Abstract
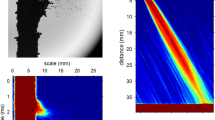
The surface jets induced by an explosion below an immersed gas bubble in water are investigated experimentally. Typical phenomena including the bubble evolution and the jet formation are observed through high-speed photography. It is found that the inner jet resulting from the shock bubble interaction is the main cause of the surface jet. The velocity of the surface jet decreases with the initial depth of the bubble, and there exists a maximum bubble depth above which no surface jet occurs.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
J.R. Asay, Material Ejection from Shock-Loaded Free Surfaces of Aluminum and Lead, SAND76-0542, (1976)
M.B. Zellner et al., Effects of shock-breakout pressure on ejection of micron-scale material from shocked tin surfaces. J. Appl. Phys. 102, 013522 (2007)
A. Antkowiak, N. Bremond, S. LeDizes, E. Villermaux, Short-term dynamics of a density interface following an impact. J. Fluid Mech. 577, 241 (2007)
C.D. Ohl, R. Ikink, Shock-wave-induced jetting of micron-size bubbles. Phys. Rev. Lett. 90, 214502 (2003)
A. Philipp, W. Lauterborn, Cavitation erosion by single laser-produced bubbles. J. Fluid Mech. 361, 77–116 (1998)
T. Kodama, K. Takayama, Dynamic behavior of bubbles during extracorporeal shock-wave lithotripsy. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 24, 723–738 (1998)
Y. Tomita, A. Shima, T. Ohno, Collapse of multiple gas bubbles by a shock wave and induced impulsive pressure. J. Appl. Phys. 56, 125 (2007)
A. Philipp, M. Delius, C. Scheffczyk, A. Vogel, W. Lauterborn, Interaction of lithotripter-generated shock waves with air bubbles. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 93, 2496 (1993)
T. Kodama, K. Takayama, N. Nagayasu, The dynamics of two air bubbles loaded by an underwater shock wave. J. Appl. Phys. 80, 5587 (1996)
T. Kodama, Y. Tomita, Cavitation bubble behavior and bubble–shock wave interaction near a gelatin surface as a study of in vivo bubble dynamics. Appl. Phys. B Lasers Opt. 70, 139–149 (2000)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2019 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Zhu, Y., Zhang, G., Yang, J. (2019). Surface Jetting Induced by Explosion in Liquid Below an Immersed Bubble. In: Sasoh, A., Aoki, T., Katayama, M. (eds) 31st International Symposium on Shock Waves 2. ISSW 2017. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-91017-8_61
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-91017-8_61
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-91016-1
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-91017-8
eBook Packages: EngineeringEngineering (R0)