15dB to 25dB. The accuracy and simplicity of this method make it more adapt to engineering applications.
This work is supported by National 863 Projects of China. Item number is 2004AA001210.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
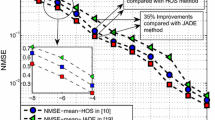
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Balachandran, K., Kadaba, S.R., Nanda, S.: Channel Quality Estimation and Rate Adption for Cellular Mobile Radio. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications. (1999) 1244–1256
Summers, T. A., Wilson, S.G.: SNR Mismatch and Online Estimation in Terbo Decoding. IEEE Transactions on Communications. (1998) 421–423
Dea-Ki Hong, Cheol-Hee Park, Min-Chul Ju.: SNR Estimation in Frequency Domain Using Circular Correlation. Electronics Letters. (2002)1693–1694
Matzner, R., Englberger, F.: An SNR Estimation Algorithm using Fourth-order Moments. Proceedings of the 1994 IEEE Symposium on Information Theory. (1994) 119
Ping G., Cihan T.: SNR Estimation for Nonconstant Modulus Constellations. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing. (2005) 865–871
Bin, L., Robert, D., Ariela, Z.: A Low Bias Algorithm to Estimate Negative SNRs in an AWGN Channel. IEEE Communications Letters. (2002) 469–472
Piet M.T. Broersen.: Finite Sample Criteria for Aautoregressive Order Selection. IEEE Transactions on Signal Procesing. (2000) 3550–3559
Mati Wax, Thomas Kailath.: Detection of Signals by Information Theoretic Criteria. IEEE Transaactions on Aacoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing. (1985) 387–392
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2006 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Wu, D., Gu, X., Guo, Q. (2006). Blind Signal-to-Noise Ratio Estimation Algorithm with Small Samples for Wireless Digital Communications. In: Huang, DS., Li, K., Irwin, G.W. (eds) Intelligent Computing in Signal Processing and Pattern Recognition. Lecture Notes in Control and Information Sciences, vol 345. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-37258-5_85
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-37258-5_85
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-540-37257-8
Online ISBN: 978-3-540-37258-5
eBook Packages: EngineeringEngineering (R0)